ecg machine - rmsc.nic.in
advertisement

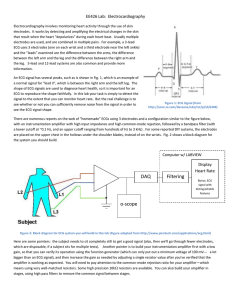
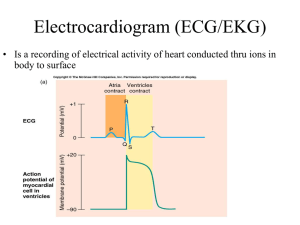
ECG MACHINE 1 CONTENTS: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. BASIC INFORMATION………………………………………………………………….03 PLACEMENT OF ELECTRODES……………………………………………………. 05 OPERATING PROCEDURES………………………………………………………….06 ECG MACHINE – CARDIOFAX SINGLE CHANNEL……………………….09 OPERATING MODES…………………………………………………………………….11 EQUIPMENT FUNCTIONS AND CONTROLS…………………………………12 PAPER LOADING………………………………………………………………………….13 TROUBLESHOOTING……………………………………………………………………15 BATTERY OR MAINS INDEPENDENT OPERATION……………………...16 CONTACTS……………………………………………………………………………………17 2 ELECTROCARDIOGRAM: It is a recording of electrical activity of heart conducted through ions in body to surfaces. Components of ELECTRODES: 1. Adhesive substance (attach to the skin to secure that the electrodes is in place) 2. Substance (reduce skin’s electrical impedance) Functions: An ECG is a way to measure and diagnose abnormal rhythms of the heart, particularly abnormal rhythms caused by damage to the conductive tissue that carries electrical signals, or abnormal rhythms caused by electrolyte imbalances. Types of ECG Recordings: a. Bipolar leads record voltage between electrodes placed on wrists & legs (right leg is ground) b. Lead I records between right arm & left arm c. Lead II: right arm & left leg d. Lead III: left arm & left leg 3 WAVES. COMPLEXES, & INTERVALS : 3 DISTINCT WAVES ARE PRODUCED DURING CARDIAC CYCLE 1. P wave caused by atrial depolarization = 2.5 mm or less in ht. and 0.11s or less in duration 2. QRS complex caused by ventricular depolarization = less than 0.12s in duration 3. T wave results from ventricular repolarization INTERVALS: PR interval - beginning of P wave to the beginning of QRS complex = 0.12 to 0.20s in duration ST segment: -Connects the QRS complex and T wave QT Interval -Measured from beginning of QRS to the end of the T wave 0.32 to 0.40s in duration (if 85 to 95 BPM) QT interval varies based on heart rate, gender, and age PP interval -Beginning of one P wave to the beginning of the next RR interval -From one QRS complex to the next QRS complex determine ventricular rate and rhythm U wave -Repolarization of the Purkinje fibers 4 Placement of electrodes Electrode label RA Electrode placement On the right arm, avoiding thick muscle. LA In the same location where RA was placed, but on the left arm. RL On the right leg, lateral calf muscle. LL In the same location where RL was placed, but on the left leg. V1 In the fourth intercostal space (between ribs 4 and 5) just to the right of the sternum (breastbone). V2 In the fourth intercostal space (between ribs 4 and 5) just to the left of the sternum. V3 Between leads V2 and V4. V4 In the fifth intercostal space (between ribs 5 and 6) in the mid-clavicular line. V5 Horizontally even with V4, in the left anterior axillary line. V6 Horizontally even with V4 and V5 in the midaxillary line. 5 OPERATING PROCEDURES: 1. Verify the order for the ECG in the client's chart. 2. Confirm the client's ID by checking two client identifiers according to your facility's policy. 3. Provide privacy and explain the procedure to the client. Explain that the test records the heart's electrical activity and that it may be repeated at certain intervals. Emphasize that no electrical current will enter the body. Tell the client that the test typically takes about 5 minutes. 4. Wash your hands. 5. Place the ECG machine close to the client's bed and plug the cord into the wall outlet or, battery-operated, ensure that it is functioning. Turn on the machine and input required client information. If the client is already connected to a cardiac monitor, move the electrodes to accommodate the precordial leads. 6. Have the client lie supine in the center of the bed with arms at his sides. You may raise the head of the bed to promote comfort. Expose the arms and legs and cover the client appropriately. The arms and legs should be relaxed to minimize muscle trembling, which can cause electrical interference. 7. If the bed is too narrow, place the client's hands under his buttocks. 8. Select flat, fleshy areas to place the limb lead electrodes. Avoid muscular and bony areas. If the client has an amputated limb, choose a site on the stump. 9. If an area is excessively hairy, clip it. Clean excess oil or other substances from the skin with soap and water to enhance electrode contact. 10.Apply disposable electrodes to the client's wrists and to the medial aspects of the ankles. Apply the pre-gelled electrode directly to the prepared site, as recommended by the manufacturer's instructions. To guarantee the best connection to the lead wire, position disposable electrodes on the legs with the lead connection pointing superiorly. 6 11.Expose the client's chest. Put a pre-gelled electrode at each electrode position. If your client is a woman, be sure to place the chest electrodes below the breast tissue. In a large-breasted woman, you may need to displace the breast tissue laterally. 12.Connect the lead wires to the electrodes. The tip of each lead wire is lettered and color-coded for easy identification. The white or RA lead wire goes to the right arm; the green or RL lead wire, to the right leg; the red or LL lead wire, to the left leg; the black or LA lead wire, to the left arm; and V1 to V6 lead wires, to the chest electrodes. 13.Check to see that the paper speed selector is set to the standard 25 mm/second and that the machine is set to full voltage. The machine will record a normal standardization mark—a square that is the height of two large squares or 10 small squares on the recording paper. 14.Ask the client to relax and breathe normally. Tell the client to lie still and not to talk when you record the ECG. 15.Press the RECORD button. Observe the tracing quality. The machine will record all 12 leads automatically, recording three consecutive leads simultaneously. Some machines have a display screen so that you can preview waveforms before the machine records them on paper. If any part of the waveform height extends beyond the paper when you record the ECG, adjust the normal standardization to half standardization. Note this adjustment on the ECG strip because this change will need to be considered in interpreting the results. 7 16.When the machine finishes recording the 12-lead ECG, remove the electrodes and clean the client's skin. After disconnecting the lead wires from the electrodes, dispose of the electrodes. 17.Assist the client to a comfortable position. Ensure the bed is in a low position. 18.Remove any remaining equipment and wash your hands. 19.Document in your notes the test's date and time and significant responses by the client. Verify the date, time, client's name, and assigned ID number on the ECG itself. Note any appropriate clinical information on the ECG. 8 ECG MACHINE CARDIOFAX - SINGLE CHANNEL 9 10 OPERATING MODES: 11 EQUIPMENT FUNCTIONS AND CONTROLS : 12 PAPER LOADING: 13 14 TROUBLESHOOTING: 15 BATTERY OR MAINS INDEPENDENT OPERATION: 16 CONTACTS: After sales service: Jaipur Office: Contact:- Mr. Rohit 9829335331 Mr. Arjun 9928009828 Jodhpur Office:Contact :- Mr. Kailash 9829009126 Medicaid Systems 389, Industrial Area, Phase-2, Chandigargh-160002 Ph.-0172-2652706, Fax-0172-2653608. Email- info@medicaid.co.in ,Website – www.mediacid.co.in RMSC SUPPORT : BIOMEDICAL ENGINEER +91-0141-2228558 bmed.rmsc@gmail.com 17