Microbiology Unit 1
advertisement

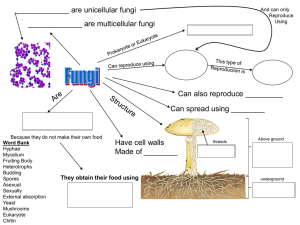
Microbiology Unit 1 Bacteria Archaea Fungi Protozoa Algae Viruses Multicellular Animal Parasites Unicellular Prokaryotes (no nucleus) Shapes: Bacillus (rodlike) Coccus (spherical) Spiral (corkscrew) Cell walls composed of peptidoglycan Reproduce by binary fission (dividing into two cells) Some autotrophs, some heterotrophs Many can “swim” using flagella Prokaryotes Cells walls lack peptidoglycan Extreme environments Methanogens: produce methane as a waste product of respiration Extreme halophiles: extremely salty environments Extreme thermophiles: hot sulfurous water Not known to cause human disease Eukaryotes (cells have a nucleus & organelles) Unicellular or multicellular Unicellular: yeast Multicellular: mushrooms, molds Cell walls composed of chitin Reproduce sexually or asexually heterotrophs Unicellular Eukaryotic Move by Pseudopods (false feet): amoebas Long flagella Numerous short cilia Can live either free or as parasites (derive nutrients from a living host) Reproduce sexually or asexually Photosynthetic Eukaryotes Sexual and asexual reproduction Cell walls composed of cellulose (like plants) Unicellular (for microbiology purposes) Living??? Acellular (not cellular) Most only seen with electron microscope Made of a core of DNA or RNA surrounded by a protein coat Can only reproduce using the cellular machinery of other organisms Helminths (parasitic worms) Two major groups: Flatworms and roundworms Microscopic in size during some stages of their life cycle