HONORS BIOLOGY PHOTOSYNTHESIS REVIEW Ch. 7
advertisement

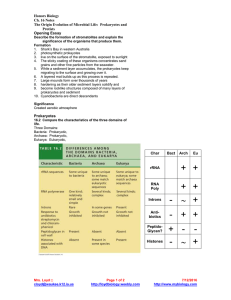
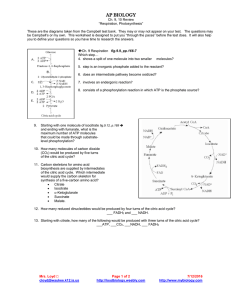
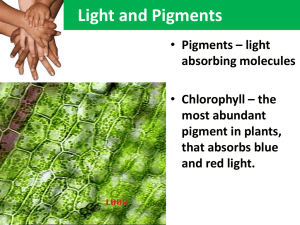
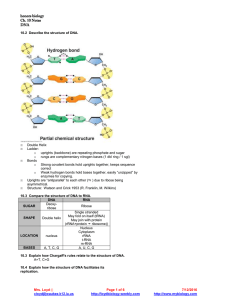
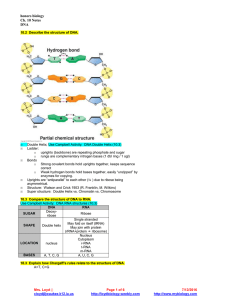
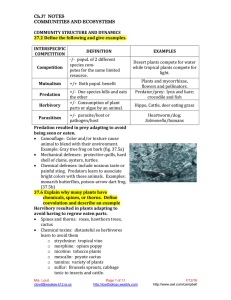
HONORS BIOLOGY PHOTOSYNTHESIS REVIEW Ch. 7 7.1 Define: Autotophs: producers: photoautotrophs: 7.2 Label the diagram of a leaf, the LM image of a mesophyll cell, the chloroplast diagram and TEM image. WORD BANK: Intermembrane space chloroplast mesophyll cells vein stroma inner membrane thylakoid thylakoid space stoma CO2 O2 leaf palisade mesophyll cells spongy mesophyll cells guard cells 7.2 Write the overall chemical equation for photosynthesis. Be sure to include the E for energy. 7.2 Refer back to the equation you just wrote. How do the reactant molecules of photosynthesis reach the chloroplast in leaves? 7.3 Explain how plants produce oxygen. Be specific. Mrs. Loyd cloyd@waukee.k12.ia.us Page 1 of 4 http://loydbiology.weebly.com 7/12/2016 http://www.mybiology.com 7.5, 7.10, 7.11 Label the diagram of the chloroplast to show the reactants and products of the light reactions and the Calvin cycle. (* denotes optional information) Word Bank: CO2 O2 H2O ATP NADPH NADP+ ADP Pi Sugars Light Energy Light Reactions Calvin Cycle *Electron Transport Chains (ETC) *Photosystem I and *PII Thylakoid membrane Thylakoid space Stroma Cellular Respiration Other compounds Cellulose Starch G3P 7.5 Refer again to the equation you wrote for photosynthesis. Know it, love it! Use the numbers for each reactant and product given below to number the diagram above. #1 Light Energy #2 CO2 #3 Water #4 O2 #5 Sugars 7.5 What are the reactants and products of the light-dependent reactions? 7.5 What are the reactants and products of the Calvin cycle? 7.5 Does the Calvin cycle use light directly? 7.5 For chloroplasts to produce sugar from carbon dioxide in the dark, they would need to be supplied with __________ & _____________. 7.6 Use the diagram to help you explain why plants are green. Wavelengths of light appear to us as colors. Which colors are used the most in photosynthesis? by chlorophyll a? Mrs. Loyd cloyd@waukee.k12.ia.us Page 2 of 4 http://loydbiology.weebly.com 7/12/2016 http://www.mybiology.com by chlorophyll b? What two functions do the other photosynthetic pigments (like carotenoids) perform? Why do leaves change color in the fall? What is the ONE molecule on the planet that can give up energized electrons? 7.13 Use the diagram to explain the “greenhouse effect.” 7.13 Explain how deforestation and the use of fossil fuels contribute to global warming. 7.14 How does the ozone layer form? 7.14 How have human activities damaged the ozone layer? 7.14 If the ozone layer is destroyed, what will be the consequences? Mrs. Loyd cloyd@waukee.k12.ia.us Page 3 of 4 http://loydbiology.weebly.com 7/12/2016 http://www.mybiology.com This section is COMPLETELY OPTIONAL!!!! Use the analogy to help explain (in actual terms, not analogy terms) how radiant energy from the sun is transformed into chemical energy. This diagram compares the chemiosomotic synthesis of ATP (as opposed to substrate-level synthesis of ATP) in mitochondria and chloroplasts. Which side of the membrane (dark gray or light gray) has the higher hydrogen ion concentration? Label a. through e. a. b. c. d. e. Mitochondria Chloroplasts Where do the electrons for the electron transport chain come from? Where do the electrons get their energy? What picks up the electrons at the end of the chain? How is the energy (given up by the electrons) used? Where are the ETC proteins embedded? Where is the pH the highest? H+ Where is the pH the lowest? H+ Mrs. Loyd cloyd@waukee.k12.ia.us Page 4 of 4 http://loydbiology.weebly.com 7/12/2016 http://www.mybiology.com