Scanners
advertisement

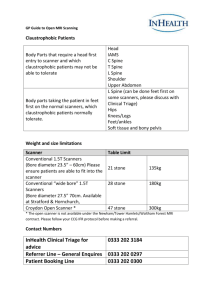
Scanners “The Computer as an Educational Tool: Productivity and Problem Solving” ©Richard C. Forcier and Don E. Descy Scanner Functions Graphics and photos Digital files Data entry Scanner Types Flatbeds Sheet-fed Film/Slide Handheld Portable Flatbed Scanners General purpose Multifunction Most common Affordable Sheet-fed Document-management Office scanners Compact tasks Film/Slide High resolution Scans slides, films, negatives, and transparencies Light is projected through the original to the other side. Handheld Works well for awkward sizes Several passes over a regularsized document Scans can turn out uneven. Portable Lightweight and compact About the size of a bestseller book Image quality isn’t as good. Scanner Features Resolution Bit depth Dynamic range Software Resolution How many dots per inch (dpi) a scanner can record Optical vs. interpolated resolution 300 dpi is sufficient for most uses. Bit Depth Amount of information that the scanner can remember about each pixel The higher the bits, the more details a scanner can record about an image’s color or gray scale. For most home uses, a 12-bit scanner is adequate. Dynamic Range Similar to bit depth Measures the ability of scanners to reproduce tones Standard flatbeds typically have a range of 2–2.5. Software TWAIN drivers allow a piece of hardware to work with a computer system. Different software caters to different audiences. Research software according to needs