JSReviewExam#1.doc
advertisement

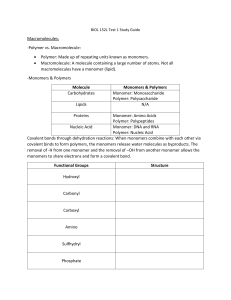
Review Sheet for Exam #1 (Morris Chapters 1 - 4) Dr. Solti This review is meant to serve as a guide to ensure your notes are complete. You will need to be able to do/understand and READ YOUR BOOK! Simply filling out this review sheet will not be enough to earn a good grade. • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Define “biology” Know the Scientific Method Characteristics of living things versus nonliving things Know characteristics of viruses and why they are not living things 1st and 2nd Laws of Thermodynamics Central Dogma Differences between Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic cells Know definition of Taxonomy, the 8 taxons, binomial nomenclature Know 3 Domains of Life Know evolution Know definition of chemistry, matter, elements Structure of atoms, three subatomic particles and their charges/characteristics Number of protons, and electrons of an element if given characteristics Arrangement of Periodic Table Importance of the electron Bonds: Covalent bonds, both polar and nonpolar, ionic bonds, and hydrogen bonds Understand what electronegativity has to do with bonding, and the rules of electronegativity Ions, cation, anion Water, its structure, bonds within and bonds outside of water, its characteristics that make it so important to biological organisms Hydrophilic, hydrophobic Acids and bases and neutral solutions pH and the concentration of hydrogen ions Organic molecules and why carbon has such diversity 7 Functional groups and their structures/characteristics Macromolecules/Polymers and their monomers and their bonds Dehydration Synthesis and Hydrolysis Structure and Functions of: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids Functions of proteins, monomers, bond, chemistry of amino acids Lipids: fats/triacylglycerols, phospholipids and steroids Structure/ function of nucleotides • differences between DNA and RNA • nucleotides in DNA, RNA or both; and their bonds • be able to give a complimentary sequence if given the sequence of one strand of DNA/RNA Carbohydrates, monomers, bonds, naming sugars and specific examples The relationships between Chromosomes, genes, DNA and proteins DNA sequence, structure, bonds, template strand, anti-parallel Steps of transcription, where it takes place in eukaryotes vs. prokaryotes Fate of eukaryotic primary transcript Translation, steps, where it takes place Comparison of eukaryote vs. prokaryote gene expression Proteins functions and structure; how a polypeptide chain is read; levels of protein folding Ribosomes; their function, their 3 pockets mRNA, codon/triplet codon, AUG; redundant, unambiguous Translation requirements and their roles tRNA and its function/anticodon Steps of translation and its termination Be able to use Table 4.1/The Codon Dictionary to generate a protein if given an mRNA sequence or DNA double strand.