June 2014 training slides
advertisement

Health Impact Assessment
Training
Kelly Muellman, AICP
MN Climate & Health Principal Planner
Linden Weiswerda
MN Climate & Health Principal Planner
June 13, 2014
2
Acknowledgements
This webinar/videoconference is supported by a
grant from the Health Impact Project, a
collaboration of the Robert Wood Johnson
Foundation and The Pew Charitable Trusts.
The opinions expressed are those of the author(s)
and do not necessarily reflect the views of the
Health Impact Project, Robert Wood Johnson
Foundation or The Pew Charitable Trusts.
3
Outline
What is HIA?
Why conduct an HIA?
What value does HIA add?
When is HIA appropriate?
HIA Examples
HIA Resources
4
What is Health Impact Assessment (HIA)?
A systematic process that uses an array of
data sources and analytic methods and
considers input from stakeholders to
determine the potential effects of a
proposed policy, plan, program, or project
on the health of a population and the
distribution of those effects within the
population. HIA provides
recommendations on monitoring and
managing those effects.
National Research Council, Improving
Health in the United States: The Role
of Health Impact Assessment, 2011.
5
2010 Avg Life Expectancy and Healthcare Spending
US ranked
42nd in life
expectancy
for 2010 and
1st in health
spending per
capita.
WHO and Global Health
Expenditure Database
http://www.gapminder.org/
6
Health Determinants
Health is a state of complete physical, mental and social wellbeing and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity.
Source: World Health
Organization
7
Why Conduct an HIA?
Identify harms and benefits before decisions are made
Identify evidence-based strategies and recommendations to
promote health and prevent disease
Support inclusive and democratic decision-making and
increase transparency in the decision-making process
Support community engagement in the decision-making
process and foster community empowerment
Advance equity and justice
Note: There are many ways to insert health into decision-making. HIA is one way.
8
Types of Decisions Influenced by HIA
•
Policy Decisions (bills by state legislature, city council
decision, local school board on district-wide policy)
•
Policy Implementation (weigh various implementation
options for a policy once it is passed)
•
Project Specific (siting, permitting, construction, design)
•
Comprehensive Plans (neighborhood plan, regional growth
plans, master planning documents)
Provided by Health Impact Project
http://www.healthimpactproject.org/
9
What topics have HIAs addressed?
Provided by Health Impact Project
http://www.healthimpactproject.org/
10
Value of HIA
HIAs directly contributed to decision outcomes—the way
projects, plans, and policies were developed or implemented
HIAs influenced changes beyond the decision under consideration
HIAs showed key stakeholders the health effects of non-health
policies and programs.
HIAs built consensus
HIAs amplified community member voices in the decision-making
process
HIAs built cross-sector relationships
Bourcier, E., Charbonneau, D., Cahill, C., & Dannenberg, A. (2014). Do health impact assessments make a difference? A national
evaluation of HIAs in the United States. Seattle: Center for Community Health and Evaluation.
11
Concerns about HIA
Concern
Response
HIA is costly
Not as costly as treatment of health impacts in
the long run
HIA is time-consuming and
will slow decision-making
process
Conducting the HIA early will bring issues to the
front of the decision-making process, potentially
speeding approval processes, and preventing
costly litigation that delays projects
HIA will stop economic
development
The role of HIA is to identify mitigations and
recommendations, not to say “don’t do that”
HIA is not scientific
Role of HIA is to pull together disparate pieces of
the best available evidence to make a broad
statement about impacts
Source: Wisconsin Department of Health Services, Health Impact Assessment: A Tool to
Increase Health Equity in Decision-Making, Great Lakes Intertribal Council, April 23, 2012
12
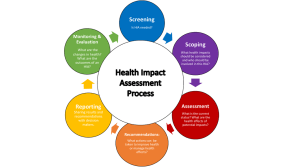
Six Steps of HIA
1. Screening - to determine if an HIA is useful for a specific project or
policy
2. Scoping - identify which health effects to consider
3. Assessment - determine which people may be affected and how
they may be affected
4. Recommendations - suggest changes to proposal to promote
positive or mitigate adverse health effects
5. Reporting - present the results to decision-makers
6. Monitoring and evaluating - determine the affect of the HIA on
the decision process
13
When is HIA appropriate?
Consider:
Decision-point
Potential health impacts
Timing
Resources (money, staff, expertise)
Political will
Types of HIAs
Type
Desk Based
Rapid
Intermediate
Comprehensive
Duration
Up to 6 weeks
6-12 weeks
12 weeks – 6 months
6 months – 1 year or
more
Effort
1 full time person
1 full time person
1 full time person,
and supporting help
1 full time person,
and supporting help
Complexity
Provides a broad
overview of potential
health impacts
Provides a more
detailed overview of
potential health
impacts
Provides a thorough
assessment of
potential health
impacts & more
detail on specific
predicted impacts
Provides a
comprehensive
assessment of
potential & predicted
health impacts
Methods
Involves collecting &
analyzing existing
data
Involves collecting &
analyzing existing
data with limited
input from experts &
key stakeholders
Involves collecting &
analyzing existing
data, gathering some
new qualitative data
from stakeholders &
key informants
Involves collecting &
analyzing data from
qualitative &
quantitative sources
LESS COMPLEXITY
MORE COMPLEXITY
Modified from Harris et al. 2007. Health impact assessment: A practical guide, Centre for Health Equity, Training, Research and Evaluation
(CHETRE), Part of the UNSW Research Centre for Primary Health Care and Equity, UNSW:
(http://www.hiaconnect.edu.au/hia_a_practical_guide.htm)
15
When not to do an HIA
No added value
Chula Vista Plan to Improve Walkability
Plan was already considering health
Health advocates involved in design
Resources better focused elsewhere
No influence on decision
Milwaukee Zoo Interchange Project
Insufficient time to complete HIA for drafts
Stakeholders (DOT) not open to considering health
Source: Wisconsin Department of Health Services, Health Impact Assessment: A Tool to
Increase Health Equity in Decision-Making, Great Lakes Intertribal Council, April 23, 2012
16
HIA Examples
Gary/New Duluth HIA
Small Area Plan
Parallel process
Health concerns:
Social Cohesion
Physical Activity
Access to Healthy Food
Healthy Corridor for All
Zoning ordinance (urban)
Lead by ISAIAH, Take Action MN,
and PolicyLink
Community driven
3 Areas of Assessment:
Healthy Economy
2. Healthy, Affordable Housing
3. Safe and Sustainable
Transportation
1.
http://www.policylink.org/atf/cf/{97c6d565-bb43-406d-a6d5eca3bbf35af0}/HEALTHYCORRIDOR_SUMMARY_FINAL_20120111.PDF
19
Goodhue County Zoning Districts HIA
Zoning ordinance (rural)
Lead by Goodhue County
Health and Human Services and
Land Use Management
Department
Areas of Assessment:
Housing; Living conditions;
Air, water, and soil quality
changes; Access to natural
resources, respiratory
health, mental well being,
physical activity; and
Economic health.
Farm to School and School Garden Policy
Oregon Bill 2800 (HB 2800), the Farm to
School and School Garden legislation
(2011)
Led by Upstream Public Health
Areas of Assessment:
1.
Employment
2.
Diet & Nutrition
3.
Farm to School & School Garden
Education
4.
Environmental Health
5.
Social Capital
Source: Henderson, T., Rader, M., Sorte, B., Ratcliffe, M. M., Lawrence, A., Lucky, J., and Harris, C. (2011) Health Impact Assessment: Farm to
School and School Garden Policy, HB 2800, Upstream Public Health and the Health Impact Project.
http://www.upstreampublichealth.org/sites/default/files/F2SHIA_FINAL.pdf
Additional HIA Examples
Paid Sick Days HIA (national, state, local)
Treatment Instead of Prison HIA (WI)
School Integration Strategies HIA (MN)
Federal Farm Bill HIA (national)
HIA for proposed coal mine at Wishbone Hill (AK)
Lower Duwamish Waterway Superfund Site (WA)
HIA for open burning enforcement in La Crosse county (WI)
22
HIA Resources
Evaluations of HIA
• Quigley & Taylor. 2004. Evaluating health impact
assessment. Public Health. 2004 Dec; 118(8):544-52.
• EPA. 2013. A Review of Health Impact Assessments in the
U.S.: Current State-of-Science, Best Practices, and Areas for
Improvement.
• Center for community Health and Evaluation (CCHE). 2014.
Do health impact assessments make a difference? A
national evaluation of HIAs in the United States.
• John Hopkins School of Public Health (Keisha Pollack ),
Health Impact Project and CDC, 2011
24
HIA at the National Level
Two major national funders
Centers for Disease Control & Prevention (CDC) (directly funds
grantees and professional organizations)
Health Impact Project (PEW and RWJF)
SOPHIA (Society of Practitioners of HIA):
http://www.hiasociety.org/
Two conferences:
HIA of the Americas Workshop (Oakland, CA)
National Health Impact Assessment Meeting (WDC)
Local Funder: Blue Cross Blue Shield of MN Foundation
Completed and in progress HIAs
Provided by Health Impact Project & CDC
http://www.healthimpactproject.org/hia/us
26
MDH’s Role in Promoting HIA
Leading/performing HIAs:
Douglas County Comprehensive Plan; St. Louis Park Comprehensive
Plan; Duluth 6th Ave Redesign Plan; Divine Mercy HIA; Gary/New Duluth
Small Area Plan HIA; Winona County Active Living Plan HIA; Lincoln Park
Small Area Plan HIA
Providing technical assistance:
Healthy Corridor for All HIA; Bottineau Transitway HIA; HIA on the Fort
DuPont Redevelopment Project DE; Second Street Redevelopment Plan
GA; Emerald Ash Borer HIA; MN School Location & Design HIA
Providing HIA training
27
MDH’s Role in Promoting HIA (II)
Promoting Health in All
Policies
EAW & Comprehensive
Plans
Tool Development (EAW,
comp planning, brownfields,
climate change)
Sharing information on HIA:
website & listserv (500+)
Promoting HIA through
Collaboration
(http://www.health.state.mn.us/divs/hia/)
28
Collaboration: Get Involved
HIA Interagency Workgroup: (12 agencies)
MN HIA Coalition: (70+ members)
(http://www.health.state.mn.us/divs/hia/coalition.html)
29
HIA Reports
Improving Health in the United States: The Role of
Health Impact Assessment
(http://www.nap.edu/catalog.php?record_id=13229)
Minimum Elements and Practice Standards for Health
Impact Assessment
(http://www.humanimpact.org/doc-lib/finish/11/9)
Guidance and Best Practices for Stakeholder
Participation in Health Impact Assessments
(http://www.hiasociety.org/documents/guide-forstakeholder-participation.pdf)
Promoting Equity through the Practice of Health Impact
Assessment:
(http://www.policylink.org/atf/cf/%7B97c6d565-bb43406d-a6d5eca3bbf35af0%7D/PROMOTINGEQUITYHIA_FINAL.PDF)
30
Resources: HIA Websites
MDH HIA webpage
(http://www.health.state.mn.us/divs/hia/)
CDC Healthy Places webpage
(http://www.cdc.gov/healthyplaces/hia.htm)
World Health Organization HIA webpage
(http://www.who.int/hia/en/)
HIA Gateway – Public Health England
(http://www.apho.org.uk/default.aspx?QN=P_HIA)
UCLA – HIA Guide web
(http://www.hiaguide.org/)
Health Impact Project website
(http://www.healthimpactproject.org/)
Design for Health website
(http://www.designforhealth.net/resources/healthi
mpact.html)
Healthy Development Measurement Tool website
(http://www.thehdmt.org/)
Source: http://www.policylink.org/atf/cf/%7B97c6d565bb43-406d-a6d5eca3bbf35af0%7D/PROMOTINGEQUITYHIA_FINAL.P
DF
31
Contact Information
Kelly Muellman, AICP
Principal Planner
MN Climate & Health Program
Minnesota Department of Health
651.201.5637
Kelly.Muellman@state.mn.us
Linden Weiswerda
Principal Planner
MN Climate & Health Program
Minnesota Department of Health
651.201.4924
Linden.Weiswerda@state.mn.us
Please complete the online evaluation:
https://survey.vovici.com/se.ashx?s=56206EE33D67C4D2
*We will send all participants links to today’s slides and the webinar
evaluation*