Nematodes and Annelids
advertisement

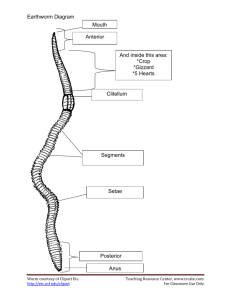
Nematodes and Annelids Phylum Nematoda (Roundworms) •Non-segmented •Bilateral symmetry •Organization - 3 germ layers – endoderm, ectoderm, & mesoderm – organ level •Pseudocoelomates (body cavity) – filled with fluid – space for organs •Tube-within-a-tube body plan – complete digestive tract with mouth and anus. •Habitat – fresh or salt water, soil, inside host (both plants & animals) Life Processes •Internal transport - fluid in pseudocoelom transports nutrients & oxygen •Support – fluid in pseudocoelom provides support (hydrostatic skeleton). •Respiration - Breathe through their skin diffusion. •Movement - longitudinal muscles – move with whiplike motion – inefficient in water, good in soil & host. •Excretion – waste is removed through the anus •Feeding & digestion – •Feed using muscular pharynx which shoots out from mouth •Food is digested in intestine •Gender - appear as separate males & females •Sexual reproduction – male injects sperm into female, she lays eggs. Roundworm anatomy Types of nematodes: • Ascaris • Contracted when one eats vegetables contaminated with human waste. • Trichina worm: • Trichinosis is contracted when eating undercooked pork containing encysted larvae. •Filaria worm: •Carried by mosquitoes and causes elephantiasis by blocking lymphatic drainage. •Pinworms: •Common infections in children. •Hookworm: •Once common in the southern United States. •Person becomes infected when walking in soil contaminated with human waste •Guinea worm: •Person becomes infected when drinking water with water fleas contaminated with guinea worm eggs. •Worm emerges from leg once fully grown. Phylum Annelida (segmented worms) • Symmetry - bilateral • Organization - 3 germ layers – organ level • Coelomates -have a body cavity – more complex organs • Segmented • Habitat – fresh or salt water, soil • Tube-within-a-tube body plan – specialized organs in digestive tract (see earthworm later) • Support - hydrostatic skeleton. • Respiration - breathe through their skin diffusion. • Internal transport - closed circulatory system with 5 aortic arches (hearts) and blood vessels that run the length of the body and branch to every segment. • Excretion – – Nephridia (tiny tubes found in each segment) remove nitrogen waste through openings in body wall – Anus removes waste from digested food. •Movement - alternating contraction of longitudinal and circular muscles found in each segment. •Response - brain connected to a ventral nerve cord . •Three classes – •Polychaeta – marine worms •Oligochaeta – earthworms •Hirudinea - leeches Earthworm, Lumbricus 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. Mouth Pharynx Esophagus Crop Gizzard Intestine Anus Aortic arches (hearts) Dorsal blood vessel Ventral blood vessel Brain Ventral nerve cord Clitellum Setae Clitellum Testis Sperm reservoir Ovary Seminal receptacle Excretory pore Nephridium Tubule H. Intestine I. Coelom J. Muscle K. Muscle L. Epidermis L1. Cuticle M1. Blood vessel M2. Blood vessel N. Nerve cord O. Nephridium P. Setae Earthworms • Have pairs of setae in each segment; when muscles contract in each segment, setae anchor in the soil, and aid locomotion. • Diet - leaves & decaying matter • Digestion: Mouth Pharynx (swallows food) Esophagus (connects pharynx & crop) Crop (stores food) Gizzard (grinds food – contains small stones swallowed by the worm) Intestine (digests food) •Gender - hermaphroditic. •Reproduction •Meet at clitellum (smooth part of worm), which secretes a ring of mucus •Each injects sperm into mucus •Tube slides forward, picking up eggs •Tube slides off body & is left behind •Fertilization occurs within tube •Worms hatch in a few weeks – no larval stage •Two sets of young Leeches • Most in fresh water, some in soil or salt water. • 2 suckers (1 small anterior, 1 large posterior) to feed. • Some are free-living predators; most are fluid feeders that attach themselves to open wounds. • Bloodsuckers cut through tissue with 3 saw-like jaws – leaves “Y” – shaped wound. • Anesthetic in saliva prevents victim from feeling attack and dilates blood vessels; anticoagulant (hirudin) in their saliva keeps blood from clotting; pouches in crop allows for storage of up to 5 times their weight – long time between feedings.