Maps and Map Skills
advertisement

Maps and Map Skills
United States Geological
Survey, 7.5 minute
topographic quadrangle
map.
• Surface features
• Location
(longitude / Latitude
Grid)
• Distance (scale)
• Direction
• Topography / elevation
(contour lines)
Location
• numerical grid overlain on map
• Longitude and Latitude
• UTM (Universal Transverse Mercator)
• Other county, state, local grids
60o E
60o N
Parallels
Meridians
North Latitude
South Latitude
West
Longitude
East
longitude
Prime Meridian
73° 37' 30"
2' 30"
73° 35' 00”
2' 30"
73° 32' 30"
2' 30"
73° 30' 00”
40° 45' 00 "
2' 30"
2' 30"
7' 30" of Latitude
40° 42' 30"
40° 40' 00"
2' 30"
40° 37' 30"
7' 30" of Longitude
73° 37' 30"
35'
32' 30"
73° 30'
40° 45'
42' 30"
Grid Coordinates
Lat. 40° 42' 30" N
Long. 73° 35' 00" W
40'
40° 37' 30"
UTM Coordinates
1000 meters
6 07 000m E.
6 09
6 10
55 000m N.
1000 meters
44
6 08
44
54
44
53
44
52
UTM Coordinates
608,400 E
4,453,300 N
1000 meters
Direction
• Compass bearing from point A to point B
• Measured in degrees around a circle
• Azimuth (0°-360°)
• Quadrant (0°-90°, NE, SE, SW, NW)
Azimuth
Quadrant
N
X
X
45o
0
W
270
0
90
315o
E
W
NW
NE
SW
SE
90
90
The
Compass Rose
180
0
S
S
Bearing 315°
Quadrant
N
N
0
0
270
90
225o
180
S
Bearing 225°
E
Bearing N 45° W
Azimuth
W
N
E
W
90
The
Compass Rose
X
NW
NE
SW
SE
45o
90
0
S
Bearing S 45° W
Magnetic Declination - the difference between
magnetic (compass) north and true (polar) north.
E
X
Magnetic Declination - the difference between
magnetic (compass) north and true (polar) north.
Geographic Pole
(True North)
TN
MN
Magnetic Pole
(Magnetic North)
East
Magnetic
Declination
West
Magnetic
Declination
Distance
• Scale: the size of the map relative to the
area it represents.
• Shown graphically (bar scale)
• Shown as a numerical fraction (ratio scale)
Map Scale - bar scale and ratio scale
Map Scale - bar scale and ratio scale
How to estimate distance
using the ratio scale
Example: what is the
distance from Axinn Library
to Nassau Coliseum?
How to estimate distance
using the ratio scale
1. Measure distance on the
map.
Use inches for miles
Use cm for kilometers
How to estimate distance
using the ratio scale
1. Measure distance on the
map.
2.5 inches
Use cm for kilometers
How to estimate distance
using the ratio scale
1. Measure distance on the
map.
2.5 inches
6.4 cm
How to estimate distance
using the ratio scale
1. Measure distance on the
map.
2. Multiply by map scale.
2.5 inches
2.5 inches x 24,000 = 60,000 inches
6.4 cm
6.4 cm x 24,000 = 153,600 cm
Scale 1:24,000
How to estimate distance
using the ratio scale
1. Measure distance on the
map.
2. Multiply by map scale.
3. Convert to miles / km.
2.5 inches x 24,000 = 60,000 inches
60,000 inches / 12 = 5000 ft
5000 ft / 5280 = .95 miles
6.4 cm x 24,000 = 153,600 cm
153,600 cm / 100 = 1,536 m
1536 m / 1000 = 1.536 km
Scale 1:24,000
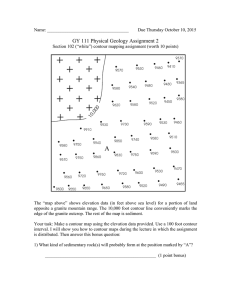
Topography / Elevation
• Represented by topographic contour lines
Closed contour lines represent a hill
(mountain) or a hole (depression).
Depression
Hill
A single contour line represents a single elevation
along its entire length. In other words, the elevations
of all points along a contour line are the same.
8400’
Bench mark
Contour lines never split, cross or
intersect. At a vertical cliff they do,
however, come together and touch.
Ocean
The elevation of a contour line is always a simple multiple of
the contour interval. By convention, each fifth contour line is
an index contour (drawn as a thicker line than adjacent
contours and numbered somewhere along the line)
8400
8200
Contour Interval = 40’
Widely spaced contour lines indicate a gentle
slope. Closely spaced contour lines indicate a
steep slope.
steep slope
{
gentler slope
{
Where a contour line crosses a stream or a
valley, the contour lines form a “V” that
points upstream or up the valley.
60’
50’
Where two adjacent closed contours indicate
opposite slopes (hachured contour next to a
normal contour) both are the same elevation.
60’
50’
40’
50’
50’
50’
50’
40’
A hachured contour line, lying between two
different contour lines, is the same elevation as
the lower line
60’
50’
40’
60’
50’
40’
50’
A closed contour line, lying between two different
contour lines, is the same elevation as the higher
contour line.
60’
50’
60’
60’
50’
The datum or zero elevation is defined as mean sea level.
The beach is always at zero elevation.
0’
Every contour line eventually closes on itself. However, any one
map will not be large enough to show the full extent of all contour
lines, and some will simply end at the edge of the map.
Where one closed contour line surrounds another, the
inner contour line marks the higher elevation. If the
contour lines are hachured, then the inner contour line
marks the lower elevation
70’
60’
60’
70’