Hearing and Balance
advertisement

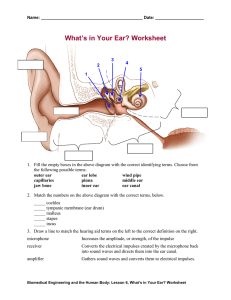
Hearing and Balance Sound The decibel (dB) is a logarithmic unit of measurement that expresses the magnitude of a physical quantity, in this case sound. It is dimensionless and is the difference between the log of the measured sound and the log of a reference sound. Sound Max 120 dB France: Limited to 100 dB http://vancouver.ca/engsvcs/projects/soundsmart/images/dbScale2-2-2.jpg Sound Range Middle C on a piano is: ~256 Hz http://www.diracdelta.co.uk/science/source/h/e/hearing range in animals/image001.jpg Figure 10-17 Ears Ear Drum From the ear there is a short canal that leads to the ear drum, a thin membrane. closing off the canal. This membrane can be easily damaged but has the ability to repair itself. The canal also secretes an acidic wax that is used to collect dust and other particles and also acts as a bactericide and fungicide. http://www.1800endoscope.com/images/eardrum.jpg Middle Ear http://www.phon.ox.ac.uk/~jcoleman/middle_ear.GIF http://media-2.web.britannica.com/eb-media/03/14303-004-A1009028.gif Figure 10-20 (2 of 8) Figure 10-20 (3 of 8) Perilymph (cytoplasm like) Endolymph (plasma like) Figure 10-20 (4 of 8) Figure 10-19, step 1 Figure 10-19, step 2 Figure 10-19, step 3 Figure 10-19, step 4 Figure 10-19, step 5 Figure 10-19, step 6 Figure 10-20 (6 of 8) Outer Cells Inner Cells The outer cells respond by vibrating at the given frequency resulting in a amplification of the sound. The inner cells are responsible for transmitting the information. 10,000 to 20,000 hair cells. Can be killed by loud sounds Figure 10-20 (8 of 8) Figure 10-20 (7 of 8) Bending of the stereocilium results in mechanically gated ion channels to open. This causes changes in K and Na ions which in turn cases voltage gated Ca channels to open. Figure 10-21a Figure 10-21b Figure 10-22a http://www.hearingaids4less.com/images/cochlea1.gif Figure 10-22a Figure 10-23a Orientation of Canals http://scienceblogs.com/afarensis/2006/05/16/bipedal_locomotion_and_semicir/ The Utricle and saccule respond to linear acceleration (turning your head left or right, for example) and the orientation of the head relative to gravity (tilting your head left or right for example). Utricle: Horizontal Saccule: Vertical The semicircular canals respond to angular accelerations. The horizontal semicircular allows you to keep your gaze fixed on an object while your head is moving (trying to read a sign in a moving car for example). Figure 10-23b Figure 10-23c Dizziness 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Sit on a swivel chair blindfolded. Turn the chair in one direction at a constant speed. Stop the chair suddenly. Remove blindfold. Ask, which direction is the chair moving. Observe eyes, not erratic eye movements. Dizziness can be caused by inconsistent information coming from the ears and eyes. Drunkenness may be partly caused by buoyancy changes in the endolymph resulting in changes to the capula. Utricle: Horizontal Saccule: Vertical Figure 10-23d The crystal are made from calcium carbonate and slide on a gelatinous substrate. Figure 10-23d Figure 10-25 - Overview