يعوبسلاا سوردلا لودج رصان للهادبع دمحم.د
advertisement

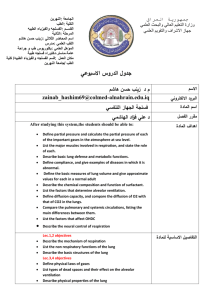
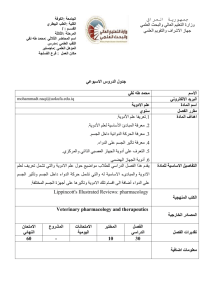
بابل: الجامعة العلوم للبنات: الكلية الحاسوب: القســم الثالثة: المرحلة محمد عبدهللا ناصر. د: اسم المحاضر الثالثي مدرس: اللقب العلمي دكتوراه علوم حاسبات: المؤهل العلمي جامعة بابل – كلية العلوم للبنات: مكان العمل جمهورية العراق وزارة التعليم العالي والبحث العلمي جهاز االشراف والتقويم العلمي جدول الدروس االسبوعي 1. االسم محمد عبداهلل ناصر.د Mohamed_1276@yahoo.com البريد االلكتروني )Computer Architecture( معمارية الحاسوب اسم المادة سنوي مقرر الفصل Identify some contributors to computer architecture and organization and relate their achievements to the knowledge area. 2. Articulate differences between computer organization and computer architecture. 3. Identify some of the components of a computer. 4. Explain the use of memory hierarchy to reduce the effective memory latency. 5. Explain how interrupts are used to implement I/O control and data transfers. 6. Be able to design an interface to memory 7. Understand how to interface and use peripheral chips 8. Discuss the generation of control signals using hardwired or microprogrammed implementations. 9. Explain basic instruction level parallelism using pipelining and the major hazards that may occur. 10. Discuss the concept of parallel processing beyond the classical von Neumann model 11.Appreciate the problems caused by cache coherency and understand the ways in which the problem can be overcome. Computer architecture is concerned with all aspects of the design and organization of the central processing unit and the integration of the CPU into the computer system itself. Architecture extends upward into computer software because a processor’s architecture must cooperate with the operating system and system software. It is impossible to design an operating system well without a knowledge of the underlying architecture. Moreover, the computer designer has to have an intimate understanding of software in order to implement the optimum architecture. Computer architecture is a key component of computer engineering and the practicing computer engineer should اهداف المادة التفاصيل االساسية لممادة have a practical understanding of this topic. Consequently, computer architecture courses should include a laboratory component where students are able to evaluate alternative designs. Therefore ,it includes the following subjects: CPU Organization, Instruction Set Design, Microprogramming, I/O, Memory management, Cache Memory, Pipeline and Vector Processing, Multiprocessors, Associative Memory, Applications (Database Machines), Non Von Neumann Architectures. 1. D. Page, A Practical Introduction to Computer الكتب المنهجية Architecture, Springer-Verlag London Limited, 2009. 1. Mostafa Abd-El-Barr, Hesham El-Rewini, Fundamentals of computer organization and architecture, John Wiley & المصادر الخارجية Sons, Inc,2005. 2. J. L. Hennessy and D. A. Patterson, Computer Architecture : A Quantitative Approach, 4th edition, Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc., 2007. 3. D. M. Harris and S. L. Harris, Digital Design and Computer Architecture”, Elsevier Inc, 2007. 4. J. L. Hennessy and D. A. Patterson, Computer Organization Design: T H E H A R D W A R E / S O F T W A R E / I N T E R F A C E, Third Edition, Elsevier Inc, 2005. االمتحان النهائي التقارير او المشاريع االمتحانات اليومية االمتحانات %06 %3 %3 %34 تقديرات الفصل . اضافة الى عدد من االمتحانات اليومية،) هناك ثالث امتحانات نظرية (عمى االقل-1 عل الطالب ان يقدم تقرير او مشروع عممي خالل السنة الدراسية (عمما انه سيعمن عن-2 .)عناوينها الحقا معمومات اضافية بابل: الجامعة العلوم للبنات: الكلية الحاسوب: اسم القســم الثالثة: المرحلة محمد عبدهللا ناصر. د: اسم المحاضر الثالثي مدرس: اللقب العلمي دكتوراه علوم حاسبات: المؤهل العلمي جامعة بابل – كلية العلوم للبنات: مكان العمل جمهورية العراق وزارة التعليم العالي والبحث العلمي جهاز االشراف والتقويم العلمي جدول الدروس االسبوعي week Date 1 28/9/2014 2 5/10/2014 Topics Covered 3 4 5 6 7 12/10/2014 19/10/2014 26/10/2014 2/11/2014 9/11/2014 8 16/11/2014 Review of syllabus Introduction to Computer Architecture. Computer Architecture and Computer Organization. A Model CPU Architecture A Model CPU Architecture Instruction Set Architecture (CISC, RISC and VLIW) Instruction Set Architecture ( VLIW), a comparison Design of CPU Control unit, Microprogrammed vs. Hardwired Control Unit Peripheral Control Strategies, Direct Memory Access 9 23/11/2014 Bus Interface 10 11 12 13 14 30/11/2014 7/12/2014 14/12/2014 21/12/2014 28/12/2014 1st Examination I/O Channels I/O Processor Register Windowing. Memory Interleaving. 15 4/1/2015 Cache Organization and Operation. 16 11/1/2015 Cache references (Direct, Set Associative and Full Associative). 17 18/1/2015 Cache performance. 18 25/1/2015 Instruction Pipelining. عطلة نصف السنة 19 15/2/2015 Arithmetic Pipelining (Integer and Floating point Multiplication). 20 22/2/2015 Vector processing 21 1/3/2015 2nd Examination 22 8/3/2015 Multiprocessor Architecture 23 24 25 26 27 15/3/2015 22/3/2015 29/3/2015 5/4/2015 12/4/2015 Interprocessor Communication Networks Interprocessor Communication Methods Cache Coherence Associative Memory, Content-Addressable Memories Arithmetic in Memory 28 29 19/4/2015 26/4/2015 Applications (Database Machines) Non Von Neumann Architecture 30 31 32 33 34 3/5/2015 10/5/2015 17/5/2015 24/5/2015 31/5/2015 Data Flow and Graph Reduction 3rd Examination Reports Discussion Reports Discussion Reports Discussion : توقيع العميد : توقيع االستاذ