Efficient image steganography with image quality control
advertisement

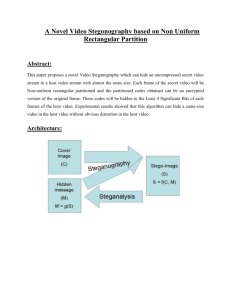
International Journal of Engineering Trends and Technology (IJETT) – Volume 34 Number 2- April 2016 Efficient image steganography with image quality control Priya Mishra#1, K.Ulagapriya#2, K, Kalaivani#3, A.Saritha #4 PG Student/ CSE Department, Vels University #1 AP/ CSE Department, Vels University #2 AP/ CSE Department, Vels University #3 AP/ CSE Department, Vels University #4 Abstract— Steganography is a popular technique to hide a data in various forms of media like image, video etc. There are several method of steganography to achieve the best and optimum solution to manipulate the image and message data,. The proposed system offers major implementation of embedding and extracting the message from an image. There are four main phases contains in the proposed technique which are Huffman encoding of message, image compression, image transformation , matrix encoding .Jpeg image contains the vector data of pixel values, which will be used further for matrix encoding . The jpeg image will be converted to bit map format to perform per mutative straddling .This method to encode a message into image is fast in terms of time and space complexity. Visual statistical attacks reduces with taking control over image quality are the main advantage of proposed system. Keywords— Steganography, cover image, stego image, Huffman encoding, jpeg encoding. Introduction The rapid development of data transfer through the internet made it easier to send the data to the destination. There is a lot of transmission media to transfer the data to destination. So in order to send the secure data to the destination without any modifications many approaches are available like "Cryptography" and "Steganography". This paper is deals with ―Image Steganography‖. Steganography are the technique of hiding private or sensitive information within something that appears to be nothing out of the usual. Unfortunately it is sometimes not enough to keep the contents of a message secret, it may also be necessary to keep the existence of the message secret. The technique used to implement this, is called steganography. Steganography is the art and science of invisible communication. This is accomplished through hiding information in other information, thus hiding the existence of the communicated information. The word steganography is derived from the Greek words ―stegos‖ meaning ―cover‖ and ―grafia‖ meaning ―writing‖ defining it as ―covered writing‖. In image steganography the information is hidden exclusively in images. The four main categories of file formats ISSN: 2231-5381 that can be used for steganography are text, image, audio and video. Given the proliferation of digital images, especially on the Internet, and given the large amount of redundant bits present in the digital representation of an image, images are the most popular cover objects for steganography. Research scope The aim of this paper is to introduce a new robust and secure image steganography system, which is based on a combination of two powerful algorithms (per mutative straddling and matrix encoding and improved f5 algorithm), this model preserves the quality of image one can reduce the size with most suitable quality of a image. LITERATURE SURVEY Year 2013 Soni, A.; Jain, J.; Roshan, R.Fragmentary Fourier change (FrFT), [1] Investigated on speculation of the traditional Fourier change, presented years prior in arithmetic writing. The upgraded calculation of partial Fourier change, the discrete variant of FrFT appeared DFrFT. This investigation of outlines the upside of discrete fragmentary Fourier change (DFrFT) when contrasted with different changes for steganography in picture handling. The outcome appears same PSNR in both space (time and recurrence) however DFrFT gives preference of extra stego key. The request parameter of this change. In the year of 2013 Akhtar, N.; Johri, P.; Khan, S., [2] Executed a variety of plain LSB (Least Significant Bit) calculation. The stego-picture quality has been made strides by utilizing bit-reversal procedure. LSB technique moving forward the PSNR of stego image. Through putting away the bit designs for which LSBs are modified, picture might be acquired effectively. For the enhancing the power of steganography, RC4 calculation had been actualized to accomplish the randomization secluded from everything message picture bits into spread picture pixels as opposed to putting away them consecutively. This strategy haphazardly scatters the bits of the message in the spread picture and in this manner, harder for unapproved individuals to remove the first message. The exhibited strategy indicates great upgrade to Least Huge Bit method in thought to security as well as picture quality. In the year of 2013 http://www.ijettjournal.org Page 67 International Journal of Engineering Trends and Technology (IJETT) – Volume 34 Number 2- April 2016 Prabakaran, G.; Bhavani, R. what's more, Rajeswari P.S. [3] Investigated on Medical records are to a great degree touchy patient data a multi secure and heartiness of restorative picture based steganography plan is proposed. This technique gives an effective and capacity security instrument for the insurance of advanced medicinal pictures. Creators proposed a feasible steganography technique utilizing Integer Wavelet Transform to ensure the X-ray medicinal picture into a solitary holder picture. [4] Displayed the novel plan installs information in whole number wavelet change coefficients by utilizing an editing capacity in a 8×8 square on the spread picture. The ideal pixel change process has been connected in the wake of inserting the message. Creators utilized the recurrence area to build the vigor of our steganography strategy. Number wavelet change maintains a strategic distance from the coasting point accuracy issues of the wavelet channel. Result demonstrates that the strategy beats versatile steganography method taking into account number wavelet change as far as crest sign to clamor proportion and limit. In the year of 2012 Das, R. furthermore, Tuithung, T. Praposed Techniques The proposed method uses improved version of f5 stenographic algorithm which is a most popular and visual statistics attack safe. This algorithm contains two phases as ‗Embedding‘ and ‗Extracting‘. Embedding phase involves steps to embed the given message into image and another one to extract the same message from the image. Algorithim Design There two different phases of this algorithm are given below. This algorithm also involves the steps of Huffman encoding to short the length of given message because it leads to preserve the quality of stego image. In case of other image format as bmp or tif, it must be converted into jpeg file format to proceed further. PREVIOUS RESEARCH Md. tahir in [1] exhibited another steganography system to conceal vast information in Bitmap picture utilizing stream manufacturer and equality . This technique utilizes the idea of odd and even equality for implanting and removing of mystery message. This technique is a change of Least Significant Bit (LSB) strategy for concealing data in pictures. Rakesh desai [2] displayed another steganography method for concealing information in pictures utilizing equality checker. This strategy utilizes the idea of odd and even equality for insertion and recovery of message. This strategy is a change over prior techniques such as slightest critical piece technique and sixth, seventh piece technique for concealing data in pictures. Alam et al in [7] displayed a depiction on how one can utilize the human vision framework and immaculate steganography to build the span of the information that we need to install in the picture. They concentrate on the property of human vision framework that expands the measure of information covering up in the bitmap (.bmp) and JPEG (.jpg) pictures for all intents and purposes. They upgrade the work of LSB and attempt to turn out with a superior result for both picture quality and the measure of information can be covered up inside it. They turn out with two methodologies; initial one is the 3-3-2 approach with no confinements on the kind of pictures being utilized and can reach up to 33.3% of size of shrouded information, and the second one is the 4-4-4 approach which increase 50%. ISSN: 2231-5381 Embedding Embedding requires an image and a text file, which contains the message to embed into given image. We can perform the stereography with lossy or lossless compression based upon of choice of format of image has been taken to inter change. A SVG (scalar vector graphics) image is a high quality vector data based image format which can be used as a stego image by matrix encoding. 1. Read the text or string from text file. 2. Perform Huffman encoding to short the length of message and convert into byte form. 3. JPEG compressor divides the uncompressed image into smaller parts of 8 x 8 pixels. 4. Discrete Cosine Transformation transfers the 8 x 8 brightness values into 8 x 8 frequency coefficients, which will be used in quantization process. 5. Quantization checks and rounds frequency coefficients to integers in range -2048 to 2047. 6. Huffman coding will be again performed to ensure redundancy free coding of quantized coefficients. http://www.ijettjournal.org Page 68 International Journal of Engineering Trends and Technology (IJETT) – Volume 34 Number 2- April 2016 Fig1. IAMGE11.JPEG Fig1. IAMGE2.JPEG The above image shows the text message embedding in a image which will not affect the image quality Above given histogram denotes the brightness of pixels across the image Extracting Extracting process is completely reverse of embedding process as given above. it also ensures the fault tolerance while extracting the message from an image. extraction of a message from a stego image also requires inter change of the format in case of BMP or other image format this algorithm has O(n) time and space complexity where n is a number of pixels in a image. 1. Get a stego image. 2. Perform Huffman Decoding for frequency coefficient redundancy calculation. 3. Jpeg compression to get an image in a smaller part of 8 x 8 pixels. 4. Matrix decoding of smaller parts of image containing 8 x 8 pixels. 5. Huffman decoding of bytes of string to get full length message. 6. Write the message into a file. AKNOLEGEMENTS This project has been carried out with the help of the teachers and family who supported for this reseach. i will specially thanks to my guide for this work madeto be done. The above image shows the text message extracting in an image which will not affect the image quality And it will not show the difference between the original image and image with message. TABLE1 COVER IMAGE IMAGE SIZE HIDDEN MESSAGE MESSAGE SIZE IMAGE1. JPEG 450 HI PRIYA 632 BITS 316/ (462* 1024*8) = 0.0083% IMAGE2. JPEG 550 HI PRIYA 512 BITS 263/ (663* 1024*8) = 0.0048% NO OF ALTERED BITS CONCLUDING AND REMARKS For concluding all of the above the two main stages are included during the steganography process, which are; embedding and extraction stages. The system implemented using Java for embedding and extraction stages. This is the conclusion remarks regarding to the proposed scheme performance. The proposed system was successfully tested with different format of images and also resizes the size of image file for purpose of portability. The above makes difficult to the unauthorized person to determine the presence of secret message. References [1] Md. Olioul Islam ―A High Embedding Capacity Image Steganography using Stream Builder and Parity Checker‖ 15th International Conference on Computer and Information Technology (ICCIT) on pp. 458-463, IEEE, December 2012. [2] Rajkumar Yadav, Rahul Rishi & Sudhir Batra, ―A New Steganography Method for Gray Level Images using Parity ISSN: 2231-5381 http://www.ijettjournal.org Page 69 International Journal of Engineering Trends and Technology (IJETT) – Volume 34 Number 2- April 2016 Checker‖, International Journal of Computer Applications (09758887) Volume 11-No. 11, December 2010. [3] Johnson, Neil; Duric, Zoran; Jajodia, Sushil (2001). Information hiding: steganography and watermarking: attacks and countermeasures. Springer. ISBN 978-0-792-37204-2. [4] Neil F Johnson, Sushil Jajodia, ―Exploring Stenography: Seeing the Unseen‖, IEEE Computer, pp 26-34, Feb 1998. [5] Currie, D.L. & Irvine, C.E., ―Surmounting the effects of lossy compression on Steganography‖, 19th National Information Systems Security Conference on pp. 194-201, Baltimore, Md, October 1996. [6] D. Artz, ―Digital Steganography: Hiding Data within Data‖, IEEE Internet Computing, vol. 5, no. 3, pp. 75-80, June 2001. [7] Alam, Shahzad, S. M. Zakariya, and M. Q. Rafiq. "Analysis of Modified LSB Approaches of Hiding Information in Digital Images." Computational Intelligence and Communication Networks (CICN), 2013 5th International Conference on pp. 280285, IEEE, September 2013. [8] Rong –Jian Chen, Shi-Jinn Horng, ―Multi-bit Adaptive Embedding Algorithm for Anti-Forensic Steganography‖ Biometrics and Security Technologies (ISBAST), International Symposium on pp. 82-89, IEEE, March 2012. [9] Chaudhary, Ankit, and Jaldeep Vasavada. "A hash based approach for secure keyless image steganography in lossless RGB images." Ultra Modern Telecommunications and Control Systems and Workshops (ICUMT), 2012 4th International Congress on pp. 941-944, IEEE, October 2012. [10] Roy, Ratnakirti. "Evaluating image steganography techniques: Future research challenges." Computing, Management and Telecommunications (ComManTel), 2013 International Conference on pp. 309-314, IEEE, January 2013. [11] Akhta, and Shahbaaz Khan. "Enhancing the Security and Quality of LSB Based Image Steganography." Computational Intelligence and Communication Networks (CICN), 2013 5th International Conference on pp. 385-390, IEEE, September 2013. [12] Dagadita, , Emil Ioan Slusanschi, and Razvan Dobre. "Data Hiding Using Steganography." Parallel and Distributed Computing (ISPDC), 2013 IEEE 12th International Symposium on pp. 159166, IEEE, June 2013. [13] M. Zawawi, R. Mahmod, N. Udzir, F. Ahmad, and J. Desa, "Active warden as the main hindrance for steganography information retrieval" International Conference in Information Retrieval Knowledge Management (CAMP), pp. 277-280, March 2012. [14] Amitava Nag, Saswati Ghosh, Sushanta Biswas, Debasree Sarkar " An Image Steganography Technique using X-Box Mapping", International Conference on Advances in Engineering, Science and Management (ICAESM -2012) on pp. 709-713, IEEE, March 2012. [15] Chen, Rong-Jian, Jui-Lin Lai, and Shi-Jinn Horng. "Antiforensic Steganography Using Multi-bit Minimum Error Replacement with Flexible Bit Location."Computer, Consumer and Control (IS3C), 2012 International Symposium on pp. [16] Nguyen, Luong Viet, Trinh Nhat Tien, and Ho VanCanh. "The method of hiding steganography without key exchanging and original image." Computer Science and Automation Engineering (CSAE), 2012 IEEE International Conference on Vol. 2, pp.408412, IEEE, May 2012. [17] Karaman, H. B., and S. Sagiroglu. "An Application Based on Steganography."Proceedings of the 2012 International Conference on Advances in Social Networks Analysis and Mining ISSN: 2231-5381 http://www.ijettjournal.org Page 70