Abstract - Technofist
advertisement
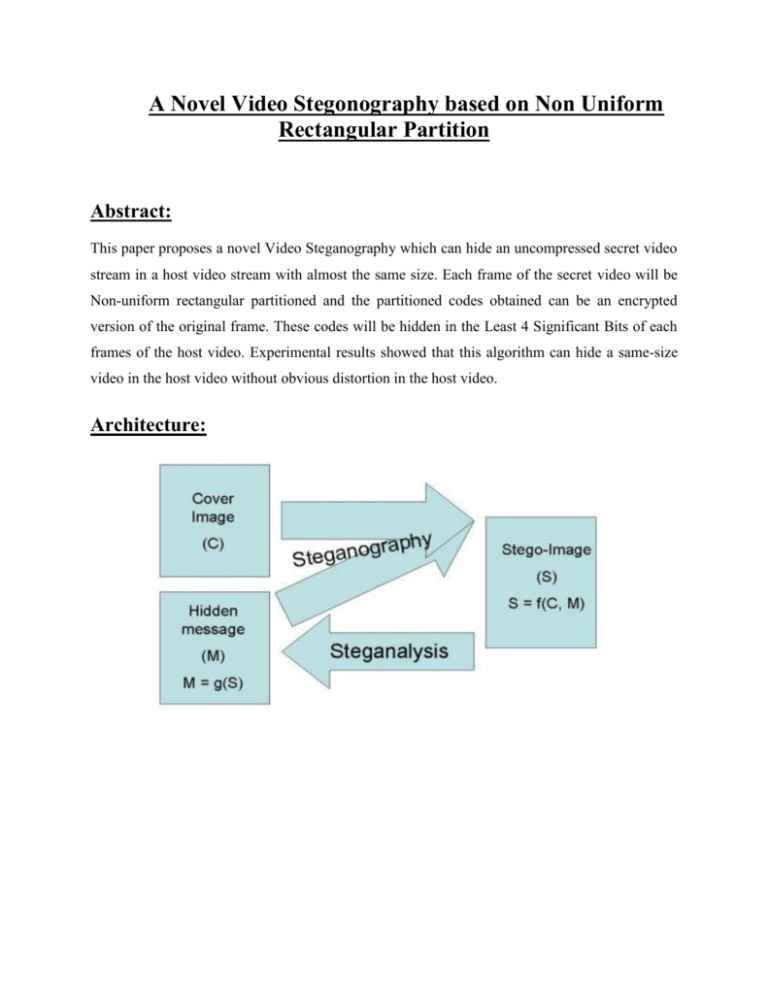
A Novel Video Stegonography based on Non Uniform Rectangular Partition Abstract: This paper proposes a novel Video Steganography which can hide an uncompressed secret video stream in a host video stream with almost the same size. Each frame of the secret video will be Non-uniform rectangular partitioned and the partitioned codes obtained can be an encrypted version of the original frame. These codes will be hidden in the Least 4 Significant Bits of each frames of the host video. Experimental results showed that this algorithm can hide a same-size video in the host video without obvious distortion in the host video. Architecture: Literature Survey: 1. AN OVERVIEW OF IMAGE STEGANOGRAPHY Steganography is the art of hiding the fact that communication is taking place, by hiding information in other information. Many different carrier file formats can be used, but digital images are the most popular because of their frequency on the Internet. For hiding secret information in images, there exists a large variety of steganographic techniques some are more complex than others and all of them have respective strong and weak points. Different applications have different requirements of the steganography technique used. For example, some applications may require absolute invisibility of the secret information, while others require a larger secret message to be hidden. This paper intends to give an overview of image steganography, its uses and techniques. It also attempts to identify the requirements of a good steganographic algorithm and briefly reflects on which steganographic techniques are more suitable for which applications. 2. On The Limits of Steganography In this paper, we clarify what steganography is and what it can do. We contrast it with the related disciplines of cryptography and traffic security, present a unified terminology agreed at the first international workshop on the subject, and outline a number of approaches |many of them developed to hide encrypted copyright marks or serial numbers in digital audio or video. We then present a number of attacks, some new, on such information hiding schemes. This leads to a discussion of the formidable obstacles that lie in the way of a general theory of information hiding systems (in the sense that Shannon gave us a general theory of secrecy systems). However, theoretical considerations lead to ideas of practical value, such as the use of parity checks to amplify covertness and provide public key steganography. Finally, we show that public key information hiding systems exist, and are not necessarily constrained to the case where the warden is passive. Existing System: DATA hiding in digital images and raw video have wide literature. In case the data is extracted, it will be encrypted. But still there is a chance that the intruder can break the code. However, we find that in most existing approaches, the choice of embedding positions within a cover image mainly depends on a pseudorandom number generator without considering the relationship between the image content itself and the size of the secret message. Disadvantages: We find that the existing PVD (Pixel value differentiation)-based approaches cannot make full use of edge information for data hiding, and they are also poor at resisting some statistical analyses. Proposed System: The method proposed in this paper is one kind of domain method which tries to get a data-hiding capacity without causing obvious distortion in the host video stream. Therefore a video stream can be embedded into the host video stream after encoding the secret video by applying the nonuniform rectangular partition. The coding process can be controlled by some key parameters which can be treated as the encryption key and this can increase the difficulty from being steg analyzed. Advantages: The implementation process is almost totally different for the two following main points: a. Adaptive non-uniform rectangular partition is used (i.e) key is embed in the video frames. b. Partition information of the hidden image is recorded and carried by the open host image. Algorithm: Image Steganography algorithm: In order to investigate the feasibility and effect of the proposed image Steganography algorithm, many experiments have been done. Each group gives (a) the hidden image, that is the original image itself, (b) the disguising image or host image, chosen arbitrarily and is significantly different from the hidden image, (c) the disguising image with information of the hidden image, (d) the reconstructed image, whose quality depends on the actual problem and the subjective judgment. Modules: 1 Encryption module: Allows trusted users to access sensitive information while traversing untrusted networks, it is highly useful for users. The services and users are limited in their tunnel traffic. 2. Protection and Detection mode: Easy testing of new rules in a live environment without disrupting the current security policy is supported. Rule sets are applied by deploying them in Protection mode to enforce secure behavior, permit or deny traffic and seal web application parameters against modification. Rule sets are tested by deploying them in Detection mode to evaluate them against traffic and log actions without enforcing them. 3. Encoding and Decoding Image Steganography: We have chosen this stage because its contents are processed internally during the image encoding/ decoding which makes it hard to be detected by image steganalysis methods and is lossless coded, thus it is not prone to quantization distortions. The data bits of the message are hidden in some of the image whose magnitude is above a predefined threshold. A single bit is hidden in the least significant bit of the larger component of each image. 4 Data hiding through image: Finally, Admin encrypt the key and embed in the image send to the newly registered member who is the authenticated. After receiving the key to the authenticated he has only the permission to take the key when extract the image. 5 Video Steganography based on image Steganography: We extend the image hidden technique to video one. Here we simply consider the steganography in the uncompressed video. That means we try to hide a key in video with almost the same size. The main idea is that we treat each frame of the videos as the images and apply the image steganography for each frame with some necessary mechanism. System Requirements: Hardware Requirements: System : Pentium IV 2.4 GHz. Hard Disk : 40 GB. Floppy Drive : 1.44 Mb. Monitor : 15 VGA Colour. Mouse : Logitech. Ram : 512 Mb. Software Requirements: Operating system : – Windows XP. Coding Language : Java Data Base : File System





















