Principles of Fiber Optic Transmission (I)
advertisement

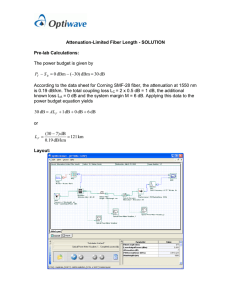
Principles of Fiber Optic Transmission (I) In This Lecture Elements of an Optical Fiber communication Optical fibers Amplitude Modulation Elements of an Optical Fiber communication • Fiber optic links contain three basic elements – transmitter – optical fiber – receiver User Input(s) Transmitter Electrical-to-Optical Conversion Optical Fiber Receiver User Output(s) Optical-to-Electrical Conversion • Transmitter (TX) – Electrical interface encodes user’s information through AM, FM or Digital Modulation – Encoded information transformed into light by means of a light-emitting diode (LED) or laser diode (LD) User Input(s) Electrical Interface Data Encoder/ Modulator Light Emitter Optical Output • Receiver (RX) – decodes the light signal back into an electrical signal – the data decoder/demodulator converts the signals into the correct format Optical Input Light Detector/ Amplifier Data Decoder/ Demodulator Electrical Interface User Output(s) Optical fibers Optical fibers carry light energy from the transmitter to the receiver. An optical fiber may be made of glass or plastic. The fiber can carry light around corners and over great distances. Comparison of fiber and copper cables Connectors The connector is attached to the optical fiber and allows it to be mated to the transmitter or receiver to provide solid contact. The connector must align the fiber end precisely with the light source or receiver to prevent signal loss. Advantages of optical fibers Can carry much more information Less expensive . Thinner Much higher data rates Much longer distances than co-axial cables Immune to electromagnetic noise Light in weight Unaffected by atmospheric agents Amplitude Modulation • One method used for converting electrical signals into light signals for transmission is amplitude modulation (AM). . Electrical energy with continuously varying voltage is converted into converted into Light with continuously varying brightness Amplitude modulation requires two components: a carrier and a signal that is imposed on the carrier—also known as the intelligence —to change it in some way Amplitude modulation requires two components: a carrier and a signal that is imposed on the carrier—also known as the intelligence —to change it in some way To modulate the amplitude of the light in a fiber optic transmitter, the intelligence is sent through a circuit that changes it to a continuously varying voltage. As the intelligence changes, the voltage controlling the light rises and falls, varying the light’s intensity to match the intelligence. Amplitude modulation suffers from two problems that can affect the quality of the signal: attenuation and noise. Noise : can be considered data without meaning; that is, data that is not being used to transmit a signal, but is simply produced as an unwanted by-product of other activities. Attenuation :Attenuation is a measure of how much a signal weakens as it travels through a medium.