Document 11123981
advertisement

K~
Name:
5C226 Exam 1
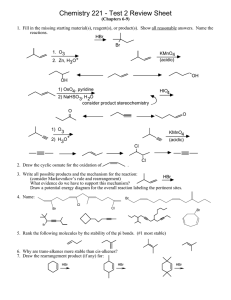
1.
't
8 Feb 2016
Prof. Urban
proVi~e
names for these compounds. (12 points)
&
>-tYl~#..;~ IY
OH
~"
3-~-2-Wl~ur-~IW<'~~~ CI
2.
Draw structures
of these compoun ds. (8 points)
.
2-ammohexanoic acid tJ \-\ 2.­
L'-chloroaniline
~N~1..
::'1
\\~~
Ul.
0
i
benzoic anhydride
J3\9
.-
I
l
\..::.)­
0
\,... \
benzyl alcohol
n
.:::::..r-­
C1 h
. ..- O\{
4.
Predict the major product of the reaction below and provide a mechanism that accounts for its
formation. (4 POin~
H'XH, aCI.
\-\
eA
~ -
5.
'.
" ~ \.
C-
C~>~.
GH 3
(Y~
~ ~~ClU3_ :~; .Y'--lCl~1
-/'~t1
~,J
~
Predict the product(s) of the reaction below and provide a complete mechanism showing
movement of electrons with curved arrows, formal charges, resonance, etc. Be sure to account
for the stereochemical course of the reaction and explain it in terms of the mechanism.
··Xnt')
~
B".
cr~
-}-I~
'ijy- ~,
~
.' •
+-
k
~) R
5
G
.~-: lL"D/
'B;":
~ r;
"88~~\H
f3rj
,I..
~B~
I\*\~
D/
OIJ r)
?~
o.Y (~,~ h'i~
Qr
',I
J
,
,.,.
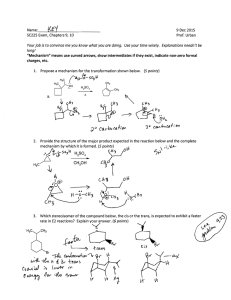
6.
Provide a complete mechanism that accounts for the formation of both of the products. In your
mechanism, show movement of electrons with curved arrows, provide all formal charges and
important resonance structures. (4 points)
&.sr
at.~
~i.·HBr..
V A"....~
.
~.'
.
.
.'
-I-
BrU~
.
@
•.G!~·~·
.@.,
. _lr)y~~B
"l~~' @ol . Ii. T~ ~'-'
&I«~
C+
2
oM
~/J
tJo1lf: I~
A
~ tHJ. CMho ~ . . uL
..-
_.
0 -
.(;,. 4J
~
fIJ1J-
CJ....~-
'2.
~
ct~ J­
IJ
~
x-J-
()
,.:
~""d
a. The product distribution shows a dependence on temperature as indicated in the table below. Why is product A favored at low temperature and product B favored at high temperature? Explain this observation. (2points)
b M",<- k~,(\e f,t. f
A
Observed Product Distribution
A
B
Low Temp
80%
20%
High Temp
20%
80%
-h
k<
B IS:fM.
A-t
low l)
I">
~
V~:\M
\ l..-eJJ;'+ID'v\.
f/<M) V (,
~
.
•
~'( i ~+ ~..(;vdd ~ -tLt. (~ .
~ n ~ ~~.
-f.o,t ~ ~1A:m
Nl
~
J.4 vj \
)'.J
I
~
"(''-<.I1M
~tao
ret)..
.tvlrw:f
i...
I"
I.b
f1"-
£
ies
s~bl< rO&vV+) B) ?t'e DMi'~'l
.
r#{.Y51 ~ (.
~ ~lJ'Ie
~ v ()
0
+~"'-Od~W\,'- fi'oJ~ ~(,\A \I~,-(JJI\--I~
f:>.. 'PfedolMiVl.e,-\-er
hk It ~~<, ~M
@uT J M ~
lJ~f1") ~l
.Il
1-..k
\
(0
_6
•
~.lr M,,:LI,I";v ...... ,
/"'II
0v
b. Provide a sketch of the energy vs. reaction coordinate plot for this reaction that shows the relative energies of the starting materials, products A and B, and any intermediates and transition states. (3 points) >­
e.n
C1J
c
w
Products
Reactants
Reaction Coordinate
/'
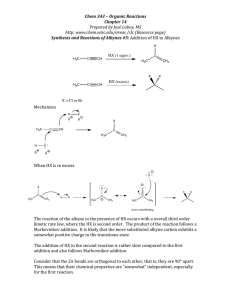
7. Fill in the blank. Provide the reagents and reaction conditions needed to transform the alkene
below into each of the indicated products. (9 pOints)
~OH?
/\
I)
~
~~,TI1P /\ -
I)
~ (0 At)2.
?
..
~
7.)rJ,,~/)H~
HO
'-
~
l\ '­
J
I/,{)i
VI"
ko (}- '{ {(Jill"
j?
"') H
..O'-J A.WIij
x<J
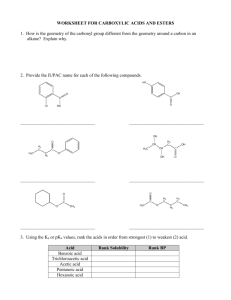
8. Fill in the blanks. Provide the missing product(s), starting materials, or reagents. Indicate
stereochemistry and/or product mixtures (major vs minor products) as appropriate. (40 points)
Q
H3C
1) OsO4' ether
•
CH 3
Ii
(JC""
H2
CHs
Pt
ct~3
Lr~
..
?
~-\ t-H 1
({>Y"
--0 + HBr
..
~~ ?
?
~ t/JJ~ ~
~",:.J
p_
Zn(Cu)
(+ b-Qm !-;f1>rJ./I.-)
?
?
co
?
Brz (excess)
..
?
1) BHa. THF
..
~~
U
H3C··"..
+
CH3
?
9. Provide a synthesis of these compounds from the indicated starting materials. More than one
step may be necessary. Your synthesis may produce both enantiomers of any target that is
chiral. (8 points)
0.
)-~\
a.
HO
CI
<))
\~ 0
~OH
b.
\;t-C:::C-H
from