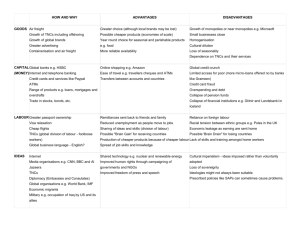
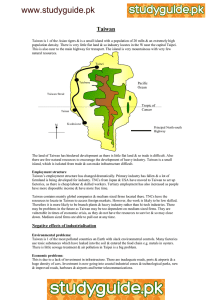
The Rise of Manufacturing in NICs – Asian Tigers
advertisement
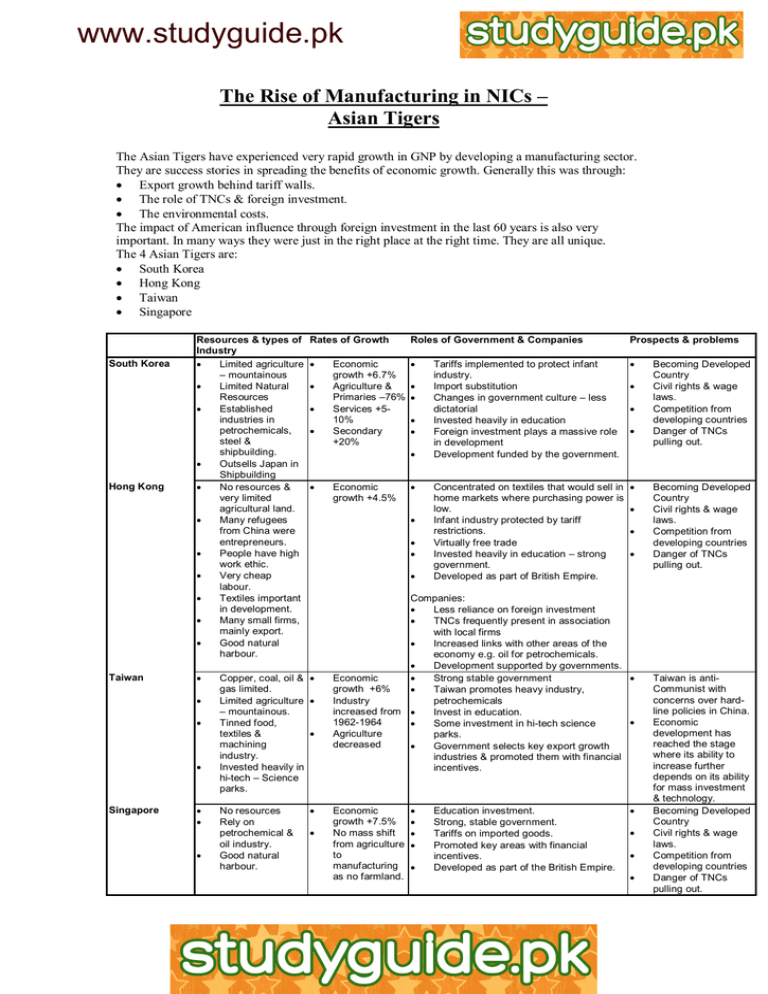
www.studyguide.pk The Rise of Manufacturing in NICs – Asian Tigers The Asian Tigers have experienced very rapid growth in GNP by developing a manufacturing sector. They are success stories in spreading the benefits of economic growth. Generally this was through: Export growth behind tariff walls. The role of TNCs & foreign investment. The environmental costs. The impact of American influence through foreign investment in the last 60 years is also very important. In many ways they were just in the right place at the right time. They are all unique. The 4 Asian Tigers are: South Korea Hong Kong Taiwan Singapore South Korea Hong Kong Taiwan Resources & types of Industry Limited agriculture – mountainous Limited Natural Resources Established industries in petrochemicals, steel & shipbuilding. Outsells Japan in Shipbuilding No resources & very limited agricultural land. Many refugees from China were entrepreneurs. People have high work ethic. Very cheap labour. Textiles important in development. Many small firms, mainly export. Good natural harbour. Singapore Rates of Growth Roles of Government & Companies Prospects & problems Tariffs implemented to protect infant industry. Import substitution Changes in government culture – less dictatorial Invested heavily in education Foreign investment plays a massive role in development Development funded by the government. Concentrated on textiles that would sell in home markets where purchasing power is low. Infant industry protected by tariff restrictions. Virtually free trade Invested heavily in education – strong government. Developed as part of British Empire. Economic growth +4.5% Copper, coal, oil & gas limited. Limited agriculture – mountainous. Tinned food, textiles & machining industry. Invested heavily in hi-tech – Science parks. No resources Rely on petrochemical & oil industry. Good natural harbour. Economic growth +6.7% Agriculture & Primaries –76% Services +510% Secondary +20% Companies: Less reliance on foreign investment TNCs frequently present in association with local firms Increased links with other areas of the economy e.g. oil for petrochemicals. Development supported by governments. Economic Strong stable government growth +6% Taiwan promotes heavy industry, Industry petrochemicals increased from Invest in education. 1962-1964 Some investment in hi-tech science Agriculture parks. decreased Government selects key export growth industries & promoted them with financial incentives. Economic growth +7.5% No mass shift from agriculture to manufacturing as no farmland. Education investment. Strong, stable government. Tariffs on imported goods. Promoted key areas with financial incentives. Developed as part of the British Empire. Becoming Developed Country Civil rights & wage laws. Competition from developing countries Danger of TNCs pulling out. Becoming Developed Country Civil rights & wage laws. Competition from developing countries Danger of TNCs pulling out. Taiwan is antiCommunist with concerns over hardline policies in China. Economic development has reached the stage where its ability to increase further depends on its ability for mass investment & technology. Becoming Developed Country Civil rights & wage laws. Competition from developing countries Danger of TNCs pulling out.