Document 10455540
Phy 2053 Announcements
1.
Exam 2 is coming soon!!
Thursday, April 2, 8:20 – 10:10 pm
Material from Chapters 5-8 of Serway/Vuille
Only the sections we covered in class
20 questions, multiple choice
Very much like the first exam
There is only one correct answer to the question “In order to receive credit for this problem, you must correctly code (“bubble in”) your UFID and your 5-digit test number…”
Æ I have correctly bubbled my UFID number and 5-digit test code.
Please get there at least 10 minutes early, and preferably 20 minutes
New protocols - stay in your seat until your exam is collected. Raise your hands; proctors will come to collect it.
If you want to avoid the long wait at the end, either (a) come early and sit at the front or (b) finish early
Please circle your answer on the exam
More Phy 2053 Announcements
Room assignments for Exam 2
BRY130: A-ELU
FLG220: EMM-HER
FLG230: HEW-LAI
FLG260: LAM-MON
FLG270: MOO-P
LIT121: R-SAW
MAEB211:SCH-T
MAT18: U-Z
You be allowed one handwritten formula sheet
(both sides), 8 ½” x 11” paper
In class review, Tuesday, March 31
Even More Phy 2053 Announcements
Make-up exam for students missing Exams
1 and 2 will be held Wednesday, April 22 from 7:20 – 9:10 pm
Room to be announced later
If you need to take a make-up because of a legitimate excuse, please send Prof. Chan and I an e-mail as soon as possible
HW Assignment 9 due two weeks from yesterday, Wednesday, March 8
But, you should do the problems from Ch 8 before the test!
Rotational Kinetic Energy
Equivalent to
KE =
KE
=
1
2
1
2
I
ω
m v 2
2
Conservation of Mechanical Energy
( KE t
+ KE r
+ PE g
+ PE ) = ( KE t
+ KE r
+ PE g
+ PE
Work-Energy Theorem: W nc
=
Δ
KE t
+
Δ
KE
R
+
Δ
PE
Example: Problem 8-44, p 262
Four objects – a hoop, a solid cylinder, a solid sphere, and a thin, spherical shell – each have a mass of 4.8 kg and a radius of 0.23 m. (a) Find the moment of inertia for each object as it rotates about the axes shown in Table
8.1. (b) Suppose each object rolls down a ramp without slipping. Rank the translational speed of each object from highest to lowest. (c) Rank the objects’ rotational kinetic energy from highest to lowest as the objects roll down the ramp.
θ http://www.photoshopsupport.com/photoshop-blog
/05/10/11-liquid-sculpture.html
http://p25ext.lanl.gov/~hubert/aerogel/
Chapter 9
Solids and Fluids
www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/volcano/anat_02.html
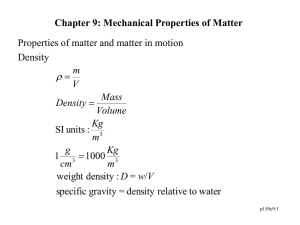
1
States of Matter
Solid
Atoms close together
Fixed positions
Electrostatic forces
Quantum mechanics!
I - crystalline
Liquid
No long range order
(usually) at higher
Temperatures
Gas
Molecules are in constant random motion
Molecules exert weak forces on each other
Average separation is large compared to the size of the molecules
Plasma
Gas heated to a very high temperature
Many of the electrons are freed from the nucleus
II - amorphous
Strength of materials
States of matter – what we don’t know
What the universe is made of:
?
?
We know about this edelweiss.in2p3.fr/Presentation/index.php
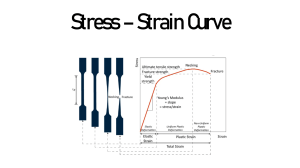
Elastic Properties of Solids
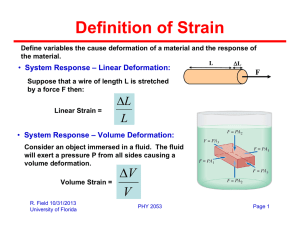
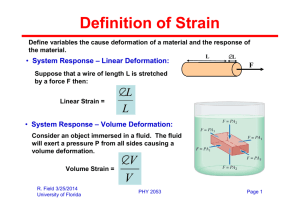
Stress is the force per unit area causing the deformation
Strain is a measure of the amount of deformation
The elastic modulus is the constant of proportionality between stress and strain
For sufficiently small stresses, the stress is directly proportional to the strain
The constant of proportionality depends on the material being deformed and the nature of the deformation
2
Quantitative characterization of mechanical properties of materials
Elastic behavior:
Hooke’s Law
Why is stress defined as force per unit area (F/A) ??
What is strain ?
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3UZuPayyAnM
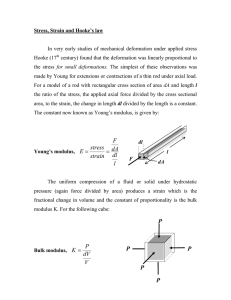
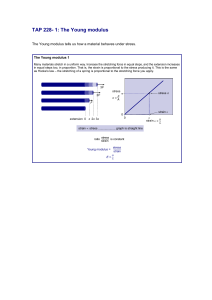
Young’s Modulus:
Elasticity in Length
A
L
0
Δ
L
F
Stress = F/A
Strain =
Δ
L/L
0
Young’s Modulus:
F
A
=
Y
Δ
L
L o
Stress = Y x Strain
or
Stress
Strain
=
Y
3