Statistics for the Behavioral Sciences
advertisement

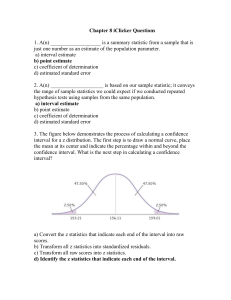
Susan A. Nolan and Thomas E. Heinzen Statistics for the Behavioral Sciences Second Edition Chapter 8: Confidence Intervals, Effect Size, and Statistical Power iClicker Questions Copyright © 2012 by Worth Publishers Chapter 8 1. A(n) ___________________ is a summary statistic from a sample that is just one number as an estimate of the population parameter. a) interval estimate b) point estimate c) coefficient of determination d) estimated standard error Chapter 8 (Answer) 1. A(n) ___________________ is a summary statistic from a sample that is just one number as an estimate of the population parameter. a) interval estimate b) point estimate c) coefficient of determination d) estimated standard error Chapter 8 2. A(n) ____________________ is based on our sample statistic; it conveys the range of sample statistics we could expect if we conducted repeated hypothesis tests using samples from the same population. a) interval estimate b) point estimate c) coefficient of determination d) estimated standard error Chapter 8 (Answer) 2. A(n) ____________________ is based on our sample statistic; it conveys the range of sample statistics we could expect if we conducted repeated hypothesis tests using samples from the same population. a) interval estimate b) point estimate c) coefficient of determination d) estimated standard error Chapter 8 3. The figure below demonstrates the process of calculating a confidence interval for a z distribution. The first step is to draw a normal curve, place the mean at its center and indicate the percentage within and beyond the confidence interval. What is the next step in calculating a confidence interval? a) Convert the z statistics that indicate each end of the interval into raw scores. b) Transform all z statistics into standardized residuals. c) Transform all raw scores into z statistics. d) Identify the z statistics that indicate each end of the interval. Chapter 8 (Answer) 3. The figure below demonstrates the process of calculating a confidence interval for a z distribution. The first step is to draw a normal curve, place the mean at its center and indicate the percentage within and beyond the confidence interval. What is the next step in calculating a confidence interval? a) Convert the z statistics that indicate each end of the interval into raw scores. b) Transform all z statistics into standardized residuals. c) Transform all raw scores into z statistics. d) Identify the z statistics that indicate each end of the interval. Chapter 8 4. Based on the figure, what is the fourth (or next) step in calculating a confidence interval? a) Convert the z statistics that indicate each end of the interval into raw scores. b) Transform all z statistics into standardized residuals. c) Transform all raw scores into z statistics. d) Identify the z statistics that indicate each end of the interval. Chapter 8 (Answer) 4. Based on the figure, what is the fourth (or next) step in calculating a confidence interval? a) Convert the z statistics that indicate each end of the interval into raw scores. b) Transform all z statistics into standardized residuals. c) Transform all raw scores into z statistics. d) Identify the z statistics that indicate each end of the interval. Chapter 8 5. Which figures below would produce larger effect sizes? a) A and B b) B and D c) A and C d) C and D Chapter 8 (Answer) 5. Which figures below would produce larger effect sizes? a) A and B b) B and D c) A and C d) C and D Chapter 8 6. What measure of effect size assesses the difference between two means in terms of standard deviation? a) statistical power b) eta squared c) Cohen’s d d) R2 Chapter 8 (Answer) 6. What measure of effect size assesses the difference between two means in terms of standard deviation? a) statistical power b) eta squared c) Cohen’s d d) R2 Chapter 8 7. What is the correct formula for Cohen’s d for a z statistic? a) b) c) d) d= (X1 – X2) + (M1+M2) __________________ R2 d= (Mx – My) – (μx – μy) __________________ Spooled d= (M – μ) ___________________ σ d= M – μ + (μ)(σ) ______________ N Chapter 8 (Answer) 7. What is the correct formula for Cohen’s d for a z statistic? a) b) c) d) d= (X1 – X2) + (M1+M2) __________________ R2 d= (Mx – My) – (μx – μy) __________________ Spooled d= (M – μ) ___________________ σ d= M – μ + (μ)(σ) ______________ N Chapter 8 8. ___________________ is a measure of our ability to reject the null hypothesis given that the null hypothesis is false. a) Statistical power b) eta squared c) Cohen’s d d) R2 Chapter 8 (Answer) 8. ___________________ is a measure of our ability to reject the null hypothesis given that the null hypothesis is false. a) Statistical power b) eta squared c) Cohen’s d d) R2 Chapter 8 9. The figure below demonstrates the process of calculating statistical power. What is the first step in calculating statistical power? a) Determine the cutoff for one-tailed test with a p level of 0.05. b) Use the numbers that characterize the two populations of interests to draw two curves that represent the hypothetical distributions of z scores in order to determine the percentage above and below the mean. c) Calculate the z statistic for the mean. d) Determine the information needed to calculate statistical power- the population mean, the population standard deviation, the hypothesizes mean for the sample, the sample size and the standard error based on this sample size. Chapter 8 (Answer) 9. The figure below demonstrates the process of calculating statistical power. What is the first step in calculating statistical power? a) Determine the cutoff for one-tailed test with a p level of 0.05. b) Use the numbers that characterize the two populations of interests to draw two curves that represent the hypothetical distributions of z scores in order to determine the percentage above and below the mean. c) Calculate the z statistic for the mean. d) Determine the information needed to calculate statistical power- the population mean, the population standard deviation, the hypothesizes mean for the sample, the sample size and the standard error based on this sample size. Chapter 8 10. Name three ways to increase statistical power. a) increase your alpha, turn a two-tailed hypothesis into a one-tailed hypothesis, and increase N b) use nonparametric statistics, increase your beta, and increase your N c) turn a two-tailed hypothesis into a one-tailed hypothesis, increase your alpha levels, and decrease N d) increase your alpha levels, increase your beta levels, and increase N Chapter 8 (Answer) 10. Name three ways to increase statistical power. a) increase your alpha, turn a two-tailed hypothesis into a one-tailed hypothesis, and increase N b) use nonparametric statistics, increase your beta, and increase your N c) turn a two-tailed hypothesis into a one-tailed hypothesis, increase your alpha levels, and decrease N d) increase your alpha levels, increase your beta levels, and increase N Chapter 8 (Answer) 11. A study that involves the calculation of a mean effect size from the individual effect sizes of many studies is called a: a) Prep test. b) meta-analysis. c) file drawer analysis. d) power test. Chapter 8 (Answer) 11. A study that involves the calculation of a mean effect size from the individual effect sizes of many studies is called a: a) Prep test. b) meta-analysis. c) file drawer analysis. d) power test.