Pelvis + Perineum
advertisement

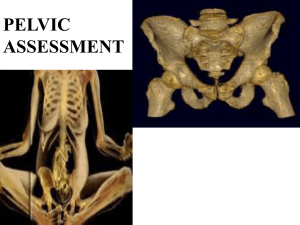
Pelvis + Perineum Pelvic Cavity Enclosed by bony, ligamentous and muscular wall Contains the urinary bladder, ureters, pelvic genital organs, rectum, blood vessels, lymphatics and nerves Pelvic inlet (superior pelvic aperture) Pelvic outlet (inferior pelvic aperture) Superior Apeture Inferior Pelvic Border Bony Pelvis Innominate bone (Ilium, ischium and pubis) Sacrum Coccyx Joined anteriorly by pubic symphysis Posteriorly by sacro-iliac joint Bony Pelvis Female Pelvis Male Pelvis Pelvis Greater Pelvis (pelvis major) Location of some abdominal viscera (ileum and sigmoid colon) Bounded by abdominal wall anteriorly, the iliac fossa posteriolaterally and L5 S1 vertebrae posteriorly AKA False Pelvis Lesser Pelvis ( pelvis minor) Location of pelvic viscera – the urinary bladder and reproductive organs such as the uterus and ovaries Bounded by the pelvic surfaces of the hip bones, sacrum, and coccyx Limited inferiorly by the musculofascial pelvic diaphragm AKA True Pelvis Pelvic Diaphragm Pelvic Walls and Floors Anterior pelvic wall – is formed primarily by the bodies and rami of the pubic bones and the pubic symphysis Lateral pelvic walls – formed by the hip bones and the obturator internus muscles (O: proximal surface of the ilium and ischium; obturator membrane I: greater trochanter of the femur) Anterior Pelvic Wall Pelvic Walls and Floor Posterior Pelvic Wall – formed by the sacrum and coccyx, adjacent parts of the ilia, and the S-I joints; piriformis muscle covers the area (O: pelvic surface of 2nd and 4th sacral segments, superior margin of the greater sciatic notch and sacrotuberous ligament, I: greator trochanter of femur) Posterior Pelvic Wall Posterior Pelvic Wall Pelvic Floor Formed by the funnel shaped pelvic diaphragm – consists of the levator ani and coccygeus muscles and their fascia Stretches between the pubis anteriorly and the coccyx posteriorly and from one lateral pelvic wall to the other Pelvic Floor - Male Pelvic Floor - Female Pelvic Floor- Lateral Inferior Female – Medial View Levator Ani Consists of three parts – the pubococcygeus, the puborectalis and the iliococcygeus. Collectively they run from the body of the pubis, the tendinous arch of the obturator fascia and the ischial spine TO the perineal body, the coccyx, the anococcygeal ligament, the walls of the prostate or vagina, the rectum and the anal canal Innervated by the nerve to levator ani from S4 and the inferior anal (rectal) nerve (from S2-S4) and the coccygeal plexus Help to support the pelvic viscera; acting together they raise the pelvic floor and assist the abdominal muscles in forced expiration activities Coccygeus Muscle O: ischial spine, I: inferior end of the sacrum, I: branches of S4 and S5 Forms a small part of the pelvic diaphragm that supports the pelvic viscera, flexes the coccyx Viscera Urinary organs in the pelvis Ureters – muscular (smooth) tubes running from kidneys to bladder 25 to 30 cm long Bladder – a hollow container surrounded by a strong smooth muscular wall Temporary reservoir for urine Apex, Body, Fundus, Neck, Uvula Ureters Bladder Bladder Bladder Pelvic Viscera - Female M v. F Bladder Viscera Bladder Continued Detrussor muscle – smooth muscles surrounds bladder Internal sphincter muscle Innervation – Parasympathetic to detrussor (S2-S4)); Sympathetic to internal sphincter (T12-L1/L2) Viscera Ureter Urinary urethral orifice in bladder to external urethral orifice External sphincter – somatic nerves from S2-S4) Prostate Female Urethra Female Urethra Male Urethra Male Urethra Uterus Rectum Alimentary canal (GI Tract) connects sigmoid colon with anus Follows the curve of the sacrum and coccyx Innervated by sympathetic (T12/L1)and parasympathetic nerves (S2-S4) Rectum Rectum and Anal Canal Perineum Lies inferior to the pelvic outlet and is separated from the pelvic cavity by the pelvic diaphragm (Levator ani and coccygeus muscles) Bounded by Pubic symphysis anteriorly; inferior pubic rami and ischial rami anterolaterally; ischial tuberosity laterally; sacrotuberous ligament posterolaterally; inferiorly by sacrum and coccyx Perineum Two Triangles – Anal triangle (posterior) contains the anus – Urogenital triangle (anterior) contains the root of the scrotum and penis in males or the external genitalia in females The perineal membrane stretches between the two sides of the pubic arch and covers the anterior part of the outlet The perineal body is an irregular fibromuscular mass located between the anal canal and the perineal membrane Perineal Membrane Perineal Body Perineum-Female Perineum - Male Perineum Muscles Bulbospongiosus – F O: central tendon of perineum, M O: central tendon of perineum and bulb of penis; F I: dorsum of clitoris, urogenital diaphragm, M I: root of penis; A: compress vagina orifice or compress urethra, N: perineal nerve, pudenal nerve Ischiocavernosus – O: ramus of ischium, I: near pubic symphysis, maintains erection of penis or clitoris Muscles - Female Muscles - Female Muscles – Male Muscles - Male Perineum Muscles External anal sphincter (skeletal muscle) – O: skin an fascia surrounding anus and coccyx, I: perineal body, A: closes anal canal, N: Inferior Anal Nerve (Somatic nerve from S2-S4) – inhibits voiding Internal Anal Sphincter – smooth muscle innervated by sympathetic NS (S2,S3,S4) – inhibits voiding External/Internal Anal Sphincter Superficial Transverse Perineal O: Ischial tuberosity I: Perineal body A: Support perineal body N: Pudenal nerve External Urethral Sphincter O: Ischial tuberosity I: surround urethra A: compress urethra to maintain urine continence N: Pudenal (S2-S4) Superficial Transverse Perineal F Superficial Transverse Perineal F Superficial Transverse Perineal M Deep Transverse Perineal O: Medial Aspect of Ischial Ramus I: Pineal Body A: Stabilizes position of the perineal body N: Pudenal N (S2-S4) Deep Transverse Perineal - F Deep Transverse Perineal -M Deep Transverse Perineal - M Deep Transverse Perineal M Superficial Perineum Female Superficial Perineum Female Superficial Perineum Male Superficial Perineum Male Peritoneum Continuous with peritoneum of abdomen Drapes over pelvic viscera in the midline to form: Pouches Folds between viscera and pelvic walls Pouches protect viscera from rectum Female Peritoneum Female Peritoneum Male Peritoneum Male Peritoneum Major Blood Supply