Sugar
advertisement
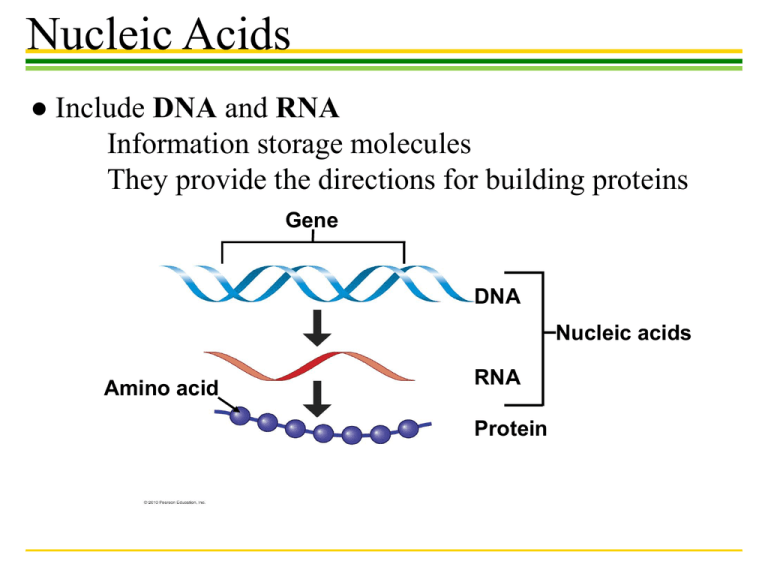
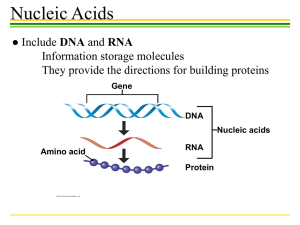
Nucleic Acids ● Include DNA and RNA Information storage molecules They provide the directions for building proteins Gene DNA Nucleic acids Amino acid RNA Protein Nucleic Acids ●Nucleic acids are polymers of nucleotides Nitrogenous base (A,G,C, or T) – DNA, deoxyribonucleic acid – RNA, ribonucleic acid Nitrogenous base A, G, C, or U Thymine (T) Phosphate group Sugar (deoxyribose) Uracil U Phosphate Phosphate group Base Sugar Sugar ribose Nucleic Acids ●Each nucleotide has one of the following bases: Nucleic Acids ●Nucleic Acid Structure Sugar-phosphate backbone Base Nucleotide pair Hydrogen bond Bases a DNA strand polynucleotide b Double helix two polynucleotide strands Nucleic Acids ●Nucleic Acid Structure Nucleic Acids DNA Structure Carbohydrates • Carbohydrates include – Small sugar molecules in soft drinks • Monosaccharides & Disaccharides – Long starch molecules in pasta and potatoes • Polysaccharides Monosaccharides • Monosaccharides are simple sugars – Glucose, found in sports drinks – Fructose, found in fruit • Honey contains both glucose and fructose Glucose Fructose Isomers Monosaccharides • In aqueous solutions, monosaccharides form rings (b) Abbreviated ring structure Disaccharides • A disaccharide is a double sugar • Disaccharides are joined by the process of dehydration synthesis Glucose Glucose Maltose Disaccharides • The most common disaccharide is sucrose, common table sugar – It consists of a glucose linked to a fructose – Sucrose is extracted from sugar cane and the roots of sugar beets Polysaccharides – They are long chains of sugar units – They are polymers of monosaccharides Glucose monomer Starch granules in potato tuber cells (a) Starch Glycogen Granules In muscle tissue (b) Glycogen Cellulose fibril in a plant cell wall Cellulose molecules (c) Cellulose Lipids ●Lipids are: Large biological molecules that do not include polymers. Hydrophobic, unable to mix with water. Oil (hydrophobic) Vinegar (hydrophilic) Lipids ●FATS ● Dietary fat consists largely of the molecule triglyceride – A combination of glycerol and three fatty acids Fatty acid Glycerol (a) A dehydration reaction linking a fatty acid to glycerol (b) A fat molecule with a glycerol “head” and three energy-rich hydrocarbon fatty acid “tails” Lipids (Fats) ●Unsaturated fatty acids – Have less than the maximum number of hydrogens bonded to the carbons ●Saturated fatty acids – Have the maximum number of hydrogens bonded to the carbons Lipids (Fats) TYPES OF FATS Saturated Fats Unsaturated Fats Margarine INGREDIENTS: SOYBEAN OIL, FULLY HYDROGENATED COTTONSEED OIL, PARTIALLY HYDROGENATED COTTONSEED OIL AND SOYBEAN OILS, MONO AND DIGLYCERIDES, TBHO AND CITRIC ACID Plant oils Trans fats ANTIOXIDANTS Omega-3 fats Lipids Phospholipids Steroids Lipids ●STEROIDS Steroids are very different from fats in structure and function. Cholesterol Testosterone A type of estrogen Biological Molecules