Indian National Congress
advertisement

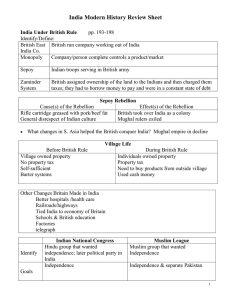
The Modern Indian independence Movement 53:00-1:05:00 Indian National Congress Founded in 1885 - Meant to increase the power of educated Indians in government By the 20th century the party advocated independence Gandhi became president of congress in 1915 - Formed an alliance with a muslim group - Several important members resigned Indian National Congress Other important members include Pandit Jawaharlal Nehru and Dr. Rajendra Prasad Worked against: - caste differences - untouchability - poverty - religious and ethnic boundaries On January 26th 1930 they officially declared their goal to be complete independence - Gandhi originally wanted home rule All-India Muslim League Formed in 1906 Meant to speak for and protect the interests of Muslims in India Major leader during the modern independence movement was Muhammad Ali Jinnah Supported the Independence movement Advocated the two-state theory: that muslims should have their own state Quit India Movement Organized in 1942 by Gandhi - Response to Viceroy Linlithgow unilaterally declaring the entrance of India into WWII Demanded independence in return for Indian involvement in WWII Gandhi called for universal strikes Most congress leaders arrested Not supported by other groups like the Muslim League Indian National Army First formed in 1942 and reformed in 1943 Led by Subhas Chandra Bose (starting in 1943) Formed with the help of the Japanese - helped fight the allies in Asia during WWII Trials of INA members led to anti-British protest in India Sepoys questioned loyalty to Britain Indian Independence Act of 1947 Created the separate dominions of India and Pakistan Legislative authority given to local assemblies Given the right to secede from the British Empire India fully independent in 1950 and Pakistan in 1956