Government Corruption in the Second Half of the 19th
advertisement

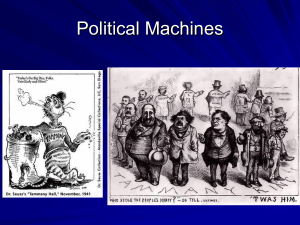
Government Corruption in the Second Half of the th 19 Century Objective 5.04 Scandals of Grant’s Administration •Credit Mobilier Scandal (1872) –Construction company –Owned by Union Pacific stockholders –RR complete, investors made millions, RR was almost bankrupt –RRs often built with the help of government grants –Congressmen were given shares at low prices in return for more grants –Leaked to the press –Caused investigation –Slap on the wrist •Whiskey Ring Scandal (1875) –Began in St. Louis –Conspiracy that diverted tax money to people instead of government –Millions of dollars for those involved before it was put down Urban Corruption •Political Machines and Party Bosses –Informal political groups; prospered due to cities growing faster than gov’ts –Run by party bosses –Provided jobs, food, housing, police and fire protection in exchange for votes Pyramid Scheme City Boss Ward bosses Local precinct workers/captains –Bosses controlled finances and grew rich through graft—getting money by illegal means –Tammany Hall •NYC •Corrupt leader 1860s/1870s— William “Boss” Tweed •Arrested for stealing millions through grafting Thomas Nast •Famous political cartoonist •Exposed corruption of Tweed and other urban politicians Response to Corruption •Republicans split –Stalwarts: supported patronage (spoils system) –Halfbreeds: supported government reform •Election of 1880 –Rutherford Hayes declines to run again –Mixed ticket for Republicans •Halfbreed—James Garfield for President •Stalwart—Chester Arthur for Vice President –Republicans win –Garfield assassinated by a Stalwart in a few months •Pendleton Act (1883) –Assassination creates more public opinion against patronage –Created Civil Service Commission— president chose federal jobs to filled according to rules –Candidate now compete for jobs through exams –Government moves away from spoils system •Election of 1884 –With Republicans split, –Dem. nominate NY Governor Grover Cleveland •Opponent of Tammany Hall –“Mugwumps”—Rep. reformers who backed Cleveland Other items to know… • Secret Ballot: Australian Ballot• Initiative- specified number of voters may propose a statute, constitutional amendment and compel a popular vote on its adoption. • Referendum: the vote on the initiative. • Recall: hold election for elected official before term is up to elect a different person to serve out the term. U.S. v. E.C. Knight, Co. (1895) • Sugar Trust • First to challenge Sherman Anti-Trust Act • Court decided that Congress could not break this trust- was within state limits- not an interstate issue. • Reason why Sherman Anti-Trust act was not effective in the early years. Review questions- answer at the end of your notes -Describe some of the corrupt practices of elected officials/industrial leaders that called for a change in the relationship between gov’t and industry. -Explain any significant legal action that was implemented to challenge the power of industry over gov’t. -Describe public reaction to the various political scandals that involved both politicians and big business leaders. -Assess the further need for change in the gov’t as it related to industry at the turn of the century (1900).