Ch5 STUDY GUIDE NAME DATE BLOCK _____ Mendel concluded
advertisement

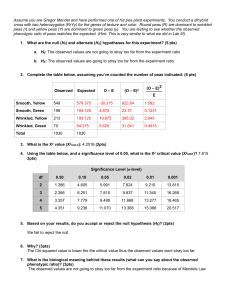
Ch5 STUDY GUIDE NAME ____________________________ DATE _________________ BLOCK _____ 1. Mendel concluded that an individual receives how many genes for each trait? 2. What ratio did Mendel obtain in the second generation every time he crossed first generation hybrids? 3. How do homologous chromosomes differ from chromatids? 4. Perform the following Punnett Square: P = purple flowers Pp x Pp p = white flowers Offspring: Purple _____ % White_____% PP _____% Pp _____% pp _____% 5. Assume for pea plants: P = purple flowers and p = white flowers Give an example of genotypes that are: (a) homozygous dominant _____ (b) heterozygous _____ and (c) homozygous recessive _____ 6. Describe the difference between genotype and phenotype and give an example of a genotype and its phenotype from problem #5. 7. How does incomplete dominance differ from Mendelian heredity where there is one dominant allele and one recessive allele? 8. Perform the following Punnett Square: BB = black chickens WW = white chickens BW = blue chickens Offspring: black _____ % white_____% blue _____% BB _____% WW _____% BW _____% BW x BW 9. Compare: Mitosis Meiosis Purpose of process Type of cell produced How chromosomes line up in metaphase Number of chromosomes in cells at end for humans 10. What contribution did Sutton make to the field of genetics? 11. What sex chromosomes do males have? Females? Perform a Punnett Square showing the probability of a male and female having a boy or girl child. Offspring: Male _____ % Female_____% 12. Define the following terms: a. b. c. d. Allele Dominant trait Fertilization Gamete e. Gene f. Heredity g. Hybrid h. Probability i. Recessive trait j. True-breeding k. Zygote 13. List 3 traits in humans that are inherited: List 3 traits in humans that are acquired: 14. (Honors) Cross RrYy x rrYY (R = round peas, r = wrinkled peas, Y = yellow peas, y = green peas) Round, yellow peas: Round, green peas: Wrinkled, yellow peas: Wrinkled, green peas: