notes for oceans
advertisement

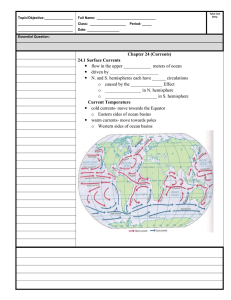
May 9, 2014 Pick up a summary worksheet and slip of white paper. On the slip: Write your name, “Oceans Test” and number from 1-20 going down the page. Goal: Review all concepts on your goal sheet. TEST DAY • After you finish your test, turn the answer sheet in (black tray). • You may use your BYOT device to find a current event about oceans (google current event oceans). • Complete the summary worksheet using your current event. • If you have no device, I will give you a current event to use. Write on page 82 of your ISN Packet page 103 • What do oceans provide? 1. transportation for seeds 2. food, medicines, and salts 3. 70% of Earth’s oxygen 104 • Where did ocean water come from? 1st - volcanic eruptions released water vapor 2nd - water vapor condensed 3rd - torrential rains formed oceans • What is salinity? the measure of the amount of dissolved solids. • What are the two most common solids dissolved in the ocean? sodium and chloride. 105 • What are the three most important gases dissolved in ocean water? oxygen, carbon dioxide, and Nitrogen. • What is photosynthesis? organism uses sunlight, water and carbon dioxide to make food and oxygen. 106 • What happens to pressure as depth increases? – Pressure increases as depth increases. • What happens to temperature as depth increases? – Temperature decreases as depth increases • What are the three temperature layers? 1. surface – warm 2. thermocline – temperature drops quickly as depth increases. 3. Deep-water - cold 108 • What sets water into motion? wind • Surface currents are caused by? wind • Waves are caused by? wind • What is the coriolis effect? It is Earth’s rotation causing currents to curve. 109 • REFER TO MAP: Warm surface currents run past Florida, North Carolina, and Iceland. Cold current runs past California. • How do surface currents affect an area’s climate? – Surface currents distribute heat from one region to another. 110 • When does a density current form? – when a mass of dense seawater sinks beneath less dense water. • Example: Iceland water freezes pure and leaves behind cold, salty water that is dense. It sinks and the water of the gulf stream moves up to replace it. 111 What would happen if density currents stopped? 1. decrease of temperature in some areas 2. increase of temperature in some areas 3. changing rainfall patterns • What is upwelling? – current bringing deep, cold, nutrient-filled water to the surface. This is caused by coastal water being pushed away and replaced by cold water. fish come to eat nutrients 113 What does a wave’s height depend on? 1. wind speed 2. length of time wind blows 3. wind velocity 114 • Describe wave motion. – Floating objects and water molecules do not move forward with a wave. They only rise and fall. The energy moves forward. 115 • How are tides created? – by the gravitational attraction of Earth and the moon and the Sun. • Spring tide? – a perfect line is formed between the Earth, moon, and sun causing higher high tides and lower low tides. • Neap tide? – a 90 degree angle is formed between the Earth, sun, and moon. 117 What are types of ocean life • 1. plankton – one celled organisms (producers) • 2. Nekton – swimming animals (fish, whales, turtle, shark, dolphin) • 3. bottom dwellers – crabs, snails, and sea urchins. – Get food by eating other dwellers, eating decomposing matter, filtering particles 118 • How is energy is transferred from organism to organism? – through food chains. • What are producers, consumers, and decomposers? – Producers (make own food), consumers (eat other organisms), and decomposers (eat decaying stuff) make up the chain. • What do all food chains begin with? – producers! 119 How does recycling in an ecosystem occur? 1. food chain 2. excretion – getting rid of wastes 3. respiration (breathing)