Microbes Kingdoms Study Guide: Archaebacteria, Eubacteria
Microbes Kingdoms Study Guide:
Archaebacteria, Eubacteria, Protists and Fungi
Archaebacteria: Prokaryotic, (no nucleus, circular DNA,), unicellular “ancient” bacteria that have been around for 3 billion years and live in harsh environments like hot springs and volcanoes. Examples include: methane maker, salt lover, heat lover
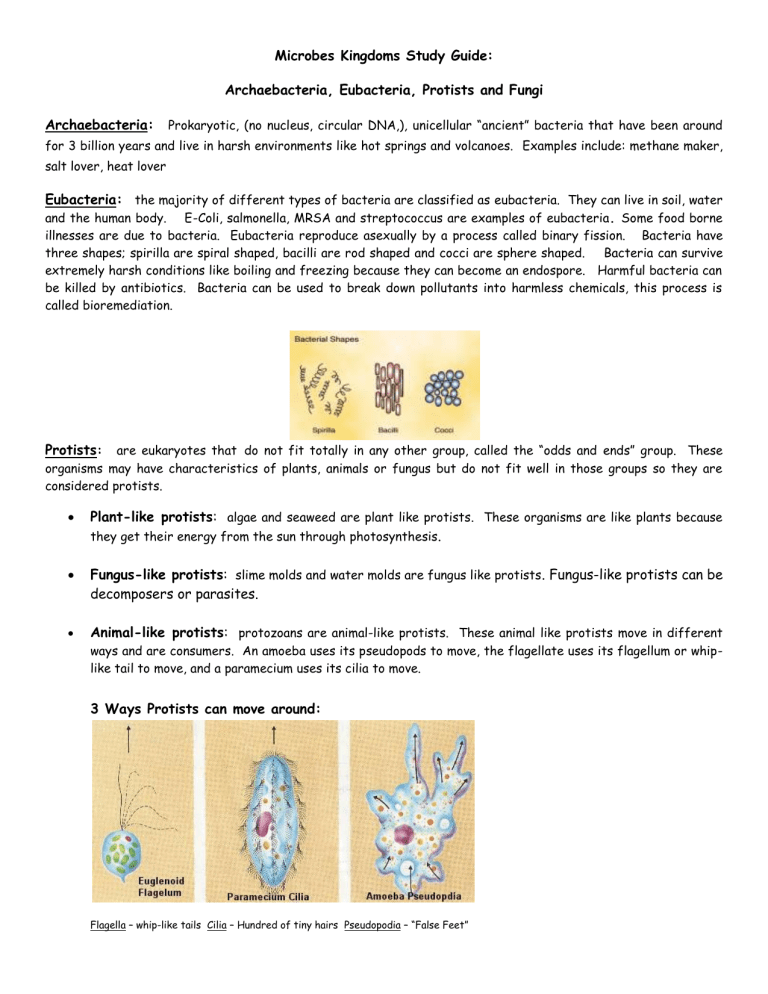
Eubacteria: the majority of different types of bacteria are classified as eubacteria. They can live in soil, water and the human body. E-Coli, salmonella, MRSA and streptococcus are examples of eubacteria. Some food borne illnesses are due to bacteria. Eubacteria reproduce asexually by a process called binary fission. Bacteria have three shapes; spirilla are spiral shaped, bacilli are rod shaped and cocci are sphere shaped. Bacteria can survive extremely harsh conditions like boiling and freezing because they can become an endospore. Harmful bacteria can be killed by antibiotics. Bacteria can be used to break down pollutants into harmless chemicals, this process is called bioremediation.
Protists : are eukaryotes that do not fit totally in any other group, called the “odds and ends” group. These organisms may have characteristics of plants, animals or fungus but do not fit well in those groups so they are considered protists.
Plant-like protists: algae and seaweed are plant like protists. These organisms are like plants because they get their energy from the sun through photosynthesis .
Fungus-like protists: slime molds and water molds are fungus like protists . Fungus-like protists can be decomposers or parasites.
Animal-like protists: protozoans are animal-like protists. These animal like protists move in different ways and are consumers. An amoeba uses its pseudopods to move, the flagellate uses its flagellum or whiplike tail to move, and a paramecium uses its cilia to move.
3 Ways Protists can move around:
Flagella – whip-like tails Cilia – Hundred of tiny hairs Pseudopodia – “False Feet”
Fungi: eukaryotes that are decomposers because they absorb nutrients from dead organisms to get energy. Examples of fungi are molds, mildew and mushrooms.
Characteristics of bacteria and viruses: how are they similar, how are they different?
Bacteria both Viruses reproduce on their own can be helpful to humans prokaryotic cells have DNA reproduce can harm or have no affect on us can’t reproduce without a host do not need energy not made of cells examples: E.Coli, salmonella, lactobacillus
Examples: cold, flu, HIV
*Viruses are not considered to be living things because they do not have cells, do not use energy and `cannot reproduce on their own.






