States of Matter Notes #8 p. 102
advertisement

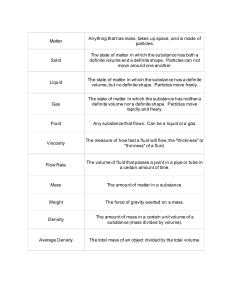
State of Matter 2. Solid 3. Liquid 4. Gas 5. Plasma Volume Shape Particles Definite Definite Vibrate in place Definite Not definite Stay close but move freely Not definite Not definite Not definite Not definite Far apart, move at high speeds in all directions Move at high speeds; found in stars, lightning, and neon lights Diagram Particles are in constant motion; amount of movement depends on their ________ _________. A. __________ _________ - total energy of all the particles in a sample of matter B. The average kinetic energy of particles in a substance is its ______________. C. _________ - movement of thermal energy from a substance with a higher temperature to one with a lower temperature _______ _____ - amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of 1 g of a substance 1° C Matter can _________ states as thermal energy is absorbed or released. A. A change from the solid to the liquid state is called _________. B. A change from the liquid to the solid state is called __________. A change from liquid to gas is called ________________. a. ____________ is vaporization that occurs below the liquid’s surface b. ________________ is vaporization that occurs at the surface of a liquid _____________ - a change from gas to liquid uring ____________the surface particles of a solid gain enough energy to become a gas. 4. Definite shape and volume 5. Found in stars, neon lights, and lightning 6. An example is a desk 7. Has the most energy 8. When water freezes it becomes this 9. An example is orange juice 10. Its molecules will completely fill a container Phases and Transitions Solid Gas Liquid sublimation deposition evaporation condensation melting freezing Phases and Transitions Solid Evaporation Gas Condensation Liquid i __________ equals the force exerted on a surface divided by the total area over which the force is exerted, or P = F / A. Example: P = F / A Water exerts a force of 100 Newtons over an area of 25 m2. What is the pressure? A. If force _____________ over an area, the pressure increases; if force over an area ________________, the pressure decreases. B. _______________ ___________ - air presses down on Earth with force. C. Pressure can be _____________as the pressure pushing down equals the pressure pushing up. D. As _____________ increases, air pressure decreases. Gas pressure in a closed container _________ with volume and temperature changes. Decreasing volume __________ pressure; increasing volume __________ pressure. B. Increasing temperature ___________ pressure; decreasing temperature ___________pressure. ______________ - an upward force on an object immersed in a fluid 17. ______________________ - buoyant force on an object is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the object. ________ is mass divided by volume. a. An object will ______ in a fluid that is denser than the object. b. An object with the same density as the fluid will stay at the ________level in the fluid. c. An object will _____ in a fluid that is less dense than the object. ________________- when a force is applied to a confined fluid, an increase in pressure is transmitted equally to all parts of the fluid. __________________ - allow people to lift heavy objects with relatively little force B. When squeezed, liquids will be pushed out of a ____________, a closed container with a hole in it.