Student Handout - Reading Community Schools
advertisement

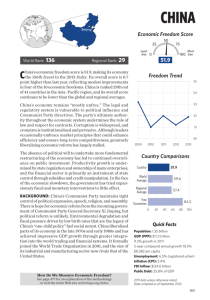
Productivity and Growth; Why Economic Growth Rates Differ Student Guide (15 points) – Two Day Lesson Name WE JUST LEARNED • How we measure long-run economic growth • How real GDP has changed over time • How real GDP varies across countries • The sources of long-run economic growth • How productivity is driven by physical capital, human capital, and technological progress TODAY’S GOAL IS to illustrate • How changes in productivity are illustrated using an aggregate production function • How growth has varied among several important regions of the world and why the convergence hypothesis applies to economically advanced countries • The factors that explain why long-run growth rates differ so much among countries • The challenges of growth posed by scarcity of natural resources, environmental degradation, and efforts to make growth sustainable • Long run economic growth is illustrated with a ongoing movement to the right of LRAS and growth of PPC curve 1. GRAPH and LABEL a AD-AS model; and the PPC curve (consumer goods/y; capital goods x) Q: CREATE a T-Chart distinguishing the differences between fiscal and monetary policy. Q: IDENTIFY one example of a fiscal policy that would shift AD to the right. Q: IDENTIFY one example of a monetary policy that would shift AD to the right. Q: IDENTIFY one example of a fiscal policy that could shift the SRAS to the right. (commodities) Q: IDENTIFY a different example of a fiscal policy that could shift the SRAS to the right. (wages) Q: IDENTIFY yet another example of a fiscal policy that could shift SRAS to the right. (productivity) *Reminder – the following SHIFTS SRAS Commodity prices Nominal wages Productivity *Reminder – the following SHIFTS AD Expectations Wealth Existing Stock of Capital Fiscal Policy Monetary Policy 2. SHARE your responses with the class. 3. READ and DISCUSS an example of the “aggregate production function”. Barry Bosworth and Susan Collins of the Brookings Institution estimated (using data from China and India) the following aggregate production function: GDP per worker = T (Physical capital per worker)0.4 (Human capital per worker)0.6 Governments can play an important role in promoting—or blocking—all three sources of long - term economic growth: physical capital, human capital, and technological progress. 1. Governments and Physical Capital Governments provide infrastructure by building roads, airports, seaports, electrical grids and many others. These systems help consumers and firms engage in economic activity that promotes economic growth. Private firms also invest in physical capital like building new factories, shopping malls, and housing developments. Firms also purchase computer systems, delivery trucks, forklifts and many other pieces of physical capital. If the government can provide infrastructure and maintain a financial system that provides for the saving and borrowing that is required for private investment, a nation’s physical capital will grow. 2. Governments and Human Capital Governments pay for the vast share of primary and secondary education. Any American child can complete high school at very little out-of-pocket expense. When nations make education a higher priority, they subsidize it. More people acquire the education and the nation prospers with long-run economic growth. 3. Governments and Technology While much R & D is done by private companies, the government subsidizes this research with grants. The government also provides direct support and grant money to professors at public and private universities and that research helps to drive technological progress. 4. Political Stability, Property Rights, and Excessive Government Intervention Suppose a firm wants to build a factory that produces gadgets in a foreign nation Kreblakistan. Firms are going to be very hesitant to invest in Kreblakistan if the government might be radically overthrown, or if the government could just claim the factory as government property. Or maybe Kreblakistan’s courts and government bureaucracies are corrupt so that day-to-day business transactions require bribes or hush money. Firms are not going to want to invest in nations such as this. At the other extreme, a nation’s government could excessively intervene in markets with high taxes, tariffs, or other anti-competitive policies. This can also slow down economic growth. Assessment (15 points) PARTICIPATE in a scenario activity. Assume you are the President and Congress wants to work with you. Provide a three-point plan to improve our economy based on current economic needs. Include in your plan fiscal policy that would improve conditions for all of the following: Physical capital, human capital, technology. HOMEWORK: Section review questions 1, 7, 9 TOMORROW WE WILL begin module 41.