Properties of Matter Lab Review
advertisement

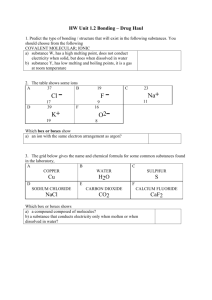
Substances have a fixed composition Elements and Compounds are pure substances • Elements can’t be broken down to simpler substances • Compounds are difficult to break down to simpler substances-separated through chemical reactions Mixtures and Solutions are not pure substances and can be easily separated without chemical reactions Color, shape, size, density, melting point, boiling point Appearance and behavior Think of appearance as being descriptive Behavior is like magnetism or being ductile or malleable The identity of the substance does not change Changing the state of matter does not change the chemical make up of the substance The identity of the substance changes New substance(s) formed Extensive properties depend on how much of a substance is present-size, weight, mass, volume Intensive properties do not depend on how much of substance is present-color, density, odor, luster, ductility, malleability, hardness, conductivity, boiling point, melting/freezing point Silver Nitrate and Copper-Single replacement reaction Cu + Ag(NO3)2 → Cu(NO3)2 + Ag One element replaces another in a compound Silver precipitate and copper nitrate produced 2HCl + Zn → ZnCl2 + H2 Single replacement reaction Hydrogen gas produced Zinc replaces hydrogen Temp change Exothermic-feels hot but the reaction is actually losing heat CuSO4 + Fe → FeSO4 + Cu Single replacement reaction Solidifies Iron replaces copper Temp change Exothermic-feels hot but the reaction is actually losing heat Decomposition reaction 2H2O2 → 2H2O + O2 Exothermic Gas is released Liquid and yeast remain What is yeast’s role in the reaction? CH3COOH + NaH3CO3 → CO2 + H2O + CH3OONa Gas is released Na actually separates and is dissolved Feels cold which would mean endothermic but it really isn’t-CO2 cools rapidly causing the cold Not a chemical reaction Chromatography Solid black ink separated into blue/brown/yellow so it is a solution Sugar simply dissolves in the water Sugar does not become something new, still a solid just mixes between the water particles Ground in to a powder Still chalk, still solid