Synchronous DRAM
advertisement
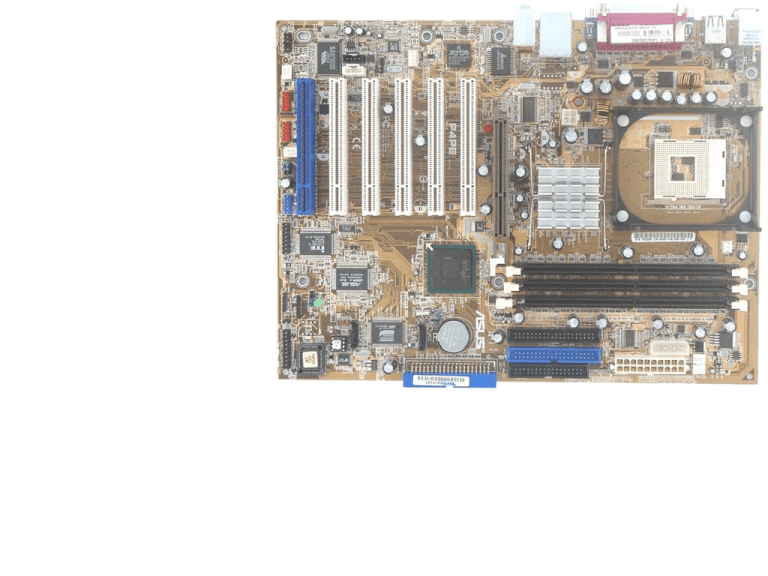
We hope you will not look like … … when you will open a computer Chipset • Microchip that support the CPU. The chipset usually contains several controllers that govern how information travels between the processor and other components. RAM • SDRAM - Synchronous DRAM - SDRAM synchronizes itself with the CPU's bus. • DDRAM - Double Data Rate-Synchronous DRAM - Type of SDRAM supports data transfers on both edges of each clock cycle • RDRAM – Rambus DRAM - fastest current memory technologies used by PCs transfers data at up to 800 MHz while SDRAM can deliver data at a maximum speed of about 100 MHz Processor (CPU) • This is a place where CPU should be put. Besides, cooler will be installed over CPU. Cooler is a necessary device since CPU produce a lot of heating and could burn out itself without cooling. Usually cooler is a fan that produced most of noise you hear when computer works. Notes • Chipset always defines a range of CPUs you can use. So, if a chipset doesn’t support the latest Intel CPU or AMD CPU you will be able to use such CPU (of course you will be able to install that, but it will not work(. • DDRAM/SDRAM/RDRAM – Those types of memory are very different. Only one type is supported by a motherboard. Moreover any of them has different speeds. If you will try to use a memory with bigger speed then usually this one will work with reduced speed (as much as motherboard can support – read provide). HDD CD-ROM Floppy… • HDD/CDROM – IDE: Integrated Drive Electronics. An IDE interface is an interface for mass storage devices, in which the controller is integrated into the disk or CD-ROM drive. • ATA 33/66/100 – Advanced Technology Attachment disk drive implementation (specification). Number means data transfer rate speed in MBps • Floppy has a special connector which is shorter. More about mass storage devices’ connectors • Notes on IDE: Devices are connected to motherboard using a special cable on which up to 2 devices can be put. The speed on this cable equals to minimum between maximum speeds supported by connected devices and motherboard. So, if motherboard enables using ATA-100 as well as HDD but CDROM, located on the same cable, enables only ATA-33 (CD and DVD devices work only with ATA-33) then speed of connection between motherboard and HDD or CDROM will be only 33 MBps. Therefore CDROM and HDD usually is not connected to motherboard by the same cable. • SCSI - Small Computer System Interface - is a parallel interface standard. SCSI interfaces provide for faster data transmission rates (up to 80 megabytes per second) than standard serial and parallel ports. In addition, you can attach many devices to a single SCSI port, so that SCSI is really an I/O bus rather than simply an interface. • SATA - Serial ATA – extended ATA with speed up to 150 MBps. • SAS - Serial Attached SCSI: extension of SCSI. These include drive addressability of up to 16,256 devices per port and reliable point-to-point serial connections at speeds of up to 3G bps. Expansion slots PCI / ISA • PCI - Peripheral Component Interconnect, a local bus standard developed by Intel Corporation (interconnection system between a microprocessor and attached devices ). Can support also older standard ISA • ISA - Industry Standard Architecture. The original specification for the EXPANSION SLOTS used on the first IBM PC. Expansion slots AGP • AGP - An interface specification from Intel that enables 3-D graphics to display quickly on personal computers. AGP is based on PCI, but is designed especially for the high throughput requirements of 3-D graphics. Usually is colored to brown. Battery • • An element that is necessary to provide a power to store user settings made in BIOS. For example a password. BIOS - built-in software that determines what a computer can do without accessing programs from a disk. On PCs, the BIOS contains all the code required to control the keyboard, display screen, disk drives, serial communications, and a number of miscellaneous functions. So, it makes it possible for a computer to boot itself. SATA II Serial Advanced Technology Attachment The standard interface for SATA controllers is Advanced Host Controller Interface (AHCI), which allows advanced features of SATA such as hot plug and Native Command Queuing. Features of SATA II devices and components (disk drives, adapters, port multipliers and selectors, cabling and connectors) support 1.5 Gbps and 3 Gbps data transfer rates PCI-E PCI Express, (PCIe) PCI-E is based around serial links called lanes. The PCIe 1.1 specification supports x1 (pronounced "by one"), x2, x4, x8, x16, and x32 lanes In each lane, the most common version PCIe 1.1 carries 250 MB/s in each direction








![practicial 1 to 7,10,11,12 by jas[1]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/026189320_1-caca47b6722b56cb0ceb9cd8ba3c9f12-300x300.png)

