21.1 Earth's Interior and Plates PPT email version no
advertisement

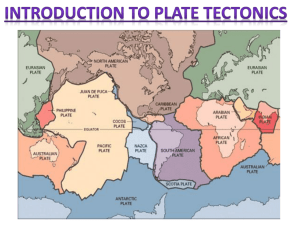
PLANET EARTH pp.729-737 Earth’s Interior and Plate Tectonics Chapter 21, Section 1 Earth’s Interior- pages 729-730 The Earth is made of multiple layers: CRUST • topmost layer of solid and cool rock the “plates” TWO TYPES OF CRUST OCEANIC CONTINENTAL HOW ARE THE TWO TYPES OF CRUST DIFFERENT? OCEANIC CRUST ~ 4-7 mi. thick -dense (basalt) *sinks under continental crust CONTINENTAL CRUST ~12-25 mi. thick -most thick beneath mountains -less dense (granite) than oceanic crust Nye & Earth’s Crust Vogue Song Thickness of the crust in KILOMETERS 2. ___________ MANTLE DENSE • located below the crust (more _______) 80 % of • ______ earth’s total volume -top (outer) part of the mantle and crust= __________________ LITHOSPHERE (rigid and cool) -bottom (inner) part of the mantle = ASTHENOSPHERE (hot, soft, and _______________________ easily deformed- like chewing gum) CRUST LITHOSPHERE = SOLID MANTL E ASTHENOSPHERE =“SOFT” 3. CORE iron and nickel • mostly made of _________________ • very hot 2 layers: 1) OUTER CORE 2)INNER CORE a. Outer core (________ LIQUID metal)- even though it’s above the boiling point they do not boil due to high pressure (no gases) b. Inner core (________ SOLID metal)- very high ____________ so atoms are forced together PRESSURE despite the HEAT ______. Layers of the Earth (NASA) Evidence of Earth’s Internal Structure S waves: can’t travel through core (outer/liquid) transverse & can’t travel through liquid P waves: can travel through core but deflected change in type of matter Layers of Earth Mr Lee PLATE TECTONICS *Early 1900sGerman scientist = Alfred Wegener _________________ Continental Drift Song What observations intrigued Wegener? • Wegener hypothesized that all of the continents fit together in the past to form PANGAEA (Greek: _____________ “ALL LANDS” ) ____________ PERMIAN 225 million years ago PRESENT DAY 650 million years in under 2 minutes What evidence exists to support the theory of plate tectonics and continental drift? How do we know this? Pangaea’ s Moving Farther Apart Song 1. ________ FOSSILS – the same kinds of animals/plants once lived on continents that are now oceans apart. Lystrosaurus land reptile Glossopteris fern Cynognathus land reptile Mesosaurus FW reptile AGE OF ROCKS (ON OCEAN FLOOR) 2. ________________________________ •Rocks are __________ YOUNGER near the center of the Atlantic Ocean. • As distance from the center increases, the rocks are OLDER _______. 3. ______________________________ MAGNETISM (discovered mid 1960s) Magnetic Reversals Explained Seafloor Animation 3. Magnetism – (discovered mid 1960s) • bands of rock on the ocean floor have alternating magnetic polarities • magnetic patterns (formed when rocks cooled) are symmetrical (same) on either side of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge Continents are on the tectonic plates and move with the plates. *Convection currents within the Earth= (hot rock rises…cooler rock falls) moves the • Convection plates. • Currents Explained Convection & Plate Movement Plate Boundaries (pages 734-737) * Classified how to plates move in relation to each other DIVERGENT boundary: _________________ • Occurs where two tectonic plates move apart and create a gap. • Forms mid-ocean ridge (from rising magma). Hot rock from the asthenosphere rises up and cools to form new igneous rock. Divergent boundary Examples of Divergent Boundaries a. MID-ATLANTIC RIDGE * ICELAND is right ON the mid-Atlantic Ridge b. RED SEA (E. Africa) Examples of Divergent Boundaries Crust in Pieces Song How is the Red Sea forming? Look at diagrams and then describe in your own words… CONVERGENT boundary: _____________________ • Occurs where two plates push together 3 different situations for convergent boundaries… a. b. c. a. Oceanic – Continental - Oceanic plate is more _______ DENSE and sinks below the continental plate. This is called _______________. SUBDUCTION SUBDUCTION FORMS: TRENCHES Mountains / Volcanoes EXAMPLES OF OCEANIC-CONTINENTAL CONVERGENT BOUNDARIES 1. CASCADE RANGE (Northwestern US) EXAMPLES OF OCEANIC-CONTINENTAL CONVERGENT BOUNDARIES 2. ANDES MOUNTAINS- W. coast of S. America. b. Oceanic – Oceanic – OLDER ________ and more ________ DENSE plate sinks below the other. EXAMPLES OF OCEANIC-OCEANIC CONVERGENT BOUNDARIES 1. Aleutian Islands, Alaska EXAMPLES OF OCEANIC-OCEANIC CONVERGENT BOUNDARIES 2. Japan c. Continental – Continental – ________ OLDER and more ________ DENSE plate sinks below the other. Cont-Cont Animation EXAMPLES OF CONTINENTAL-CONTINENTAL CONVERGENT BOUNDARIES HIMILAYAN MOUNTAINS (like MT EVEREST and K2) The 10 highest mountains in the world are found here * Convergent Boundaries create ____________ VOLCANOES and ________________, EARTHQUAKES especially around the “RING OF FIRE” _________ PACIFIC Ocean in the _______________. What is special about Hawaii? Hot Spot Animation TRANSFORM boundary: 3. ___________________ • Occurs where two plates slide past each other horizontally- along a fault Fault = a break in a body of rock. One block slides relative to the other (lots of friction) FAULT TRANSFORM FAULT BOUNDARY What do you see? How did this happen? EXAMPLE OF A TRANSFORM FAULT BOUNDARY San Andreas FaultCalifornia/Mexico TRANSFORM FAULT BOUNDARYvisuals… A Review of Earth’s Interior and Plate Tectonics Video Divergent Continental crust rift valley Convergent Cont/Cont. plates mountain range Transform Plates move against each other. Stress builds up… Stress is released earthquake! Oceanic crust midocean ridge Oceanic/Oceanic or Oceanic/Continental subduction