Presentation Slides
advertisement

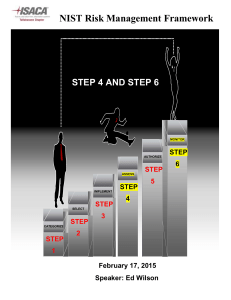
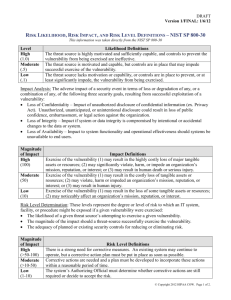
IT Best Practices for Community Colleges Part 1: IT Risk Management Donald Hester February 9, 2010 For audio call Toll Free 1-888-886-3951 and use PIN/code 360619 Housekeeping • Maximize your CCC Confer window. • Phone audio will be in presenter-only mode. • Ask questions and make comments using the chat window. Adjusting Audio 1) If you’re listening on your computer, adjust your volume using the speaker slider. 2) If you’re listening over the phone, click on phone headset. Do not listen on both computer and phone. Saving Files & Open/close Captions 1. Save chat window with floppy disc icon 2. Open/close captioning window with CC icon Emoticons and Polling 1) Raise hand and Emoticons 2) Polling options CISOA Conference http://cisoa.net IT Best Practices for Community Colleges Part 1: IT Risk Management Donald Hester IT Best Practices for Community Colleges Series 1 Spring 2010 • Part 1 Risk Management • Part 2 Business Continuity • Part 3 Configuration Management • Part 4 Awareness Training Series 2 Fall 2010 8 Risk Management How do you justify a new firewall? Is it more than you need? Is it less than you need? How does someone outside of IT know it was the right choice? How do you demonstrate due care? 9 Risk Management Definitions Risk: the potential for any loss Asset: something of value Probability: the likelihood of an event Control: something that reduces risk (countermeasure, safeguard) Threat: event that has an undesirable impact, potential danger Vulnerability: weakness Exposure: open to threat Residual risk: risk left over after controls are put in place Acceptable risk: risk accepted by management Threat Vulnerability Threat Asset Vulnerability Countermeasure Risk Assessment Asset Risk Management Definitions Risk Management: process of reducing risks because it cannot be eliminated Risk Analysis: identify assets and potential losses Risk Assessment: determination of recommended controls that would reduce risk to an acceptable level Vulnerability Assessment: used for the risk analysis, determines vulnerabilities Risk Management Process not a goal SDLC (Systems Development Life Cycle) Any change in environment changes your risk level Risk Management Management’s role • Balance cost with operational goals • Acceptable levels of risk (risk apatite) • Use the risk analysis process for decision- • • • • making Cost benefit analysis (ROI) Determine if controls are in place Sign-off forms to take responsibility Risk analysis team Risk Management can choose how to deal with risk once they have all the information and recommendations. After they have the results form the risk analysis they can determine how they want to mitigate risks. Mitigating risks to an acceptable level. Any risk remaining is residual risk. How you can react to risks? Reduce the risk • Apply countermeasures and controls (mitigation) Accept the risk • Accept the risk with or without controls Transfer the risk • Buy insurance (mitigation) Reject the risk • Ignore the risks Risk Analysis Purpose • 1st step in Risk Management • Ensure that the security program (controls) are adequate and appropriate for the real risks Goals • Identify assets • Identify risks • Connect risks and assets • Determine impact • Cost vs. benefit • Prioritize control selection/implementation Risk Analysis Phases We need to determine what we have, what it is worth, what could happen to it, how often it could happen, what the impact would be if it did happen, so that we could determine what controls should be used based on cost, and document everything we discovered. Phase 1 Identify assets, determine their value and classify them. Types of Assets Physical • Hardware • Buildings Information • Data • Software • Documentation Human Resources Reputation Value of Assets Acquisition costs Impact to • Productivity Development costs • Usefulness Maintenance costs • Reputation Value to user, customer • Operations Value to enemy • Competitiveness Market value (how much someone will pay) Replacement costs Liability Phase 2 Identify the risks associated with the assets. Threat / Vulnerability pare Types of Risk Physical Loss • Theft • Environmental Errors and Omissions • Humans • Software Malfunction • Equipment failure Misuse Attacks Internal or External Intentional or unintentional Action or inaction Phase 3 Impact analysis Risk Analysis Quantitative • Formal • Numeric • Monetary • Statistical Qualitative • Informal • Rating • Gut feeling • Educated guess • Delphi method Impact Analysis Impact • What is the asset worth; AV (Asset Value) • How bad would it be; EF (Exposure Factor) • One time loss; SLE (Single Loss Expectancy) • How many times a year; ARO (Annualized Rate of Occurrence) • How much loss in a year; ALE (Annualized Loss Expectancy) AV * EF = SLE; SLE * ARO = ALE Prioritize Risks Select Risks with the highest probability and the highest impact potential. Meteorite to hit the data center would be a low probability with a high impact Virus would be a high probability with a potential for a high impact Risk Based Controls should focus on addressing • High probability attack • High impact attacks Consistent implementation Automated and continuously monitored Additional technical activities should be used to defend systems Rev1/8/2010 Phase 4 Determine what controls can be used, what the cost associated with each control and recommend controls. Control Selection Mitigates the risk ALE before the control ALE after the control Control complexity Cost / Benefit Comparison ROI (Return on Investment) Hidden costs • Productivity • Maintenance Control Selection (cont.) Limited resources • Time • Funding • Resources • Personnel With limited resources choices have to be made about which security controls are most important A prioritized approach in implementing controls is required Prioritized by greatest risk first Rev1/8/2010 A Prioritized Baseline of Controls How do we prioritize controls Intelligence • Knowledge of actual attacks Controls that can prevent know attacks should be given a higher priority A consensus report has been developed to document 20 critical controls Rev1/8/2010 Phase 5 Documentation Documented Risk Assessment NIST Risk Assessment Process 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. System Characterization Threat Identification Vulnerability Identification Control Analysis Likelihood Determination Impact Analysis Risk Determination Control Recommendation Results Document NIST SP 800-30 Why NIST? “State, local, and tribal governments, as well as private sector organizations, are encouraged to use the guidelines, as appropriate." NIST SP 800-100 California Information Security Strategic Plan (OCT 2009) "...by adopting the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) 800-37 guidelines for certification and accreditation of information systems. Applying NIST guidelines to state government systems will demonstrate California’s leadership in building a resilient, secure, and trustworthy digital infrastructure." "Establish a California modified version of the NIST 800-30 risk management standard as the risk management standard for all state agencies." 36 "Establish a California-modified version of the NIST 800-53 recommended security controls within all state agencies." Resources NIST SP 800-30 Risk Management Guide for IT Systems Information Technology Standards and Practices for Local Governments, September 2007 By Maze & Associates California Information Security Strategic Plan (OCT 2009) Cybersecurity and Privacy Concepts, Strategies & Goals Volume 4 Twenty Critical Controls for Effective Cyber Defense: Consensus Audit Guidelines version 2.1, 11 Aug 2009 37 Q&A Donald E. Hester CISSP, CISA, CAP, MCT, MCITP, MCTS, MCSE Security, Security+ Maze & Associates @One / San Diego City College www.LearnSecurity.org http://www.linkedin.com/in/donaldehester http://www.facebook.com/group.php?gid=245570977486 Evaluation Survey Link Help us improve our seminars by filing out a short online evaluation survey at: http://www.surveymonkey.com/s/10SpIT1 IT Best Practices for Community Colleges Part 1: IT Risk Management Thanks for attending For upcoming events and links to recently archived seminars, check the @ONE Web site at: http://onefortraining.org/