1.2 Linear Measure and Precision
advertisement

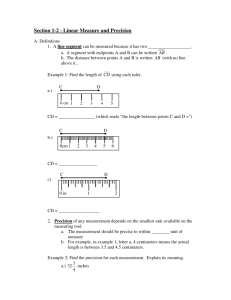
1.2 Linear Measure and Precision 1.2 Linear Measure and Precision Objectives: Measure segments and determine accuracy of measurement 1.2 Linear Measure and Precision Objectives: Measure segments and determine accuracy of measurement Compute with measures 1.2 Linear Measure and Precision A line segment CAN be measured (unlike a line or ray) because it has 2 endpoints 1.2 Linear Measure and Precision A line segment CAN be measured (unlike a line or ray) because it has 2 endpoints F G m 1.2 Linear Measure and Precision Precision: Depends on the SMALLEST unit available on the measuring tool. Measurement should be precise to within 0.5 unit of measure 1.2 Linear Measure and Precision Precision: Depends on the SMALLEST unit available on the measuring tool. Measurement should be precise to within 0.5 unit of measure 7 cm means that the ruler was divided into 1 cm – it could be 6.5 cm to 7.5 cm in actual length 1.2 Linear Measure and Precision Precision: Depends on the SMALLEST unit available on the measuring tool. Measurement should be precise to within 0.5 unit of measure 8.5 cm means that the ruler was divided into ½ cm – it could be 8.25 cm to 8.75 cm in actual length 1.2 Linear Measure and Precision Estimate the length of this rectangle. about 4.5 cm Smallest unit is 1mm So precision is ± ½ mm 45 mm ± .5 mm 44.5 to 45.5 mm 1.2 Linear Measure and Precision What does the measurement “5 inches” mean? 1 inch increments ½ of 1 = ½ Range: 5 – ½ = 4.5 in. 5 + ½ = 5.5 in. 8 ½ inches? ½ inch increments, therefore (½ ) of (½ ) = ¼ in. Precise to ¼ inch add ¼ and subtract ¼ Between 8 ¼ to 8 ¾ inches 1.2 Linear Measure and Precision Measures are real numbers so all operations can be used on them. Use 2 endpoint letters to show measure of a segment. AB is a measure – a length A B C AB = 5 in. DB = 34 in. AB + DB = 5 + 34 = 39 in. CD Is not a measurement (note bar) D 1.2 Linear Measure and Precision We know that part + part = whole This is true for line segments in Geometry – Called “Segment Addition Postulate” A 10 cm part B 4 cm + part = the whole 14 cm C 1.2 Linear Measure and Precision Betweenness of points: for any two real numbers a and b, there is a real number n between a and b such that a<n<b A a n B b C AB + BC = AC A, B, C must be collinear and B must be between A and C 1.2 Linear Measure and Precision Find y and PQ if P is between Q and R; PQ = 2y, QR = 3y + 1, and PR = 21. P, Q and R are collinear Draw a figure to represent this information and solve. Q 2y P 21 3y + 1 2y + 21 = 3y + 1 20 = y PQ = 2●20 = 40 R 1.2 Linear Measure and Precision Congruent segments: Two segments having the same measure. If AB = CD, then AB CD B 5 cm D 5 cm A C If AB CD, then AB = CD 1.2 Linear Measure and Precision Homework: 1.2 page 17 12 - 45 multiples of 3, 46-49, 56, 57