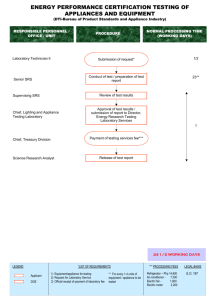
vSphere vSwitch Traffic Collection
advertisement

Quick Start Guide:
TrafficWatch
Capture Type & Requirements
2
Overview
3
Getting Started
5
Deploying the RN50 virtual appliance
7
Deploying the RN50 physical appliance
36
vSphere vSwitch Traffic Collection
No VLANs
12
1 VLAN
16
Multiple VLANs
18
Multiple VLANs (untagged traffic not allowed)
22
Setting up multiple vNICs
27
vSphere dvSwitch Traffic Collection
Port Mirroring
31
Cisco SPAN
37
Cisco NetFlow
39
Cisco ASA NetFlow
41
Verifying Traffic Collection
45
1
Visit riscnetworks.com or email sales@riscnetworks.com to connect with your account manager.
Supported Capture Types
o SPAN Port to physical pRN50
o VMware promiscuous mode
configuration with vRN50 (Virtual
RN150) on a VMware vSwitch,
dVSwitch, or virtual port group
o
Netflow export from network
devices to vRN50 (Virtual RN50) or
physical RN50 Appliance
Virtual RN50 Requirements
One of the following Hypervisors for
appliance deployment:
o VMware ESX or ESXi Server
o VMware Workstation
o VMware Player
System Resources:
o 2 Gigabytes of Hard Drive Space
TrafficWatch Requirements
o
Virtual RN150 bootstrapped and
assessment started
o
Virtual RN50(s) and/or Physical
RN50(s)
Physical RN50 Requirements
o
3 Category5 Patch Cables
o
120V Receptacle
o 2 Gigabytes of memory
Required Ports between the vRN50 and the
vRN150:
o TCP Ports 2500, 22, 123, 3306 (all bidirectional)
o UDP Port 161
o ICMP
Required Port for vRN50 Netflow
collection:
o UDP Port 9996
2
Visit riscnetworks.com or email sales@riscnetworks.com to connect with your account manager.
TrafficWatch Setup Guide
This document will provide step-by-step instructions on deploying the Virtual and Physical
RN50 appliances for use in traffic collection including VMware vSphere Virtual Switch
Promiscuous mode, Distributed Virtual Switch Port Mirroring, SPAN (Port Mirroring), and
NetFlow. The specific configuration depends on conditions in the environment, and we will
cover the individual steps involved for each use-case. The possible use-cases are detailed below.
o Promiscuous-Mode Mirroring will expose inter-VM traffic on a VMware virtual switch
for collection by the RN50 virtual appliance. It is similar to using a physical RN50 on a
physical switch to collect mirrored traffic using SPAN, yet is specific to the VMware
virtual switch. Traffic flowing through the virtual switch will be mirrored, and captured
by the RN50 virtual appliance.
o VDS Port Mirroring will expose inter-VM traffic on a VMware distributed virtual switch
(dvSwitch) for collection by the RN50 virtual appliance. Traffic flowing through the
VDS will be mirrored, and captured by the RN50 virtual appliance.
o SPAN (Switched Port Analyzer), copies traffic from one or more ports, one or more
EtherChannels, or one or more VLANs and sends the copied traffic for analysis to the
Physical RN50 virtual appliance.
o NetFlow is a protocol designed for network monitoring. It aggregates traffic statistics
based on layer 3 and layer 4 flow information in order to determine the top talkers in the
environment, and to describe the various protocols and interactions taking place. Devices
with NetFlow enabled will gather and record flow statistics and periodically push this
data to the RN50. Because NetFlow data is aggregated, and does not include packet
contents, the relative volume of data is small.
3
Visit riscnetworks.com or email sales@riscnetworks.com to connect with your account manager.
VMware Traffic Collection
Deploying TrafficWatch will require a standard assessment using the RN150 virtual appliance.
An existing, running, assessment can be used, or a new assessment can be created. TrafficWatch
will require the RN150 appliance for command-and-control, as well as for data uploads to the
RISC Networks NOC for final report generation. The RN50 appliance is used to collect mirrored
traffic from the virtual switch, so an RN50 appliance will need to be deployed on each
ESX/vSphere host, or one appliance per virtual switch. The RN50 appliances will require
connectivity with the RN150 appliance.
If VLANs are in use in the environment, additional steps may be required. The VMware vSwitch
or VDS port groups must be configured appropriately in order to collect mirrored traffic from
tagged VLANs. There are four use-cases:
1.
VLANs are not in use in the environment
2.
VLANs are in use, but traffic is only collected from one particular VLAN
3.
VLANs are in use, and untagged traffic is permitted in the environment
4.
VLANs are in use, and untagged traffic is NOT permitted in the environment
Details on configuration for each use-case are provided below. The specific steps involved are
different depending on whether the classic vSwitch or the Distributed Virtual Switch (VDS) is in
use. The step-by-step instructions to follow are broken up into two sections depending on which
VMware switching technology is in use. In any case, the initial deployment steps are the same.
4
Visit riscnetworks.com or email sales@riscnetworks.com to connect with your account manager.
Getting Started
1.
Browse to the web portal at https://portal.riscnetworks.com/ and log in
2.
Access the assessment details by selecting View Detail
5
Visit riscnetworks.com or email sales@riscnetworks.com to connect with your account manager.
3.
Access the TrafficWatch section by selecting TrafficWatch
4.
Download the RN50 virtual appliance by selecting Download RN50 VA
5.
Browse to the download location and unzip the MyIT-RN50-VirtualNode.zip file
6
Visit riscnetworks.com or email sales@riscnetworks.com to connect with your account manager.
6.
Connect to the ESX/vSphere host or vCenter via the vSphere Client
7.
In the vSphere client, select File, then Deploy OVF Template
8.
9.
Browse to the location of the unzipped RN50 download
Select the MyIT-RN50-Virtual-Appliance2.0.ovf file
10.
Continue to deploy the virtual appliance according to local standards
a. The RN50 OVF defines the basic requirements of the appliance
7
Visit riscnetworks.com or email sales@riscnetworks.com to connect with your account manager.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
i. 5GB disk allocation (thick or thin provisioned)
ii. 2GB memory allocation
b. Accepting the defaults is recommended
Select the appropriate Destination Network
Select Finish to finish the deployment
Power on the appliance
Access the appliance via the VMware console
Continue with DHCP or set a static IP configuration by selecting Edit in the
Interfaces section.
8
Visit riscnetworks.com or email sales@riscnetworks.com to connect with your account manager.
16.
Access the RN150 section
17.
Select TrafficWatch from the drop-down list and select Proceed
9
Visit riscnetworks.com or email sales@riscnetworks.com to connect with your account manager.
18.
Select Proceed
19.
Enter the IP address of the RN150 appliance and select Add
10
Visit riscnetworks.com or email sales@riscnetworks.com to connect with your account manager.
20.
Test the connection
21.
The RN50 appliance is now ready to collect NetFlow/ESX traffic.
11
Visit riscnetworks.com or email sales@riscnetworks.com to connect with your account manager.
Configuring the vSphere Virtual Switch (vSwitch)
Use-Case: No VLANs in use
Each vSwitch Port Group defaults to a VLAN ID of 0, (traffic is not tagged). The RN50 virtual
appliance will be able to collect traffic from any VM connected to a Port Group set with a VLAN
ID of 0. The vSwitch must be configured for Promiscuous-Mode. The steps to do so are as
follows:
1. In the vSphere client, Select the ESX host
2. Select the Configuration tab
12
Visit riscnetworks.com or email sales@riscnetworks.com to connect with your account manager.
3. Select the Networking link under Hardware
4. Select vSphere Standard Switch
13
Visit riscnetworks.com or email sales@riscnetworks.com to connect with your account manager.
5. Select the Properties link
6. The vSwitch configuration page should now be visible
7. Select the vSwitch
8. Select Edit
14
Visit riscnetworks.com or email sales@riscnetworks.com to connect with your account manager.
9. Select the Security tab
10. Check the box next to Promiscuous Mode
11. Select Accept on the Promiscuous Mode drop-down list
12. Select Ok
15
Visit riscnetworks.com or email sales@riscnetworks.com to connect with your account manager.
Collecting Traffic from a Single VLAN Port Group
If VLANs are in use but the RN50 appliance is only intended to collect traffic from VMs on one
particular VLAN, then the RN50 appliance needs to be connected to the Port Group that is
configured for that VLAN.
1. In the list of guest Virtual Machines select and right click the RN50 virtual appliance.
2. Select Edit Settings
16
Visit riscnetworks.com or email sales@riscnetworks.com to connect with your account manager.
3. Select Network Adapter
4. In the Network Connection section, select the Port Group associated with the appropriate
VLAN
5. Select Ok
17
Visit riscnetworks.com or email sales@riscnetworks.com to connect with your account manager.
vSphere vSwitch Traffic Collection from multiple
VLANs where untagged traffic is permitted in the
environment.
If VLANs are in use in the environment and the RN50 appliance is intended to collect traffic
from all VLANs, the appliance must be configured to connect through a Port Group set to VLAN
ID 4095. This is a VMware-specific VLAN ID that is untagged, yet allows for communication
with VMs on all VLANs within the vSwitch. If a Port Group configured for VLAN ID 4905
already exists, then a new Port Group need not be created.
The steps for configuration are as follows:
1. Access the vSwitch Networking Properties
2. In the vSphere client, Select the ESX host
3. Select the Configuration tab
18
Visit riscnetworks.com or email sales@riscnetworks.com to connect with your account manager.
4. Select the Networking link under Hardware
5. Select vSphere Standard Switch
19
Visit riscnetworks.com or email sales@riscnetworks.com to connect with your account manager.
6. Select the Properties link
7. Select Add
20
Visit riscnetworks.com or email sales@riscnetworks.com to connect with your account manager.
8. Select Virtual Machine (default selection)
9. Define Network Label
10. Enter 4095 in the VLAN ID section
11. Select Next
12. Select Finish
21
Visit riscnetworks.com or email sales@riscnetworks.com to connect with your account manager.
vSphere vSwitch Traffic Collection from multiple
VLANs where untagged traffic is NOT allowed in the
environment.
If VLANs are in use and the RN50 appliance is intended to collect traffic from all VLANs, yet untagged
traffic is not permitted in the environment, extra configuration is necessary. First, the appliance needs
to be configured to connect through a Port Group set to VLAN ID 4095. This is a VMware-specific VLAN
ID that is untagged, yet allows for communication with VMs on all VLANs within the vSwitch. In this
configuration the RN50 appliance will not be able to communicate across the environment with the
RN150 appliance, so an additional interface must be created and configured on the RN50 appliance. If a
Port Group configured for VLAN ID 4095 already exists, a new Port Group need not be created.
The steps for configuration are as follows:
Create VLAN PortGroup 4095
The steps for configuration are as follows:
1. Access the vSwitch Networking Properties
2. In the vSphere client, Select the ESX host
22
Visit riscnetworks.com or email sales@riscnetworks.com to connect with your account manager.
3. Select the Configuration tab
4. Select the Networking link under Hardware
23
Visit riscnetworks.com or email sales@riscnetworks.com to connect with your account manager.
5. Select vSphere Standard Switch
6. Select the Properties link
24
Visit riscnetworks.com or email sales@riscnetworks.com to connect with your account manager.
7. Select Add
8. Select Virtual Machine (default selection)
9. Select Next
25
Visit riscnetworks.com or email sales@riscnetworks.com to connect with your account manager.
10. Define Network Label
11. Enter 4095 in the VLAN ID section
12. Select Next
13. Select Finish
26
Visit riscnetworks.com or email sales@riscnetworks.com to connect with your account manager.
Enable the RN50 Virtual Appliance Virtual Network
Interfaces
Configure Interface 1
1. In the list of guest Virtual Machines select and right click the RN50 virtual appliance.
2. Select Edit Settings
27
Visit riscnetworks.com or email sales@riscnetworks.com to connect with your account manager.
3. Select Network Adapter 1
4. In the Network Connection section, select the VLAN 4095 Port Group
5. Select Ok
28
Visit riscnetworks.com or email sales@riscnetworks.com to connect with your account manager.
Enable the RN50 Virtual Appliance Virtual Network
Interfaces:
Configure Interface 2
6. In the list of guest Virtual Machines select and right click the RN50 virtual appliance.
7. Select Edit Settings
29
Visit riscnetworks.com or email sales@riscnetworks.com to connect with your account manager.
1. Select Network Adapter 2
2. In the Network Connection section, select the Port Group with access to the RN150
virtual appliance.
3. Select Ok
30
Visit riscnetworks.com or email sales@riscnetworks.com to connect with your account manager.
vSphere dvSwitch Port Mirroring Configuration
The steps for configuration are as follows:
1.
2.
3.
4.
Access vSphere Client
Select Home
Select Networking
Select the Ports tab
5. Record and save the Port ID numbers for each VM that you wish to include for collection
6. Record and save the Port ID numbers for each RN50 virtual appliance deployed.
7. Right select the dvSwitch and select Edit Settings.
31
Visit riscnetworks.com or email sales@riscnetworks.com to connect with your account manager.
8. Select the Port Mirroring tab
9. Select Add
32
Visit riscnetworks.com or email sales@riscnetworks.com to connect with your account manager.
10. Supply the Port Mirroring Session Name and Description
11. Select Allow normal IO on destination ports
12. Select Next
33
Visit riscnetworks.com or email sales@riscnetworks.com to connect with your account manager.
13. Enter the Source Port IDs (Port IDs recorded in step 5)
14. Add the Source Port IDs by selecting >>
15. Enter the Destination Port IDs (Port IDs recorded in step 6)
16. Add the Source Port IDs by selecting >>
34
Visit riscnetworks.com or email sales@riscnetworks.com to connect with your account manager.
17. Enable Port Mirroring
18. Select Finish
19. Verify Port Mirroring Session
35
Visit riscnetworks.com or email sales@riscnetworks.com to connect with your account manager.
SPAN Configuration (Part 1) Physical RN50
Configuration
1. Plug in RJ45 patch cable from the last port (port 4 or port 6 depending on the hardware
model) to a PC.
2. Plug in RJ45 patch cable from port 1 to existing network.
3. Plug in RJ45 patch cable from port 2 to SPAN port (only necessary when using SPAN).
4. Plug in AC adapter.
5. Configure PC.
IP: 1.1.1.2
Subnet mask: 255.0.0.0
Gateway: 1.1.1.1
6. Open web browser and browse to 1.1.1.1
7. Select ‘Interfaces’.
8. Set static IP address on Interfaces section.
9. Select ‘Dashboard’.
10. Select ‘RN150’.
11. Select ‘TrafficWatch‘ in the dropdown box.
12. Select ‘Proceed’.
13. Enter RN150 IP address.
14. Select Add, then select ‘Test’.
15. Proper configuration will result in receiving ‘Test Successful.’
36
Visit riscnetworks.com or email sales@riscnetworks.com to connect with your account manager.
SPAN Configuration (Part 2)
(SPAN configuration may vary depending on the device. Please consult your manufacturer’s
documentation for further information regarding port mirroring support for your device.)
1. Switch# configure terminal (Enter global configuration mode.)
2. Switch(config)# monitor session session_number source interface interface-id [, | -] [both | rx |
tx]
o Specify the SPAN session and the source port (monitored port).
o For session_number, specify 1.
o For interface-id, specify the source port to monitor. Valid interfaces include physical
interfaces and port-channel logical interfaces (port-channel port-channel-number).
o (Optional) [, | -] Specify a series or range of interfaces. Enter a space before and after the
comma; enter a space before and after the hyphen.
o (Optional) Specify the direction of traffic to monitor. If you do not specify a traffic
direction, the source interface sends both sent and received traffic.
•both—Monitor both received and sent traffic.
•rx—Monitor received traffic.
•tx—Monitor sent traffic.
3. Switch(config)# monitor session session_number destination interface interface-id
[encapsulation {dot1q}]
o Specify the SPAN session and the destination port (monitoring port).
o For session_number, specify 1.
o For interface-id, specify the destination port. Valid interfaces include physical
interfaces.
o (Optional) Specify the encapsulation header for outgoing packets. If not specified,
packets are sent in native form.
o •dot1q—Use 802.1Q encapsulation.
37
Visit riscnetworks.com or email sales@riscnetworks.com to connect with your account manager.
4. Switch(config)# end (Return to privileged EXEC mode)
5. Switch# show monitor [session_number} (Verify your entries)
6. Switch# copy running-config startup-config (Optional, save your entries in the configuration
file.)
38
Visit riscnetworks.com or email sales@riscnetworks.com to connect with your account manager.
NetFlow Version 5 Configuration
Cisco includes NetFlow version 5 support on many devices. Please refer to the documentation
for your specific devices to determine if they support NetFlow.
NetFlow can be a powerful tool in a RISC Networks TrafficWatch engagement. When deploying
NetFlow for TrafficWatch, the RN50 virtual appliance is configured as the NetFlow collector,
and each exporter, the infrastructure device reporting NetFlow statistics, counts as a node
towards the available node entitlement.
Quick Setup:
1.
Deploy RN150 as normal and start assessment
2.
Download and deploy RN50
3.
Select TrafficWatch
4.
Enter IP address of RN150
5.
Access devices that will export NetFlow
6.
Enable NetFlow version 5
7.
Configure NetFlow to export to the IP address of the RN50, port 9996
8.
Verify configuration in the portal
9.
Disable RN50 in portal
Configure device for NetFlow:
1.
Generic Cisco IOS commands (may vary depending on device):
2.
Router# configure terminal
3.
Router(config)# ip cef
4.
Router(config)# interface
5.
Router(config-if)# ip route-cache flow
6.
Router(config-if)# exit
7.
Router(config)# ip flow-export version 5
<interface> #For each participating interface
#For each participating interface
39
Visit riscnetworks.com or email sales@riscnetworks.com to connect with your account manager.
8.
Router(config)# ip flow-export destination <RN50
9.
Router(config)# end
10.
Verify collection of NetFlow statistics
11.
Router# show ip flow export
IP address> 9996
12.
Router# show ip cache [verbose] flow #Summarizes active flows, indicates how much
NetFlow data is being exported
40
Visit riscnetworks.com or email sales@riscnetworks.com to connect with your account manager.
Cisco ASA NetFlow Configuration
Configuring NSEL Collectors
To configure NSEL collectors, enter the following command:
Command
Purpose
flow-export
destination interfacename
ipv4-address|hostname
udp-port
Configures an NSEL collector to which NetFlow packets are sent.
Thedestination keyword indicates that a NSEL collector is being
configured. The interface-name argument is the name of the ASA
interface through which the collector is reached. The ipv4address argument is the IP address of the machine running the
collector application. The hostnameargument is the destination IP
address or name of the collector. The udp-port argument is the
UDP port number to which NetFlow packets are sent. You can
configure a maximum of five destinations. After a destination is
configured, template records are automatically sent to all
configured NSEL collectors.
Example:
hostname (config)#
flow-export
destination inside
209.165.200.225 2002
Note Make sure that collector applications use the Event Time
field to correlate events.
Configuring Flow-Export Actions Through Modular Policy Framework
To export NSEL events by defining all classes with flow-export actions, perform the following steps:
Command
Purpose
Step 1 class-map
Defines the class map that identifies traffic for which
NSEL events need to be exported.
Example:
Theflow_export_class argument is the name of the
hostname (config-pmap)# class map.
flow_export_class
class-map
flow_export_class
Step 2 Do one of the following:
match access-list
flow_export_acl
Example:
Configures the access list to match specific traffic.
The flow_export_acl argument is the name of the
access list.
hostname (configcmap)# match accesslist flow_export_acl
match any
Example:
Matches any traffic.
hostname (configcmap)# match any
Step 3 policy-map
flow_export_policy
Example:
Defines the policy map to apply flow-export actions to
the defined classes. Theflow_export_policy argument
is the name of the policy map.
41
Visit riscnetworks.com or email sales@riscnetworks.com to connect with your account manager.
hostname(config)#
policy-map
flow_export_policy
Note If you create a new policy map and apply it
globally according to Step 6, the rest of the
inspection policies will be deactivated.
Alternatively, to insert a NetFlow class in the
existing policy, enter the class
flow_export_class command after thepolicymap global_policy command.
For more information about creating or
modifying Modular Policy Framework, see
the "Configuring Modular Policy Framework"
section.
Step 4 class flow_export_class Defines the class to apply flow-export actions.
Example:
The flow_export_class argument is the name of the
class.
hostname (configpmap)# class
flow_export_class
Step 5 flow-export event-type
event-type destination
flow_export_host1
[flow_export_host2]
Example:
hostname (configpmap-c)# flow-export
event-type all
destination
209.165.200.230
Step 6 service-policy
flow_export_policy
global
Example:
Configures a flow-export action.
Theevent_type keyword is the name of the
supported event being filtered. The supported event
types are flow-create, flow-denied, flow-teardown,
and all. The flow_export_hostargument is the IP
address of a host. Thedestination keyword is the IP
address of the configured collector.
Attaches the service policy globally.
Theflow_export_policy argument is the name of the
policy map.
hostname (config)#
service-policy
flow_export_policy
global
Configuring Template Timeout Intervals
To configure template timeout intervals, enter the following command:
Command
Purpose
flow-export
template timeoutrate minutes
Specifies the interval at which template records are sent to all
configured output destinations. The template keyword indicates the
template-specific configurations. The timeout-rate keyword specifies
the time before templates are resent. The minutesargument specifies
the time interval in minutes at which the templates are resent. The
default value is 30 minutes.
Example:
hostname
(config)# flowexport template
timeout-rate 15
Delaying Flow-Create Events
To delay the sending of flow-create events, enter the following command:
42
Visit riscnetworks.com or email sales@riscnetworks.com to connect with your account manager.
Command
Purpose
flow-export
delay flowcreate seconds
Delays the sending of a flow-create event.
The seconds argument indicates the amount of time allowed for the delay
in seconds. If this command is not configured, there is no delay, and the
flow-create event is exported as soon as the flow is created. If the flow is
torn down before the configured delay, the flow-create event is not sent;
an extended flow teardown event is sent instead.
Example:
hostname
(config)#
flow-export
delay flowcreate 10
Disabling and Reenabling NetFlow-related Syslog Messages
To disable and reenable NetFlow-related syslog messages, perform the following steps:
Command
Purpose
Step 1 logging flow-export
syslogs disable
Example:
hostname(config)#
logging flow-export
syslogs disable
Step 2 logging message xxxxxx
Example:
hostname(config)#
logging message 302013
Step 3 logging flow-export
syslogs enable
Disables syslog messages that have become
redundant because of NSEL.
Note Although you execute this command in global
configuration mode, it is not stored in the
configuration. Only the no logging message
xxxxxx commands are stored in the
configuration.
Reenables syslog messages individually,
where xxxxxx is the specified syslog message that
you want to reenable.
Reenables all NSEL events at the same time.
Example:
hostname(config)#
logging flow-export
syslogs enable
Clearing Runtime Counters
To reset runtime counters, enter the following command:
Command
Purpose
clear flow-export counters
Examples
Resets all runtime counters for NSEL to zero.
hostname# clear flow-export counters
Monitoring NSEL
To monitor NSEL, enter one of the following commands:
Command
Purpose
43
Visit riscnetworks.com or email sales@riscnetworks.com to connect with your account manager.
show flow-export
counters
Shows runtime counters, including statistical data and error data, for
NSEL.
show logging flowexport-syslogs
Lists all syslog messages that are captured by NSEL events.
show running-config
logging
Shows disabled syslog messages, which are redundant syslog
messages, because they export the same information through
NetFlow.
44
Visit riscnetworks.com or email sales@riscnetworks.com to connect with your account manager.
Verifying TrafficWatch Collection
1. Access web portal at https://portal.riscnetworks.com
2. Select View Detail
3. Select TrafficWatch
45
Visit riscnetworks.com or email sales@riscnetworks.com to connect with your account manager.
4. Verify registration for virtual RN50, physical RN50, and NetFlow export nodes
5. Verify TrafficWatch Stats
(vSwitch Promiscuous mode, SPAN, and dvSwitch Port Mirroring will display as Mirror for
Collection Type)
(NetFlow will display as NetFlow for Collection Type)
46
Visit riscnetworks.com or email sales@riscnetworks.com to connect with your account manager.
For NetFlow:
6. Locate IP address of NetFlow exporter
7. Verify that "Collection Type" displays as "NetFlow" and that it is recording statistics (it
may take some time to update in the portal)
8. Once NetFlow configuration is validated, the RN50 can be disabled in the portal
9. Each flow exporter is considered a node, so disabling the RN50 will remove it from the
node entitlement
47
Visit riscnetworks.com or email sales@riscnetworks.com to connect with your account manager.
10. Disable the RN50 by sliding the button to the left
Please Contact help@riscnetworks.com if additional assistance is needed.
48
Visit riscnetworks.com or email sales@riscnetworks.com to connect with your account manager.