Teacher: CORE Applied Biology I Year: 2014
advertisement
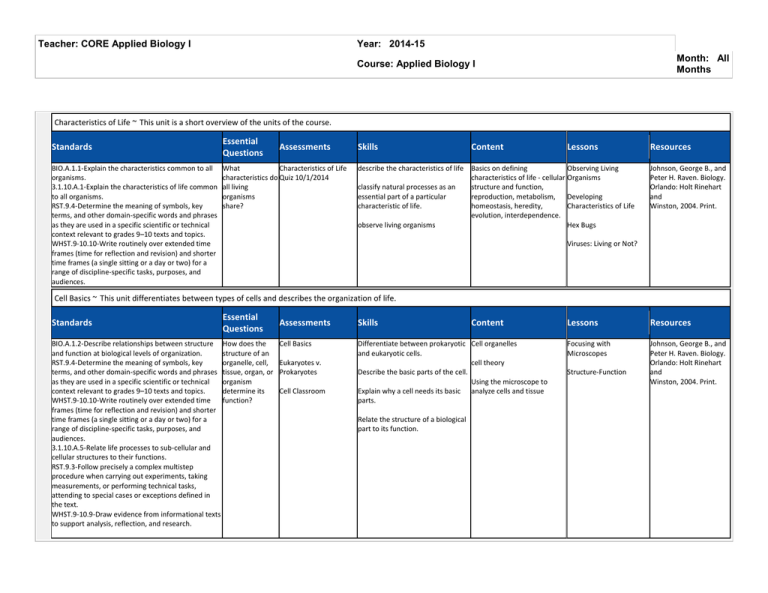
Teacher: CORE Applied Biology I Year: 2014-15 Month: All Months Course: Applied Biology I Characteristics of Life ~ This unit is a short overview of the units of the course. Standards BIO.A.1.1-Explain the characteristics common to all organisms. 3.1.10.A.1-Explain the characteristics of life common to all organisms. RST.9.4-Determine the meaning of symbols, key terms, and other domain-specific words and phrases as they are used in a specific scientific or technical context relevant to grades 9–10 texts and topics. WHST.9-10.10-Write routinely over extended time frames (time for reflection and revision) and shorter time frames (a single sitting or a day or two) for a range of discipline-specific tasks, purposes, and audiences. Essential Questions Assessments What Characteristics of Life characteristics do Quiz 10/1/2014 all living organisms share? Skills Content Lessons describe the characteristics of life Basics on defining Observing Living characteristics of life - cellular Organisms classify natural processes as an structure and function, essential part of a particular reproduction, metabolism, Developing characteristic of life. homeostasis, heredity, Characteristics of Life evolution, interdependence. observe living organisms Hex Bugs Resources Johnson, George B., and Peter H. Raven. Biology. Orlando: Holt Rinehart and Winston, 2004. Print. Viruses: Living or Not? Cell Basics ~ This unit differentiates between types of cells and describes the organization of life. Standards Essential Questions BIO.A.1.2-Describe relationships between structure How does the and function at biological levels of organization. structure of an RST.9.4-Determine the meaning of symbols, key organelle, cell, terms, and other domain-specific words and phrases tissue, organ, or as they are used in a specific scientific or technical organism context relevant to grades 9–10 texts and topics. determine its WHST.9-10.10-Write routinely over extended time function? frames (time for reflection and revision) and shorter time frames (a single sitting or a day or two) for a range of discipline-specific tasks, purposes, and audiences. 3.1.10.A.5-Relate life processes to sub-cellular and cellular structures to their functions. RST.9.3-Follow precisely a complex multistep procedure when carrying out experiments, taking measurements, or performing technical tasks, attending to special cases or exceptions defined in the text. WHST.9-10.9-Draw evidence from informational texts to support analysis, reflection, and research. Assessments Skills Cell Basics Differentiate between prokaryotic Cell organelles and eukaryotic cells. cell theory Describe the basic parts of the cell. Using the microscope to Explain why a cell needs its basic analyze cells and tissue parts. Eukaryotes v. Prokaryotes Cell Classroom Relate the structure of a biological part to its function. Content Lessons Resources Focusing with Microscopes Johnson, George B., and Peter H. Raven. Biology. Orlando: Holt Rinehart and Winston, 2004. Print. Structure-Function Water and Solutions ~ This unit analyzes the special properties of water and how those properties are important for the sustenance of life on earth. Standards BIO.A.2.1-Describe how the unique properties of water support life on Earth. RST.9.4-Determine the meaning of symbols, key terms, and other domain-specific words and phrases as they are used in a specific scientific or technical context relevant to grades 9–10 texts and topics. 3.2.10.A.1-Predict properties of elements using trends of the periodic table. Identify properties of matter that depend on sample size. Explain the unique properties of water (polarity, high boiling point, forms hydrogen bonds, high specific heat) that support life on Earth. WHST.9-10.10-Write routinely over extended time frames (time for reflection and revision) and shorter time frames (a single sitting or a day or two) for a range of discipline-specific tasks, purposes, and audiences. Essential Questions Assessments Why is water such a Properties of Water unique substance? Properties of Water How do water's Quiz properties support living organisms? Skills Content Determine which property of water Properties of water is displayed by a given situation. Polarity and hydrogen Describe how hydrogen bonding bonding gives water its special properties. pH scale, acids, and bases Differentiate between acids and bases Lessons Resources Properties of Water Lab Stations Johnson, George B., and Peter H. Raven. Biology. Orlando: Holt Rinehart and Winston, 2004. Print. Lessons Resources Carbon Compounds ~ This unit analyzes carbon as the backbone of organic molecules. Standards Essential Questions Assessments BIO.A.2.2-Describe and interpret relationships Why is carbon the Carbon Compound quiz between structure and function at various levels of perfect base atom biochemical organization (i.e., atoms, molecules, for the diversity of Carbon's Importance and macromolecules). living organisms? WHST.9-10.10-Write routinely over extended time frames (time for reflection and revision) and shorter time frames (a single sitting or a day or two) for a range of discipline-specific tasks, purposes, and audiences. RST.9.4-Determine the meaning of symbols, key terms, and other domain-specific words and phrases as they are used in a specific scientific or technical context relevant to grades 9–10 texts and topics. Skills Content Explain bonding properties of carbon as related to organic molecules Organic compounds - carbon Carbon Compounds compounds, functional groups Carbon Compound Stations Dehydration Synthesis Distinguish between organic and inorganic compounds Hydrolysis Summarize how large carbon molecules are synthesized Summarize how large carbon molecules are broken down Describe the structure of ATP and how this structure holds energy ATP hydrolysis Johnson, George B., and Peter H. Raven. Biology. Orlando: Holt Rinehart and Winston, 2004. Print. Molecules of Life ~ This unit classifies the macromolecules carbohydrates, protein, lipids, and nucleic acids in terms of their structure, function, and source in nature. Standards Essential Questions Assessments BIO.A.2.2-Describe and interpret relationships How do the Most Important Organic between structure and function at various levels of structures of Compound biochemical organization (i.e., atoms, molecules, macromolecules and macromolecules). relate to their Macromolecule Quiz 3.1.10.A.7-Describe the relationship between the functions? structure of organic molecules and the function they serve in living organisms. Explain how cells Why are store and use information to guide their functions. macromolecules RST.9.4-Determine the meaning of symbols, key necessary for terms, and other domain-specific words and organisms' survival? phrases as they are used in a specific scientific or technical context relevant to grades 9–10 texts How do organisms and topics. obtain the RST.9.5-Analyze the structure of the relationships necessary among concepts in a text, including relationships macromolecules of among key terms (e.g., force, friction, reaction life? force, energy). RST.9.7-Translate quantitative or technical information expressed in words in a text into visual form (e.g., a table or chart) and translate information expressed visually or mathematically (e.g., in an equation) into words. WHST.9-10.1.a-Introduce precise claim(s), distinguish the claim(s) from alternate or opposing claims, and create an organization that establishes clear relationships among the claim(s), counterclaims, reasons, and evidence. WHST.9-10.1.b-Develop claim(s) and counterclaims fairly, supplying data and evidence for each while pointing out the strengths and limitations of both claim(s) and counterclaims in a discipline-appropriate form and in a manner that anticipates the audience's knowledge level and concerns. WHST.9-10.9-Draw evidence from informational texts to support analysis, reflection, and research. WHST.9-10.10-Write routinely over extended time frames (time for reflection and revision) and shorter time frames (a single sitting or a day or two) for a range of discipline-specific tasks, purposes, and audiences. Skills Content Distinguish between subclasses of Carbohydrates macromolecules monosaccharides, disaccharides, Explain the specific relationship polysaccharides between monomers and polymers of macromolecules Protein - amino acids, polypeptides Relate the structure to the function of each macromolecule Lipids - sterols, hormones, fatty acids Compare and contrast DNA to RNA Nucleic Acids - DNA, RNA Identify the source of each macromolecule for various living organisms Lessons Resources Nucleic Acids Johnson, George B., and Peter H. Raven. Biology. Orlando: Holt Rinehart and Winston, 2004. Print. Food Lab Balanced Meal Adjusted Diets Enzymes ~ This unit describes how the enzyme functions and its importance to maintaining life processes. Standards 3.1.10.A.2-Explain cell processes in terms of chemical reactions and energy changes. BIO.A.2.3-Explain how enzymes regulate biochemical reactions within a cell. RST.11.2-Determine the central ideas or conclusions of a text; summarize complex concepts, processes, or information presented in a text by paraphrasing them in simpler but still accurate terms. RST.11.3-Follow precisely a complex multistep procedure when carrying out experiments, taking measurements, or performing technical tasks; analyze the specific results based on explanations in the text. Essential Questions How do enzymes regulate chemical reactions in cells? Assessments Skills Content Lessons Resources Enzyme Quiz Describe how enzymes interact with their substrates Enzyme function Affecting Enzyme Function Johnson, George B., and Peter H. Raven. Biology. Orlando: Holt Rinehart and Winston, 2004. Print. Lactase Lab Reaction energetics Predict how changes in pH, temperature, or concentration of substances could affect enzyme activity Why do enzymes only work in particular conditions? Pineapple Enzyme Lab Catalase Lab Photosynthesis ~ Analyze the process of photosynthesis and the energy conversions that occur in the chloroplast. Standards BIO.A.3.1-Identify and describe the cell structures involved in processing energy. BIO.A.3.2-Identify and describe how organisms obtain and transform energy for their life processes. 3.1.B.A.2-Identify the initial reactants, final products, and general purposes of photosynthesis and cellular respiration. Explain the important role of ATP in cell metabolism. Describe the relationship between photosynthesis and cellular respiration in photosynthetic organisms. Explain why many biological macromolecules such as ATP and lipids contain high energy bonds. Explain the importance of enzymes as catalysts in cell reactions. Identify how factors such as pH and temperature may affect enzyme function. WHST.9-10.1.c-Use words, phrases, and clauses to link the major sections of the text, create cohesion, and clarify the relationships between claims) and reasons, between reasons and evidence, and between claim(s) and counterclaims. Essential Questions How does the chloroplast transform energy from the sun into chemical energy? Assessments Skills Photosynthesis quiz Identify parts and their functions of Light-Dependent Reactions the chloroplast. Chloroplast Structure Describe the two phases of photosynthesis. Calvin Cycle Photosynthesis Lab State the reactants and products of photosynthesis. Describe the energy transformations that occur in each phase of photosynthesis. Content Lessons Resources Plastid Structure Comparison Johnson, George B., and Peter H. Raven. Biology. Orlando: Holt Rinehart and Winston, 2004. Print. Cellular Respiration ~ Analyze the process of cellular respiration and the energy conversions that occur in the mitochondria. Standards Essential Questions Assessments 3.1.B.A.2-Identify the initial reactants, final products, and How is the mitochondria built to Cellular Respiration general purposes of photosynthesis and cellular carefully extract the energy from Quiz respiration. Explain the important role of ATP in cell glucose? metabolism. Describe the relationship between photosynthesis and cellular respiration in photosynthetic organisms. Explain why many biological macromolecules such as ATP and lipids contain high energy bonds. Explain the importance of enzymes as catalysts in cell reactions. Identify how factors such as pH and temperature may affect enzyme function. BIO.A.3.1-Identify and describe the cell structures involved in processing energy. BIO.A.3.2-Identify and describe how organisms obtain and transform energy for their life processes. 3.1.10.A.5-Relate life processes to sub-cellular and cellular structures to their functions. HS-LS1.5-Use a model to illustrate how photosynthesis transforms light energy into stored chemical energy. HS-LS1.7-Use a model to illustrate that cellular respiration is a chemical process whereby the bonds of food molecules and oxygen molecules are broken and the bonds in new compounds are formed resulting in a net transfer of energy. Skills Content Identify parts and their Glycolysis functions of the mitochondria. Krebs' Cycle Describe the three phases of cellular respiration. Mitochondria Structure Lessons Resources Energy Transformation Relationships Johnson, George B., and Peter H. Raven. Biology. Orlando: Holt Rinehart and Winston, 2004. Print. Material Transformation State the reactants and Electron Transport Chain products of cellular respiration. Fermentation - lactic acid Describe the energy and alcoholic transformations that occur in each phase of cellular respiration. Explain why fermentation occurs and the products created. Cell Transport ~ Determination of how cells maintain homeostasis by utilizing the cell membrane to transport materials into and out of the cell. Standards Essential Questions Assessments BIO.A.4.1-Identify and describe the cell structures involved How is the cell membrane Cell Transport and in transport of materials into, out of, and throughout a cell. designed to complete its Homeostasis BIO.A.4.2-Explain mechanisms that permit organisms to function of protection and maintain biological balance between their internal and regulation? Passive Transport Quiz external environments. 3.1.10.A.5-Relate life processes to sub-cellular and cellular Why can some molecules cross structures to their functions. the cell membrane without WHST.9-10.1.c-Use words, phrases, and clauses to link the energy while others require major sections of the text, create cohesion, and clarify the energy? relationships between claims) and reasons, between reasons and evidence, and between claim(s) and What roles does the cell counterclaims. membrane play in maintaining WHST.9-10.2.b-Develop the topic with well-chosen, homeostasis in a single cell and relevant, and sufficient facts, extended definitions, in a multicellular organism? concrete details, quotations, or other information and examples appropriate to the audience's knowledge of the topic. WHST.9-10.2.c-Use varied transitions and sentence structures to link the major sections of the text, create cohesion, and clarify the relationships among ideas and concepts. Skills Content Lessons Explain how an equilibrium is Passive Transport Osmosis established as a result of diffusion, osmosis, diffusion. facilitated diffusion, ion Immune System channels Determine which method of transport a given particle Equilibrium would undergo. Active Transport - sodiumDescribe each type of potassium pump, transport. endocytosis, exocytosis Distinguish between passive Role of receptor proteins and active transport. and result of their activation Describe how the golgi apparatus and ER work together to move materials throughout the cell. Resources Johnson, George B., and Peter H. Raven. Biology. Orlando: Holt Rinehart and Winston, 2004. Print. Cell Reproduction ~ Describes the processes of mitosis and meiosis, comparing and contrasting the results. Standards Essential Questions Assessments Skills Content Lessons Resources 3.1.10.A.4-Describe the cell cycle and the process and significance of mitosis. BIO.B.1.1-Describe the three stages of the cell cycle: interphase, nuclear division, cytokinesis. WHST.9-10.2.d-Use precise language and domain-specific vocabulary to manage the complexity of the topic and convey a style appropriate to the discipline and context as well as to the expertise of likely readers. WHST.9-10.1.c-Use words, phrases, and clauses to link the major sections of the text, create cohesion, and clarify the relationships between claims) and reasons, between reasons and evidence, and between claim(s) and counterclaims. What process do cells use Mitosis Quiz to reproduce? Mitosis - Meiosis Why is meiosis a different Comparison process from mitosis? Mitosis phases. Time for Mitosis Lab Johnson, George B., and Peter H. Raven. Biology. Orlando: Holt Rinehart and Winston, 2004. Print. Describe the steps of mitosis and meiosis. Meiosis phases. Compare and contrast the process and outcomes of Human mitosis and meiosis. reproductive cycles. Relate human reproduction to meiosis. Modeling Meiosis "The Case of the Dividing Cell" article Hybrid medical mitosis video Cancer Warriors video http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/body/cancerwarrior.html