Linkage - MAH-SBHS
advertisement

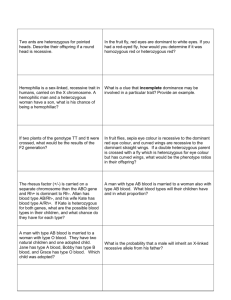
DO NOW (Just write answers) What is incomplete dominance Define recessive Where does the variation in gametes arise from in meiosis What is the purpose of meiosis What is mitosis What is an allele What does homozygous and heterozygous mean THIS TERM Week 1: GENETICS Week 2: GENETICS Week 3: GENETICS Week 4: ANIMALS Week 5: EXAM WEEK Week 6: ANIMALS Week 7:ANIMALS Week 8: PLANTS Week 9: FIELD TRIP Week 10: PLANTS THIS TERM HOMEWORK – BIOZONE AND EXAM QUESTIONS (past test results) IN CLASS WORK ETHIC HELP: WED LUNCHTIMES REVIEW – USE WHITE BOARDS Write the combinations for gametes for the following crosses HhBB x HHBb PpHh x ppHh RrFf x rrFF TO DO ON BOARDS IF FINISHED GRAB WORKSHEET FROM FRONT In summer squash, white fruit colour (W) is dominant over yellow fruit colour (w) and disk-shaped fruit (D) is dominant over sphere-shaped fruit (d) If a heterozygous white coloured sphere shaped squash was crossed with a yellow coloured homozygous disk shaped squash what would the phenotype ratio of their offspring be? EXAM QUESTION 2004 In horses, black coat colour is influenced by the dominant allele (B) and chestnut coat colour by the recessive allele ( b). Trotting gait is due to dominant gene (T), pacing gait to the recessive allele (t). A horse trainer wanted to find the genotype of a black trotter she bought.. a) Give the genotype and phenotype of the horse she would use to find out the genotype of a black trotter. Explain your answer b) Use a punnett square to work out the phenotypic ratio of all possible offspring when a black male heterozygous for both traits is mated with a female heterozygous for both traits. c) Explain why, when breeding chestnuts together she would not get any black foals, but when breeding black horse she could get chestnut foals SEX LINKAGE This occurs when genes are located on the sex chromosomes either the X or the Y chromosome (note: autosomes are the other chromosomes) Example: Colour blindness Sex linked gene located on the X chromosome N = normal XN = normal vision Y = male n = colour blind Xn = colourblind PROBLEM: Can a woman with normal vision whose father was colour blind have colour blind children if she marries a normal visioned male? Genotypes? Do a cross? Continue with extra questions