Chapter 2
advertisement

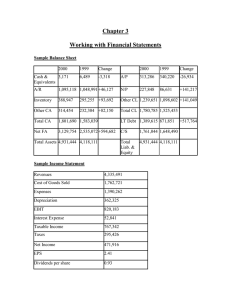
Chapter 5 Balance Sheet and Statement of Cash Flow ACCT-3030 1 1. Introduction to Balance Sheet How important is the balance sheet? Is the balance sheet useful? What are the limitations of the balance sheet? What information is available on the balance sheet? ACCT-3030 2 2. Important Concepts Liquidity ◦ the speed with which the firm’s assets or liabilities are converted into cash or paid Financial flexibility ◦ the ability of an enterprise to take effective actions to alter the amounts and timing of cash flows Solvency ◦ the ability of an enterprise to pay its debts as they mature ACCT-3030 3 2. Important Concepts (con’t) Operating capability ◦ the entity’s ability to maintain a given physical level of operations Capital maintenance ◦ a method of measuring income by comparing beginning capital with ending capital Capital Structure ◦ shows the sources of capital provided to the entity ACCT-3030 4 3. Recognition in the Bal. Sheet Recognition means recording the item in the AIS or disclosing it in the notes to the financial statements General Recognition Criteria ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ meet the definition of an element be measurable be relevant have faithful representation ACCT-3030 5 4. Balance Sheet Classifications Assets ◦ Current cash and cash equivalents (3 months or less maturity) investments accountants receivable inventories prepaid assets investments property, plant, and equipment intangible assets other assets ◦ Noncurrent ACCT-3030 6 4. Balance Sheet Classifications Liabilities ◦ Current accounts payable notes payable unearned revenues accrued liabilities current portion of long-term debt ◦ Long-term liabilities notes payable bonds payable ACCT-3030 7 4. Balance Sheet Classifications Stockholders’ Equity ◦ Contributed capital preferred stock common stock paid-in capital… ◦ Retained earnings ACCT-3030 8 5. Disclosures Notes ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ summary of significant accounting policies contingencies contractual situations related party transactions subsequent events MD&A Management’s responsibilities ACCT-3030 9 6. Other Comparative financial statements Interim financial statements SEC reports ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ 10-K 10-Q 8-K proxy statement EDGAR XBRL ACCT-3030 10 7. Alternative Valuation Methods To be recognized an item m/b measurable ◦ alternative bases of measurability could be used Historical cost (input value) ◦ the exchange price of the asset when it was acquired Replacement cost (current cost) (input value) ◦ the amount of cash necessary to currently obtain the same asset Current market value(current exit value)(output value) ◦ the amount of cash that could be obtained from selling the asset in an orderly transaction between market participants ACCT-3030 11 7. Alternative Valuation Methods Net realizable value (output value) ◦ the amount of cash that may result when the asset is sold in the future in the ordinary course of business Present value (discounted cash flows) ◦ considers the time value of money - values items at the present value of all future cash flows Price level adjusted (constant dollar) reporting What is current GAAP? ACCT-3030 12 8. Financial Statement Analysis Horizontal analysis Vertical analysis Liquidity ratios ◦ working capital ◦ current ratio ◦ quick ratio Financing (coverage) ratios ◦ debt to equity ◦ debt to assets ◦ times interest earned ACCT-3030 13 8. Financial Statement Analysis Activity ratios ◦ receivables turnover ◦ inventory turnover ◦ asset turnover Profitability ratios ◦ profit margin ◦ return on assets ◦ return on equity ACCT-3030 14 9. Cash Flow Statement Only basics now - More in 3040 Required statement Classifications on statement ◦ operating activities direct method indirect method ◦ investing activities ◦ financing activities ACCT-3030 15 9. Cash Flow Statement ACCT-3030 16