Sources of Gov't Revenue-
advertisement

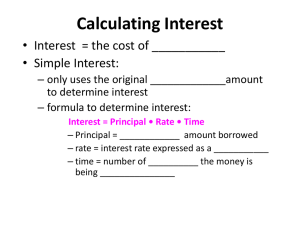
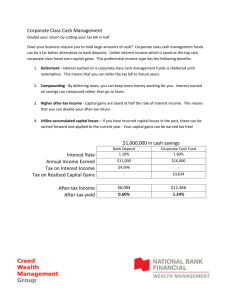
Sources of Gov’t Revenue--TAXES Chapter 9 Criteria for Effective Taxes • 1. Equity – Must be fair – Want to avoid tax loopholes —when people find a flaw in tax laws that allow some people to avoid paying taxes – The belief of “fairness” is different for each person • 2. Simplicity – Written so anyone can understand it – Ex. Individual income tax —a tax on peoples earnings is actually 1,000 of pages long but the IRS puts it in terms everyone can understand • Sales tax —tax on most consumer goods – Different for each state • 3. Efficiency – Must be easy to collect – Must be cost efficient ex. Toll booths collect a tax. Toll must be = or > the cost of employment and upkeep of booths 2 Principles of Taxation • 1. Benefit Principle – Those who benefit from the g or s should pay in proportion to the amount of benefit received • Example: gasoline. Tax is included in price of gas. If you drive more, you pay more taxes because you receive the benefit of better roads, more police protection, etc. GAS TAX PER GALLON • 2. Ability to Pay – Belief that people should be taxed on their ability to pay • Example: indiv. income tax—people who have a higher income are taxed at a higher percentage Video: Understanding your paycheck-on a separate sheet to turn in • 1. What is the difference between gross and net • • • • • • pay? 2. What must be deducted from your paycheck? 3. List some optional deductions. 4. What can you do to minimize your taxes or your taxable income? 5. How many tax brackets are there? 6. How can you increase your income? 7. What is compounding? Types of Taxes • Proportional – The same % of tax on everyone regardless of income • Example: if tax is 20%, a person with a $10,000 income pays $2,000. A person with a $100,000 income pays $20,000 • 2. Progressive – Imposes a higher % of tax on people w/ a higher income – Claims a larger $ amount and larger % of income • Example: income tax • 3. Regressive – Tax that imposes a higher rate on low incomes than on high incomes • Social Security Tax – Tax on income up to $80,400. If you make more than this, you do not have to pay a tax on the amount above $80,400. Example: if you made $80,400 or less you would pay around 7.5 cents per dollar earned in SS tax If you earned 300,000 you would only be paying 1.7 cents per dollar earned Vocabulary—Grab a book! • 1. sin tax • 2. individual income tax • 3. sales tax • 4. payroll withholding system • 5. IRS • 6. tax return • 7. indexing • 8. FICA • 9. medicare • 10. payroll taxes • 11. • 12. • 13. • 14. • 15. • 16. • 17. • 18. • 19. • 20. corporate income tax excise tax luxury good estate tax gift tax custom duty user fees intergovernmental revenues property tax tax assessor QUIZ ON MONDAY USING YOUR VOCAB!!!!! Chapter Review Page 252 • Do Identifying Key Terms 1-13 (not number 9) – Just the word—you do NOT have to write out the definition • Reviewing the Facts – 1, 3, 4, 5, 6, 9 and 11 • Either write out the question and answer • OR • Answer the question in complete sentences. True or False Questions • Make 10 true or false questions about taxes (chapter 9) or spending (chapter 10). • I will email these out tonight or tomorrow for review.