PowerPoint
advertisement

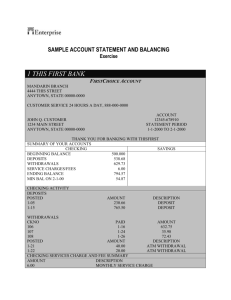
• Managing Personal Finances Next Generation Science/Common Core Standards Addressed! • CCSS.ELA Literacy.RST.9‐10.8 Assess the extent to which the reasoning and evidence in a text support the author’s claim or a recommendation for solving a scientific or technical problem. • CCSS.ELA Literacy. RST.11‐12.9 Synthesize information from a range of sources (e.g., texts, experiments, simulations) into a coherent understanding of a process, phenomenon, or concept, resolving conflicting information when possible Agriculture, Food and Natural Resource Standards Addressed! • CRP.01.01. Model personal responsibility in the workplace and community. • CRP.01.01.01.a. Define personal responsibility and distinguish how it applies in workplace and community (e.g., make educated choices, listen and follow directions, ask for help when needed, meet expected standards, etc.). Bell Work! STUDENT LEARNING OBJECTIVES • Conduct budgeting of personal finances. • Develop financial goals. • Understand how to use and balance a checking account. • Compare characteristics of various types of investments. Terms • Bonds • Budget • Certificates of deposit • Checking account • Financial planning process • Goal Terms Continued • Insured savings account • Mutual funds • Overdrafts • Stocks • United States savings bonds Interest Approach • How much money do you spend in a week? • How do you decide what purchase? Why is Financial Management important? • • • • Knowing financial standing Setting priorities and needs. Planning credit needs. Tax planning and reporting Some disadvantages to personal financial management. • Initial set-up takes time • Regular updating required Budget • Formal written or unwritten plan • Includes sources of income and expenses How do I prepare a Budget • To prepare a budget one needs to consider sources of income and items purchased. • A budget categorizes the uses of cash as to whether they are a necessity or a luxury. Six Steps in Financial Planning • Gather personal and financial data. • Establish financial goals and objectives. • Analyze financial information to identify alternatives to achieve goals and objectives. • Develop a financial plan. • Implement the plan. • Review the plan on a regular basis. Checking Account • A checking account is an account in which a user makes deposits and may write checks or use a debit card to be paid from the account. Advantages of a Checking Account • Reduces need to carry large quantities of cash. • May be able to accrue interest while money is in the account. • Safe way to pay by mail or online. • Most all businesses accept checks or the use of a debit card. • Most banks provide online services. Disadvantages • • • • A checking account may require monthly fees. Time is required to balance the checkbook There may be minimum balance requirements. Stolen or lost checks or debit card can result in loss of money from the account. • Large charges are levied against overdrafts, when a check is written in an amount greater than the account balance. • Avoid use of “Pin” numbers to avoid “Hacking”! • Protect your password used for online banking. Styles of checkbooks • Duplicate check-carbon copy remains in the checkbook. • Stub-information remains in the checkbook. • Safety paper-a watermark that makes photocopying obvious. • Desk set-large binder with three checks per page. Balancing Checkbook Note: Using online services simplifies the following practices. • Mark deposits and checks that have cleared • • • • the bank. Add to the current balance those checks that are written but not cleared. Subtract any deposits made but not cleared. Subtract any service charges and add any interest. Compare the ending balances in the checkbook against the monthly statement. What types of investments are available? • • • • • • Insured savings account Savings bonds Certificates of deposit Bonds Mutual funds Stocks Insured Saving Account • Available through banks, saving and loans associations, and other financial institutions. • They are insured by a government agency. • They are considered safe & convenient. • All savings accounts are insured to a specified limit of $ 250,000,00 by the FDIC. Certificates of Deposit • CDs are savings certificates worth a specific amount of money, for a specific amount of time, with a set interest rate. • Usually pays a higher interest rate than passbook savings accounts and are fairly convenient. • A penalty is assessed if money is withdrawn prior to the “maturity” date. US Savings Bonds • Available through many financial institutions. • Can be purchased through payroll deductions. • Involve investing in the federal government by buying bonds with a set maturity date at a price below the face value of the bond. Bonds • Bonds are certificates of debt. • Issued by corporations or government agencies. Bonds promise payments of interest on specific dates. • Original investment is also paid back at maturity. ( investment plus interest) • Bonds are long term investment. Mutual Funds • Investors pool their money. • Professional money managers manage the pool of money for the individual investors. Interest is paid to the investor based on the amount invested. • Quite often the investment is made by payroll deduction. Stocks • Stocks represent a share of ownership in a company. • The value of the stock can increase or decrease based on performance of the company. Review/Summary • How would you conduct budgeting of personal finances? • How are financial goals developed? • How to use and balance a checking account. • Compare characteristics of various types of investments. The End!