-
What does the integumentary system consist of?
skin, hair, nails, glands, some muscles (like pili), sense receptors (nervous), hypodermis
-
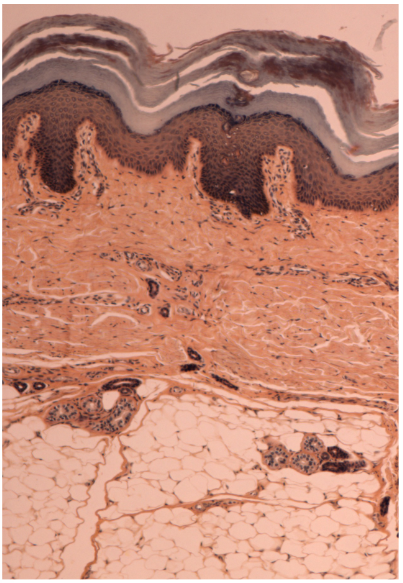
What are the skin layers?
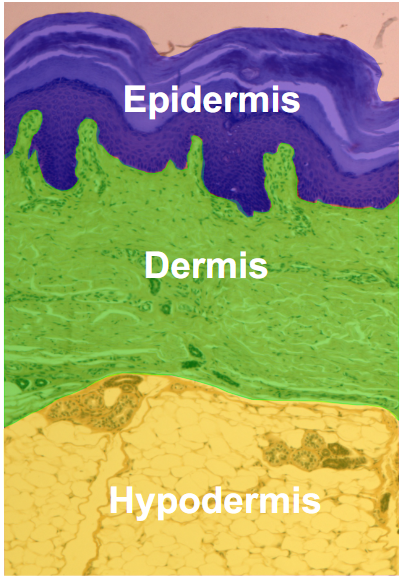
3rd isnt a skin layer
-
What are the characteristics of epidermis?
Stratified squamous epithelium and avascular
-
What are the 4-5 strata of the epidermis?
Stratum Basale, Stratum spinosum, stratum granulosum, stratum lucidum, stratum corneum
-
What is the order top down of the strata in the epidermis?
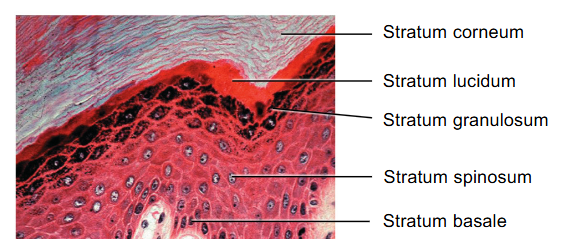
-
What is stratum Basale? What is it made up of?
- a single row of cells of two cell types
- keratinocytes (90%), this goes through mitosis, makes keratin (a tough protein), pushes cells towards surface as more are produced by mytosis
- melanocytes (10%), produces pigment (melanin) for UV protection. everyone has same amount, but diff amounts of melanin produced and shades of it
- blood (hemoglobin) in dermis can give pink tinge to pale skin
-
what does stratum Spinosum do?
low levels of mitosis
-
what does stratum granulosum do?
- no mitosis, last layer of living cells
- contains granules that help produce keratin (strength) and start to produce waterproofing glycolipids (prevents water loss)
-
What is stratum lucidum?
- dead layer, not visible in thin skin, only thick
- no mitosis, flat cells
-
What is stratum corneum?
- many layers of flat dead cells filled with keratin (tough protein)
- glycolipids between cells creates waterproof layer (prevents water loss)
- shed on this layer, then replaced from below
-
what does the dermis contain?
- vascular
- has two sublayers (CT): papillary & reticular layer
- contains blood vessels, nerves, glands, hair follicles, arrector polo muscles
-
What is the papillary layer of the dermis?
- areolar connective tissue
- vascular
- projects into the epidermis (dermal papillae),
which in thick skin forms the epidermal ridges (fingerprints)
-
What is the reticular layer of the dermis?
- between papillary layer and hypodermis
- forms most of dermis
- dense regular connective tissue
-
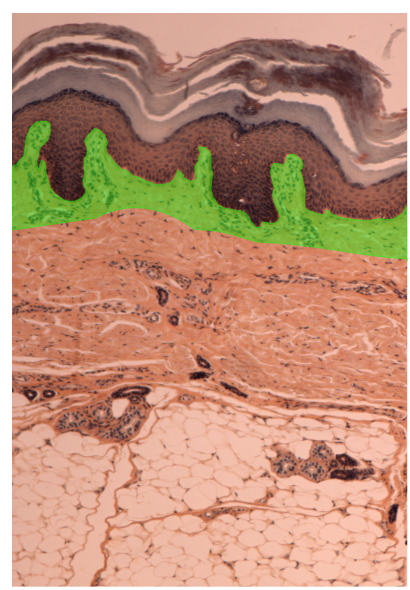
what layer is this?
The papillary layer of the dermis
-
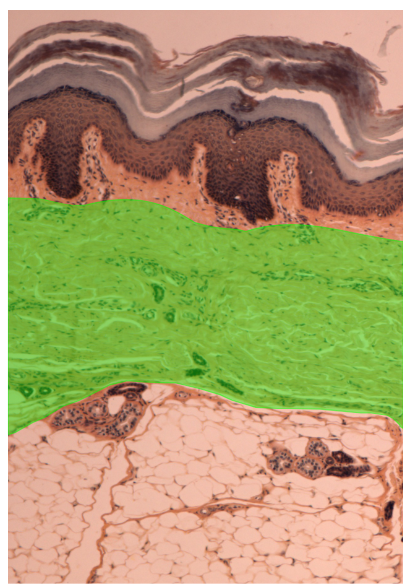
what layer is this?
the reticular layer of the dermis
-
What are the characteristics of thick vs thin skin?
- thick vs thin refers to epidermis, not the dermis
- thin skin: lucidum absent, hair follicles, glands, arrector pilli muscles
- thick skin: palms and soles, lucidum present, no hair, glands, or pilli
-
What are the 3 derivatives of the epidermal?
hair, nails, skin exocrine glands
-
What are the parts of hair?
- hair is all dead skin cells
- root, part of hair embedded in skin
- shaft, visible out of skin surface
- hair follicle, surrounds root (made of up pieces)
-
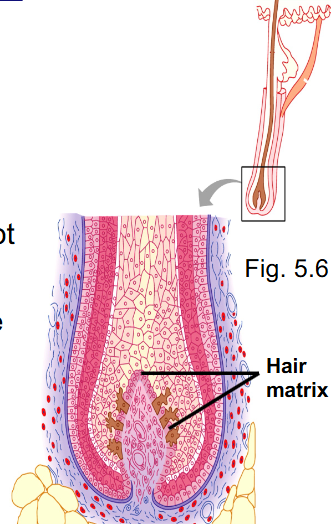
What makes up the hair follicle?
- epithelial root sheath (several epidermal layers extend into the dermis)
- bulb (expanded region of base of root)
- matrix (single layer of cells derived from basale cells, site of hair growth and melanin for hair colour)
-
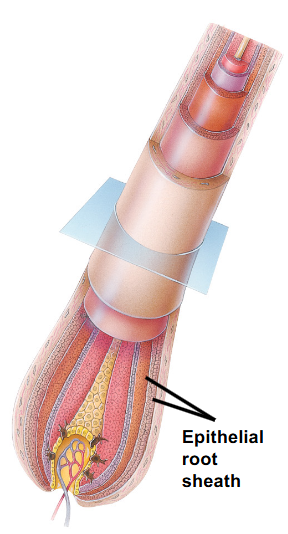
What is associated with each hair follicle?
- outer CT sheath (formed in dermis, holds follicle in place)
- hair papilla (formed in dermis, contains blood for growing hair, extends up from beneath matrix)
- root hair plexus (free nerve endings sensors)
- sebaceous oil gland (opens into follicle)
- arrector pili muscle (smooth muscle, goosebumps)
-
What are nails? what do they consist of?
- very keratinized epidermal cells
- consists of: nail root (under skin), body (visible), free edge
-
What are the skin exocrine glands?
sebaceous glands, sudoriferous glands, ceruminous glands, mammary glands
-
What is the sebaceous gland?
- connects to hair follicles
- secretes sebum (oily, mix of fats, salts, and proteins)
- lubricates hair and skin, antibiotic
-
What is the sudoriferous gland?
- sweat glands
- secretory portions in dermis of thick and thin skin
- ducts open onto skin surface
- fcns: temp regulation, waste removal, antibiotic action
-
What are the ceruminous glands?
- modified sweat glands
- in ear canal
- produces ear wax
-
What are the mammary glands?
- modified sweat glands
- produce milk
-
What are cutaneous sense receptors? What are the 4 major types?
- sensory receptors are a sensory neuron (part of nervous system)
- specialized cell that responds to stimuli (touch, temp, pain, etc)
- 4 types: touch receptors, pressure receptors, thermoreceptors, nociceptors
-
Where are the touch receptors?
- free nerve endings in epidermis
- root hair plexuses (nerve endings in end of hair follicle)
- tactile (meissners) corpuscles (sensitive to small touch, CT capsule around nerve ending)
- in dermal papillae
-
What are the pressure receptors?
- free nerve endings in dermis
- Lamellar (pacinian) corpuscles, CT wrapped nerve endings, deep in dermis or hypodermis
-
What are the thermoreceptors?
- free nerve endings for temperature
-
What are the nociceptors?
- free nerve endings for pain
- in the dermis and epidermis, 3rd degree burns take them all out
-
What is the hypodermis?
- adipose connective tissue below skin that stores (1/2) of bodys adipose tissue (insulation)
- NOT part of the skin
- also called the subcutaneous layer and superficial fascia
-
What is Albinism?
Lack of melanin production by melanocytes
-
What is psoriassi?
- Autoimmune disorder that causes accelerated mitosis or keratinocytes in the stratum basale.
- immature keratinocytes accumulate in the epidermis and the stratum corneum fails to shed, resulting in a thick scaley area of the surface of the skin

