-
What is a body cavity and what are the two main types?
They are enclosed spaces that house and protect organs
1. Dorsal Body cavity (includes cranial cavity and vertebral cavity)
2. Ventral body cavity (includes thoracic (chest) cavity, abdominal cavity, and pelvic cavity)
-
What does the Dorsal body cavity consist of?
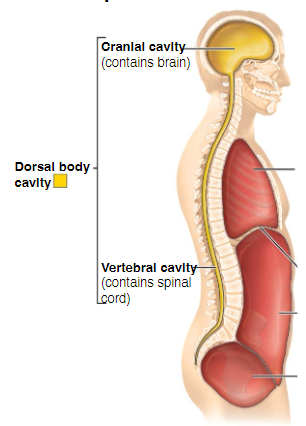
1. The cranial cavity (head)
2. The vertebral cavity (spinal cord)
-
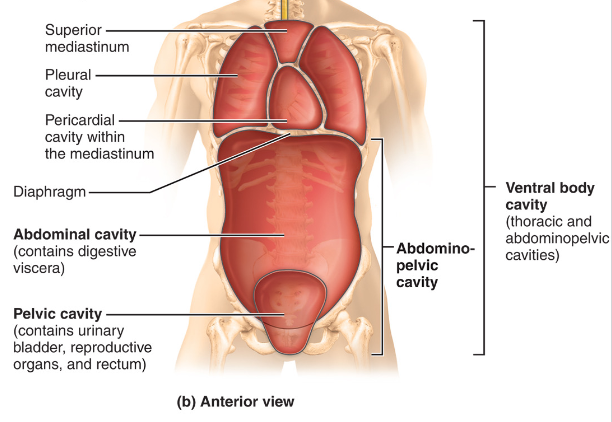
What does the Ventral Body cavity consist of?
1. The thoracic cavity (chest)
- pericardial cavity (heart)
- pleural cavity (lungs)
2. Abdominal cavity (digestive organs)
3. Pelvic cavity (urinary bladder, reproductive organs, rectum)
-
What is a membrane and what do they do?
- Consists of 1-2 tissue types (connective, and epithelial if theres 2 types)
- lines inner and outer surfaces of the body and organs
-
What are the four membrane types?
Mucous membranes (mucosa), serous membranes (serosa), Synovial membranes, and cutaneous membranes
-
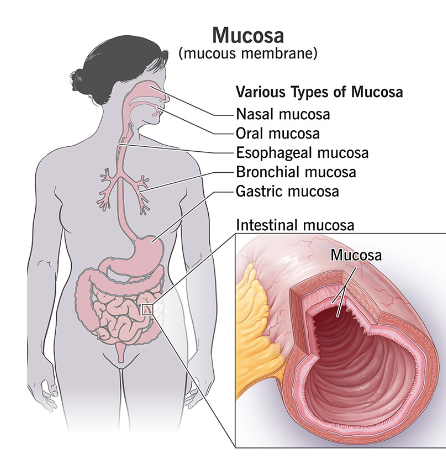
What does the Mucous membrane do and what are its layers?
- lines cavities of the body open directly to body exterior
2 layers:
- Epithelial layer (in contact with lumen, avascular, many goblet cells)
- Lamina propria (connective tissue that connects epithelial to wall of organ. Made of loose areolar connective tissue (so vascular), nourishes epithelial cells)
-
Where is the mucosa?
-
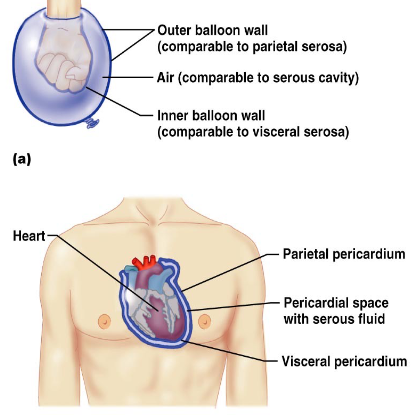
What are serous membranes and what do they do?
- line closed body cavities (ones not open to exterior) and covers external surfaces of organs in these cavities
- double layered membranes (each layer has simple epithelium bound to an areolar connective tissue)
- epithelial layer secretes fluid into serous cavity (slippery)
-
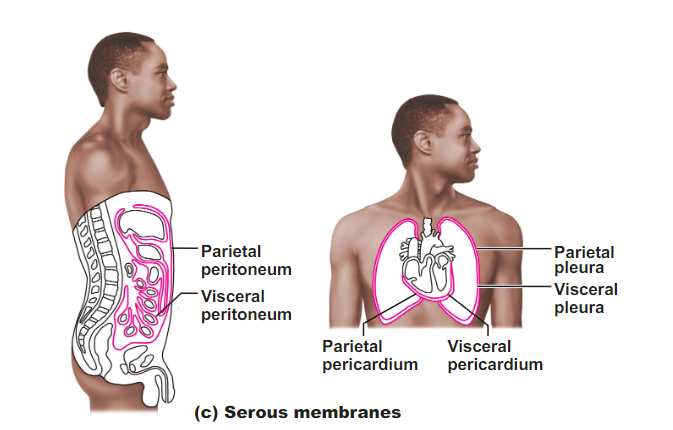
What are the names of the different Serous membrane layers and locations?
1. Parietal layer (against cavity wall) location names:
- Parietal pleura
2. Visceral layer (against organ) location names:
- Pericardium (heart)
- peritoneum (abdominal organs)
- visceral pleura (lungs)
-
Where is the Serous membrane?
-
What is the Synovial membrane and where is it?
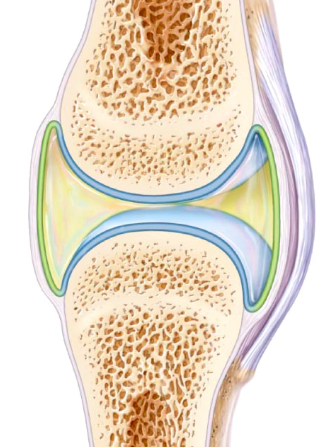
- Just Areolar connective tissue, no epithelium (so not an organ)
- found in joints
-
How do the Serous membrane layers work (name wise)?
-
What is the cutaneous membrane and where is it?
it is the skin, made:
- epidermis (stratified squamous epithelium)
- dermis (connective tissue (aerolar and dense regular))