-
What are the stages of the pre-embryonic period? And when is that?
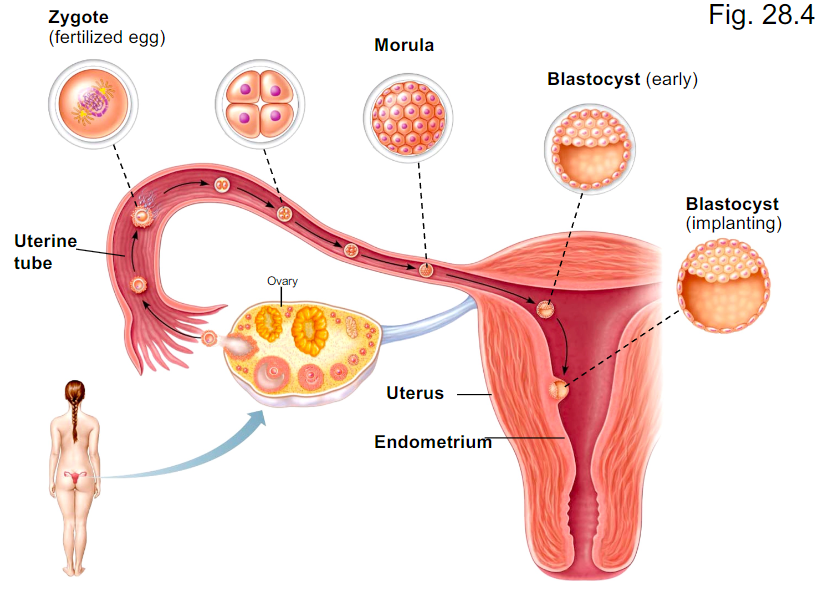
- The first two weeks
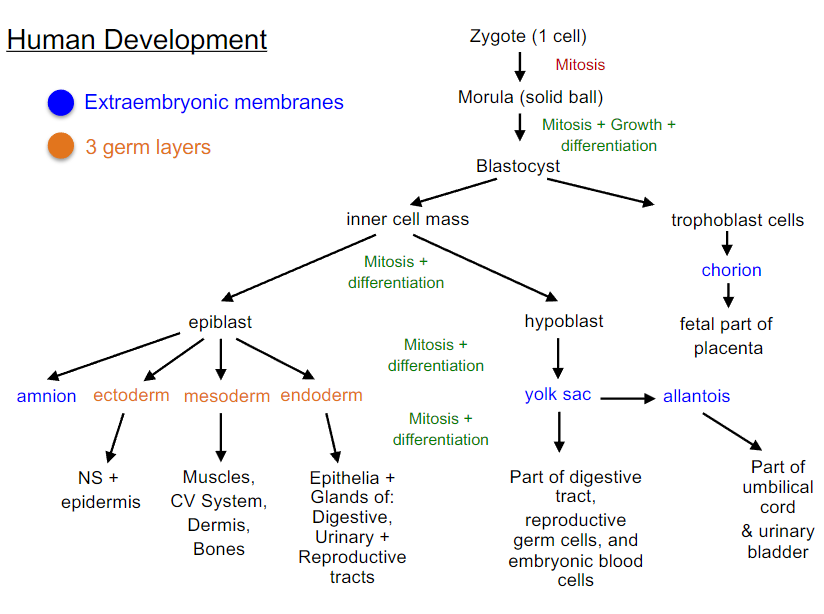
- Stages: Zygote, Morula, Blastocyst (which after implantation differentiates into epiblast and hypoblast)
-
What is the Zygote and what does it do?
- It is one diploid cell that forms in the uterine tube
- undergoes 4-5 mitotic divisions called cleavage divisions (to form morula)
-
What is the Morula and what does it do?
- is in the fallopian tube
- solid ball of 16-32 cells (but same size as ovum/zygote)
after cells continue to divide and begin to differentiate into diff cell types with specific form and fcn
-
What are the features Blastocyst pre-implantation?
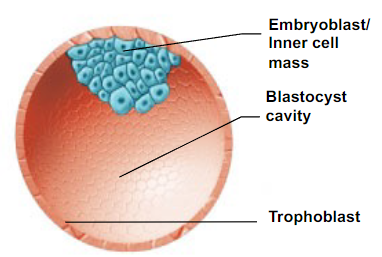
- blastocoel/blastocyst cavity (fluid-filled)
- the embryoblast (inner cell mass), which will later divide and differentiate to form the embryo
- trophoblast (made of trophoblast cells) which will divide and differentiate to form chorion (which provides nutrients to the embryo)
-
What does the blastocyst do?
Travels from fallopian tube to uterus where it implants itself to the endometrium of the uterine wall. Then develops further (another flashcard).
-
What development does the blastocyst do after implantation?
1. the embryoblast differentiates into a bilayered (2 cell layers) embryonic disc
made of:
- epiblast (which undergoes mitosis to form amnion (fluid-filled amniotic cavity) and 3 germ layers of the embryo)
- hypoblast, which undergoes mitosis to form the yolk sac
2. extraembryonic membranes start to form
-
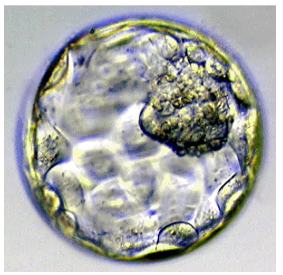
What stage of the pre-embryonic period is this?
Pre-implantation blastocyst
-
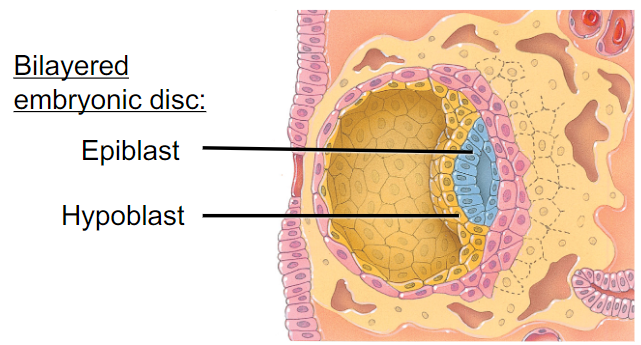
What stage are the labeled items in picture formed?
Post-implantation blastocyst
-
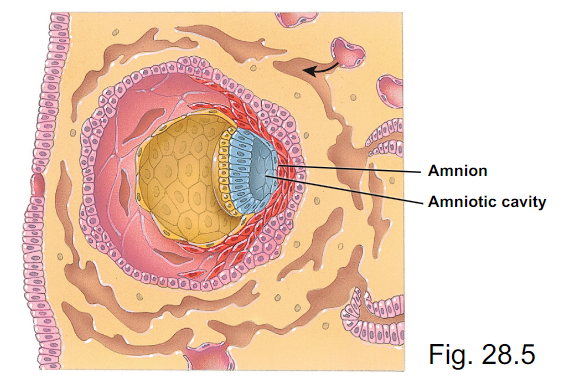
What stage are the labeled items in picture formed?
Post cell differentiation and mitosis of the epiblast cells formed after implantation of the blastocyst
-
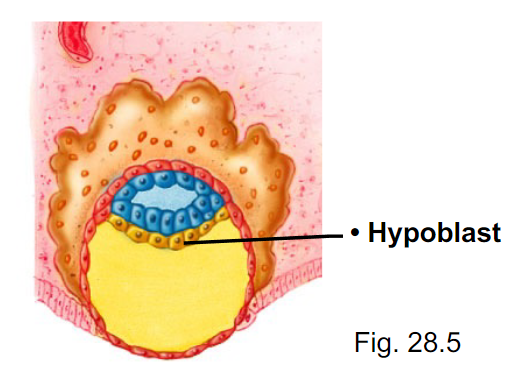
After undergoing mitosis, what does the labeled cell layer form?
The yolk sac
-
When is the embryonic period and what happens in it?
- 3rd to 8th week of pregnancy
- the 3 germ layers formed in mitosis of the epiblast cells,ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm, are now forming the embryo
-
What does the ectoderm layer develop?
Forms the nervous system and epidermis of the skin
*dev in time, not all in this period*
-
What does the mesoderm layer develop?
forms muscles, cardiovascular system, dermis, and most bones
*dev in time, not all in this period*
-
What does the endoderm layer develop?
will form the epithelial linings of the digestive, respiratory, urinary and reproductive systems and their associated glands
*dev in time, not all in this period*
-
What are milestones the embryo hits in the embryonic period?
- major organ systems almost completely formed (but will need to grow)
- heart begins to beat
- limb buds differentiate (some fingers by end of period)
-
What are the 4 extraembryonic membranes?
Chorion, amnion, yolk sac, and allantois
-
Where does amnion come from and what does it do?
- derived from epiblast
- forms amniotic cavity which surrounds embryo/fetus with amniotic fluid (fluid works as shock absorption and temp regulation)
-
What does the yolk sac come from and what does it do?
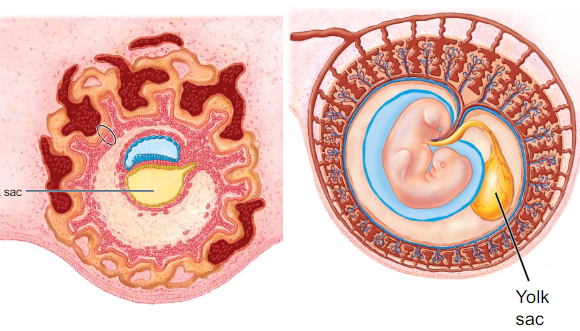
- derived from hypoblast
- forms part of digestive track
- source of reproductive germ cells & embryonic blood cells
-
What is the allantois and what does it do?
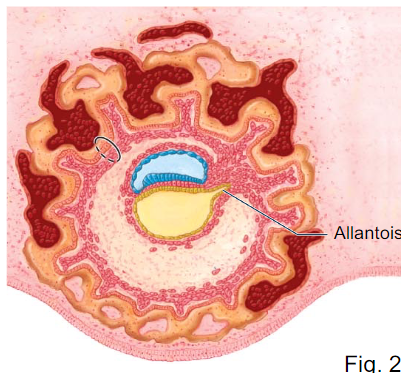
- a projection off the yolk sac
- forms umbilical cord and urinary bladder
-
What is chorion and what does it do?
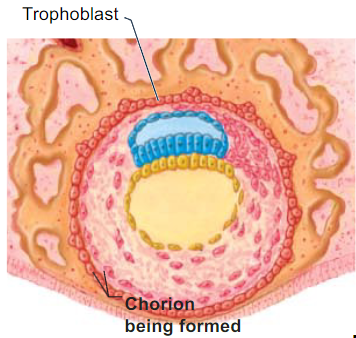
- derived from trophoblast cells
- surrounds all embryonic membranes
- projections of the chorion are chorionic villi (another flashcard)
-
When is the fetal period and what happens in it?
- 9th to end of 40th week
- growth and maturation of organs occurs
-
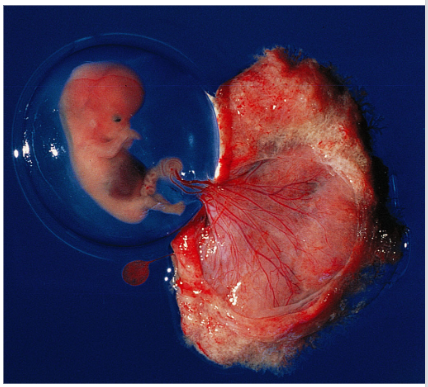
What is the chorionic villi and what does it do?
- projection of chorion that contains blood vessels that will form fetal part of the placenta (where nutrients, wastes, oxygen/carbon dioxide move between fetal and maternal blood)
-
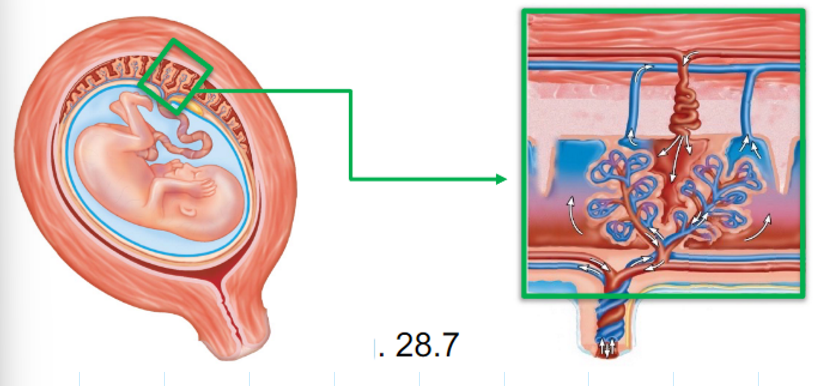
What is this?
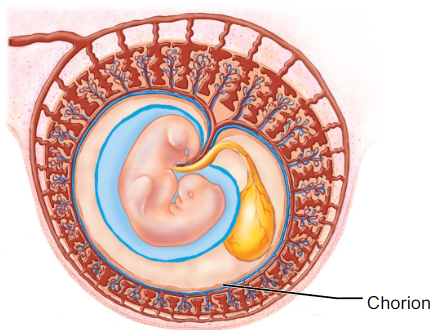
Chorionic Villi, a projection of the chorion.
-
Redraw early human development chart