-
Constructive interference (dark or bright)Bright
-
Destructive interference (dark or bright)dark
-
True or False: In constructive interference, two waves amplify each other to make a bigger wave.True
-
If the path difference is a multiple (1lambda, lambda, 3lambda,..) of wavelength the interference is...Constructive
-
If the path difference is an odd multiple of half the wavelength, the interference is...destructive
-
The path difference for two waves interfering at a point is 3.5 times the wavelength of the wave. What type of interference is expected to occur?Destructive
-
What two things must be valid for there to be interference of light?The sources are coherent, which means that the waves they emit must maintain a constant phase with respect to one another.The waves have identical wavelengths.
-
For constructive interference, valid only if phase difference is a result of the path difference:
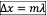 (with any even multiple of pi)
(with any even multiple of pi) -
1. For destructive interference, valid only if phase difference is the result of path difference:
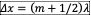 (w/ odd multiple of pi)
(w/ odd multiple of pi) -
In general, in order to have constructive interference, the waves must be in phase
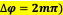 ( (EVEN MULTIPLE OF PI)
( (EVEN MULTIPLE OF PI) -
to have destructive interference, they must be completely out of phase
 () (ODD MULTIPLE OF PI).
() (ODD MULTIPLE OF PI). -
What is Huygens’ principle and what does it allow us to understand about light?
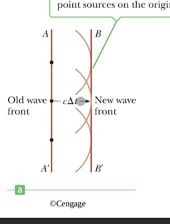 a. Huygens’ principle is a statement that all points of a wave front of light in a vacuum or transparent medium may be regarded as new sources of wavelets that expand in every direction . It allows us to understand and describe the wave nature of light and various optical phenomena such as reflection, refraction, interference and diffraction . b. “Each new point on the wave acts like a new source that generates. Spherical waves.” At slits c. The new wave is drawn tangent to the circular wavelets radiating from the point sources on the original wave front.
a. Huygens’ principle is a statement that all points of a wave front of light in a vacuum or transparent medium may be regarded as new sources of wavelets that expand in every direction . It allows us to understand and describe the wave nature of light and various optical phenomena such as reflection, refraction, interference and diffraction . b. “Each new point on the wave acts like a new source that generates. Spherical waves.” At slits c. The new wave is drawn tangent to the circular wavelets radiating from the point sources on the original wave front. -
. According to Young's Double Slit Experiment, when the path lengths are equal..
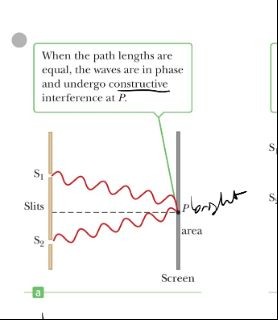 The waves are in phase and undergo constructive interference at P
The waves are in phase and undergo constructive interference at P -
According to Young’s Double-Slit Experiment, when the pathlengths differ by a wavelength…
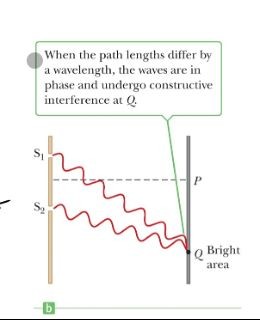 The waves are in phase and undergo constructive interference at Q
The waves are in phase and undergo constructive interference at Q -
According to Young’s Double-Slit Experiment, when the pathlengths differ by half a wavelength…
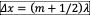 The waves are 180 degrees out of phase and undergo destructive interference at R.
The waves are 180 degrees out of phase and undergo destructive interference at R. -
What is Young’s double slit experiment and what does it show?Young’s double slit experiment is an experiment that shows light is a wave that can interfere and a particle that can be detected.
-
What’s the formula to find the path difference in young’s double slit experiment?
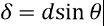
-
What's the formula for finding the location of the bright fringes in young's double slit experiment?
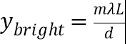
-
What's the formula for finding the location of the dark fringes in young's double slit experiment?
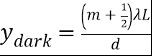
-
What’s the formula for fining the width of each fringe?a. W=change in L /2d
-
How to find m=0?a. Central brightest fringe
-
In young double slit experiment, L is the...L is the distance from the double slit to the screen where the interference pattern is observed in Young's double slit experiment
-
In young double slit experiment, d is the...is the distance between the slits
-
Typically, in the double slit experiment, L isMuch greater than d
-
To find angular location of the bright and dark fringes...
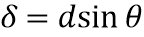 a. For bright: =mlambda. For dark: =(m+1/2)lambda
a. For bright: =mlambda. For dark: =(m+1/2)lambda -
For double-slit experiment, y tells youLocation of fringe from center fringe
-
For m=0 for dark fringesIt is the first dark fringe above the central bright fringe
-
How do you find the separation between two adjacent dark and bright fringes (assuming they are the same size)a. Lambda(L)/d b.
-
1. If the distance between the slits is doubled in Young's experiment, what happens to the width of the central maximum?W=change in L /2d The width is halved. (see formula)
-
A Young's double-slit experiment is performed with three different colors of light: red, green, and blue. Rank the colors by the distance between adjacent bright fringes, from smallest to largest.
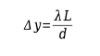 Red has the longest wavelength and blue the shortest so... Blue green red
Red has the longest wavelength and blue the shortest so... Blue green red -
In a double-slit experiment, when the wavelength of the light is increased, the interference pattern
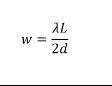 Spreads out.
Spreads out. -
If a Young's double slit experiment carried out in air, is repeated in water, what happens to distance between the bright fringes?

-
Memorize this formula find distance between fringes? (not on formula sheet)
-
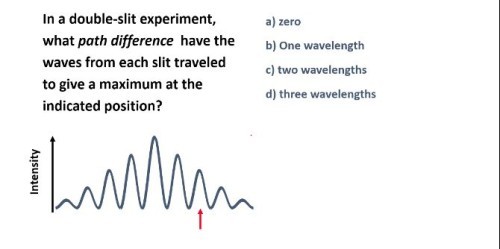
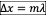 Since it is a peak, it is a constructive interference. For constructive interferences, path difference is and m=2 so the answer is two wavelengths
Since it is a peak, it is a constructive interference. For constructive interferences, path difference is and m=2 so the answer is two wavelengths

