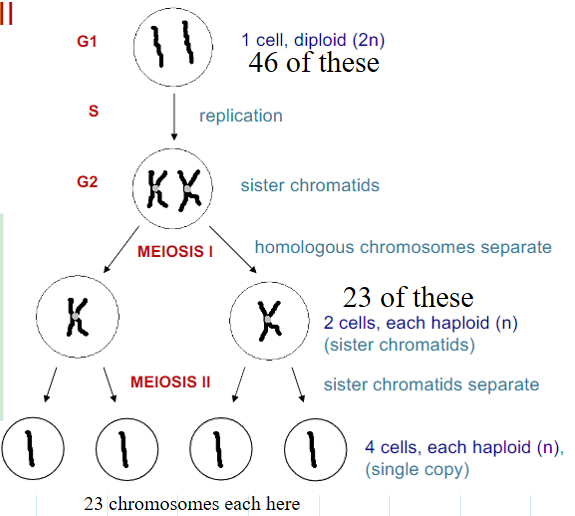
-
2 cell types based on chromosome content
Gametes (haploid (n), 23 chromosomes) and Somatic Cells (Diploid (2n), 46 chromosomes)
-
Chromosome Type in Somatic Cells
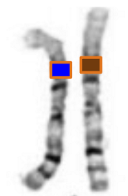
Homologous Chromosomes
- highly similar in length and centromere position.
- have genes for the same trait in the same location (locus) but they may be different versions of that genetic trait (alleles). they're equivalent, not identical
-
Chromosome make up in somatic cells
- 23 chromosomes from ovum and 23 from sperm make up 46 pairs
- chromosomes 1-22 are autosomal (contain genes for traits)
- chromosome 23 contains genes for biological sex, it gets X from ovum and X or Y from sperm
-
The 2 stages of the somatic cell cycle
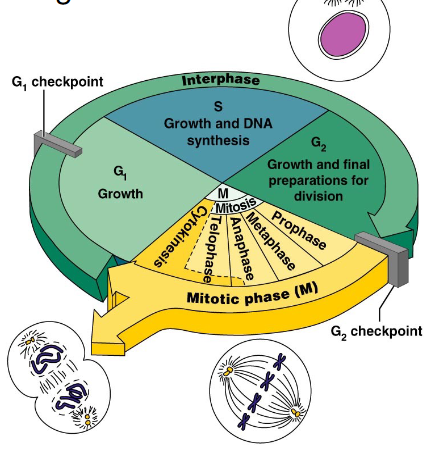
1. Interphase (G1, S, G2 phases) where growth, and prep happens
2. Mitotic (M phase) where mitosis happens
note: Cells that remain in the stage (i.e. don't divide again once mature) are said to be in G0 phase
-
What is the interphase G1 phase of somatic cell reproduction?
- G1 phase: growth, metabolism, centrosome replication begins
-
What is the interphase S phase of somatic cell reproduction?
- chromosomes replicate (but are still thread like and not individually visible)
- the replicates are called "sister chromatids" and attach at centromere
- this stage ALWAYS occurs before any cell division
- centrosome replication continues
-
What are kinetochores and what phase of interphase do they form?
proteins called kinetochores form on centromere to be site of attachment for spindle microtubules during mitosis and meiosis
-
What is the interphase G2 phase of somatic cell reproduction?
- Growth and metabolism
- production of enzymes & other proteins needed for cell division
- centrosome replication is completed
-
What is the interphase M phase of somatic cell reproduction?
- Where mitosis happens (Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase)
- When this ends then mitosis and cytokinesis are complete, and resulting diploids enter G1 again and cycle restarts
-
Trick for remembering interphase stages?
- G1 and G2 are both Growth stages (and metabolism and replication)
- S phase, Synthesis, is doubling chromosomes
- M phase is Mitosis
-
What are the stages of somatic cell formation?
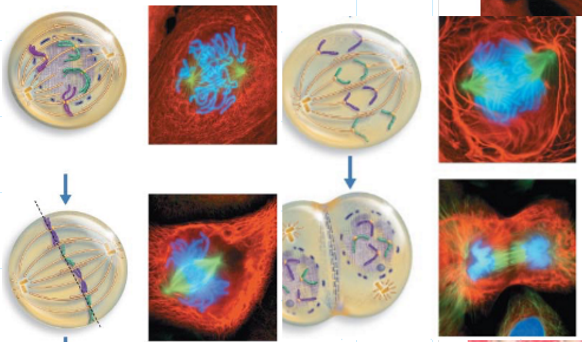
Interphase: G1, S, G2, M
then during M stage is mitosis: Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
-
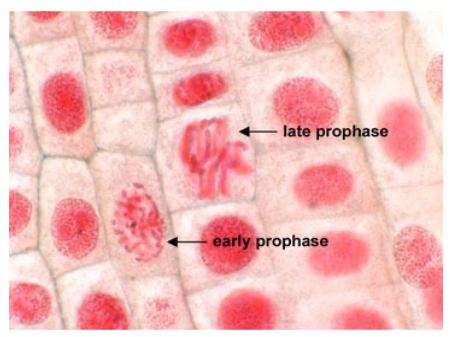
What happens during prophase?
- chromosomes condense and becomes individually visible
- nucleoli disappear and nuclear envelope breaks up
- centrosomes move to opposite poles of cell
- spindle microtubules grow and attach to kinetochore proteins of each sister chromatid and begins to move them to center
-
What happens during Metaphase?
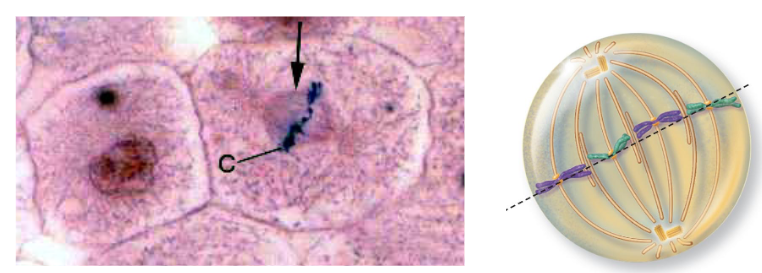
46 replicated chromosomes line up on cell equator
-
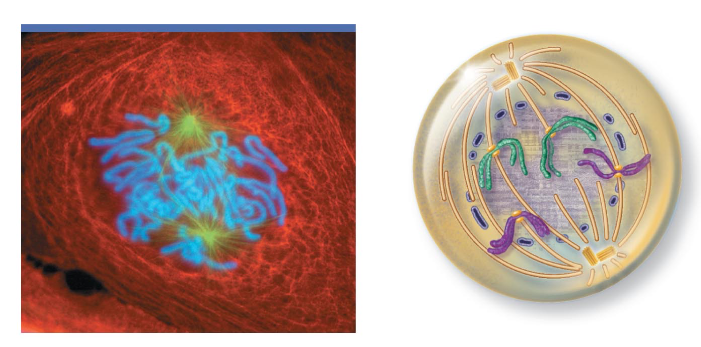
What phase of mitosis is this?
Prophase
-
What happens during Anaphase?
- spindle microtubules shorten and pull kinetochores away from each other, results in separation of sister chromatids to now have 92 individual chromosomes which migrate to each pole
- cytokinesis begins (division of cytoplasm)
-
What happens during telophase?
- chromosomes unravel once more to thread like strands
- nucleoli and nuclear envelope reappear
- spindle disassembles
- cytokinesis continues (or sometimes ends here)
-
What is the difference between Gamete formation and Somatic Cell formation?
Gamete: reproduces by meiosis, splits from one cell into 4 (makes sperm or ovum)
Somatic Cell: reproduces by mitosis, splits from one cell to 2
-
What are the stages of Meiosis?
Interphase stages (G1, S, G2, M) then Meiosis 1 (Prophase 1, Metaphase 1, Anaphase 1, telophase 1), then Meiosis 2 (Prophase 2, metaphase 2, anaphase 2, telophase 2)
-
When does cytokinesis begin and end in mitosis?
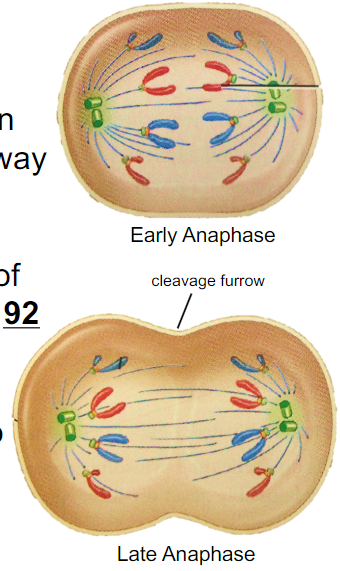
Begins in anaphase and ends after telophase
-
What happens during Meiosis 1?
Prophase 1: homologous chromosomes attach together and form tetrads
Metaphase 1: 23 tetrads line up along the cell equator
Anaphase 1: tetrads separate and a homologous chromosome goes to each pole
Telophase 1: chromosomes unravel once more to thread-like strands, nucleoli and nuclear envelope reappear, spindle disassembles, cytokinesis continues (or sometimes ends here)
-
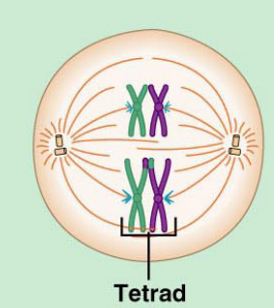
What stage of meiosis is this?
Metephase 1
-
What state are the cells after meiosis 1 and cytokinesis?
- each cell has 23 chromosomes (haploid now)
- these cells do NOT have homologous chromosomes
- each cell has a copy of each autosomal chromosome and one sex one
- the two haploid cells enter interphase (G1)
-
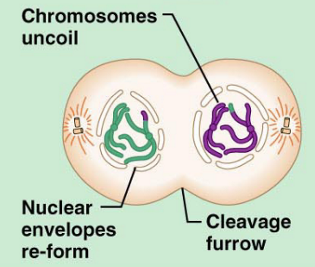
What stage of Meiosis is this?
Telophase 1
-
What happens during Meiosis II?
Prophase II: sister chromatids attach together, nucleoli and nuclear envelope dissapear
Metaphase II: 23 chromosomes line up along the cell equator
Anaphase II: sister chromatids separate and a chromosome goes to each pole, cytokinesis starts
Telophase II: chromosomes unravel once more to thread-like strands, nucleoli and nuclear envelope reappear, spindle disassembles, cytokinesis continues (or sometimes ends here)
-
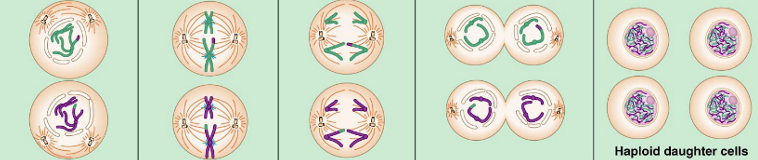
What process is this?
Meiosis II
-
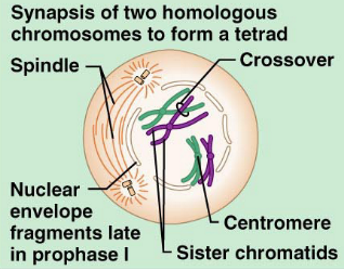
What stage of Meiosis is this?
Prophase 1
-
Whats the point of Meiosis?
- Turn diploid germ cells into haploid gametes (ovum/sperm)
- 2 haploid gametes (ovum & sperm) will combine their 23 chromosomes to a zygote with 46 chromosomes
-
How many chromosomes line up at equator in mitosis and meiosis 1 & 2?
Mitosis: 46 chromosomes (sister chromatids)
Meiosis 1: 23 tetrads (homologous chromosomes)
Meiosis II: 23 chromosomes (sister chromatids)
-
State after cytokinesis in Meiosis 1?
2 haploid cells with nearly identical copies of 23 chromosomes with sister chromatids
-
State after cytokinesis in Meiosis II?
- Gametes now
- 4 haploid cells that each has a copy of 23 chromosomes (not sister chromatids)
-
Meiosis stages from interphase to cytokinesis?