-
Lenses can either be...Converging or diverging lenses
-
Converging lenses are (convex or concave)Convex
-
Diverging lenses are (convex or concave)Concave
-
In lenses, the focal length is the image distance that corresponds to an/a
infinite object distance.
-
A thin lens has how many focal points?Two.
-
A thin lens has two focal points_, one on each side of the lens. One focal point corresponds to parallel rays traveling from the left and the other corresponds to parallel
rays traveling from the right.
-
What is the thin lens equation?
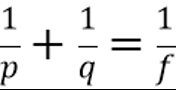
Where p is the object location and q is the image location and f is the focal length.
-
a converging lens has a_______ focal lengthpositive
-
diverging lens has a ______ focal lengthnegative
-
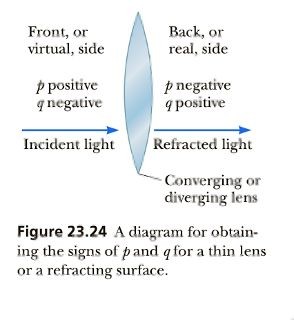
p is the object distance from the lens. It is positive if..
 the object is on the left of the lens and negative if it is on the right of the lens.
the object is on the left of the lens and negative if it is on the right of the lens. -
q is the image distance from the lens. It is positive if the image is onthe right of the lens and negative if it is on the left of the lens.
-
Front side of the lens is on the...
 Left
Left -
The back side of the lens is on the...Right
-
the front/left side, is the (real or virtual side)Virtual
-
the back/right side, is the (real or virtual)real
-
For lenses, p and q are positive where the light is, where the object or image is real. For real objects, the light originates with the object in front of the lens, so p is positive there as indicated in Figure 23.24. If the image forms in back of the lens, q is positive there, as well

-
In converging lens, the focal point is (real or virtual)Real
-
In diverging lens, the focal point is (real or virtual)Virtual
-
True or False: Focal point of a converging (convex) lens is realTrue
-
True or false: Focal point of a diverging (concave) lens is realFalse
-
Which of the following is not a property for the image formed by a diverging (concave lens)? A.) upside-down B.) virtual C.) SmallerA.) upside-down
-
Lens maker formula (not commonly used):
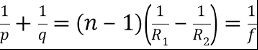
-
If q is positiveThe image is real, and at the back/right of the lens
-
If q is negativeThe image is virtual and on the front/left of the lens.
-
If p is positiveThe object is in front/left of the lens
-
If q is negative...the object is in the back or right of the lens.
-
When the object is in front of and outside the focal point of a converging lens, the image is…
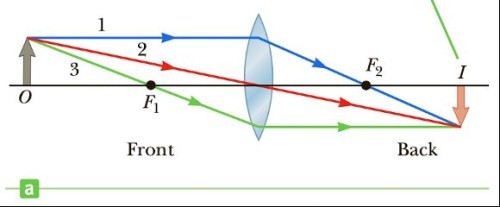
real, inverted, and on the back side of the lens. Magnification can change depending on distance?
-
When the object is between the focal point and a converging lens, the image is…
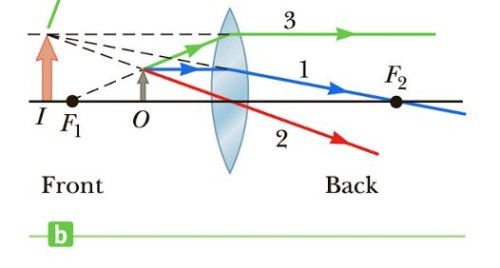
virtual, upright, larger than the object, and on the front side of the lens.
-
When an object is anywhere in front of a diverging lens, the image is
virtual, upright, smaller than the object, and on the front side of the lens.
-
True or False: For a diverging (concave) lens, ‘q’ is always negative (for real objectsTrue A: Because the image is virtual and on the same side of the lens as the object.
-
If the image is on the same side it is...Virtual (q negative)
-
A lens forms a real image from an object which is larger than the object. What kind of lens is it? A.) converging lens B.) diverging lens C.) flat lens D.) weird lensA.) Converging lens It has to be real which none of the options are able to produce. Also larger. The object would probably be farther than the focal point of the lens.
-
In diverging lens, the focal point is defined to be the pointwhere the diverged rays appear to originate
-
For a converging lens the focal point of a lens is the point where light raysthat enter the lens parallel to its axis converge
-
True or False: An object is placed to the left of a converging lens. The image can be upright or invertedTrue (can be real or virtual depending on distance from focal point?)
-
True or False: An object is placed to the left of a converging lens. The image is always to the right of the lensFalse (can be real or virtual so it can be on either side)
-
A lens forms a virtual image from an object which is larger than the object. What kind of lens are we dealing with?Converging lens; since image is larger. Cannot be larger with diverging since the image is always smaller.
-
True or False: An object is placed to the left of a converging lens. The image is always smaller or the same size as the object.False; depending on distance it can also be larger?
-
Your friends eyes appear to be smaller than what they really are when you look at them through her glasses. What kind of lenses are used in her glasses?Concave (diverging lens) since the image is virtual and smaller
-
To find total magnification of multiple lenses in seriesMultiply magnification of each lens
-
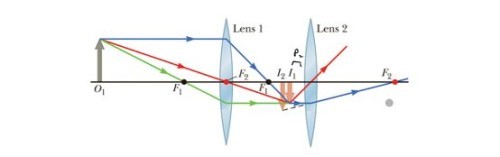
combination of lens example