-
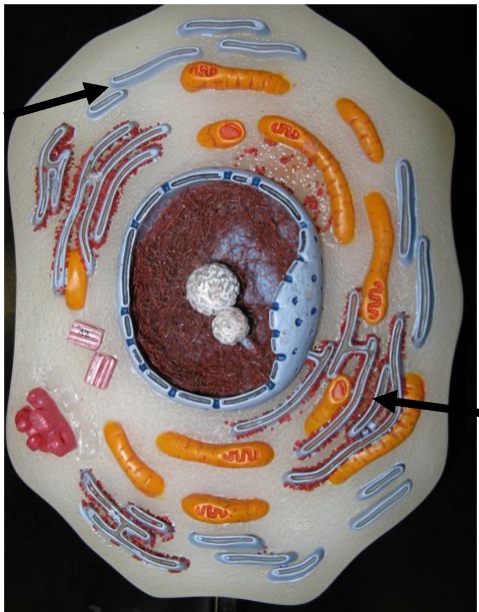
What are the orange things here? What do they do?
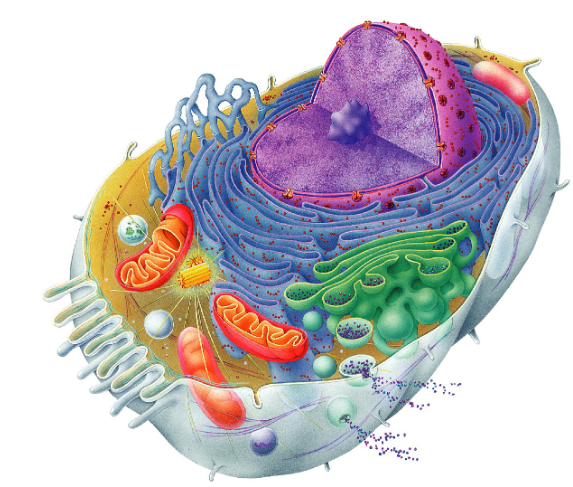
The mitochondria (mitochondrion singular), fcns as a site for ATP synthesis
-
Where is the golgi apparatus?
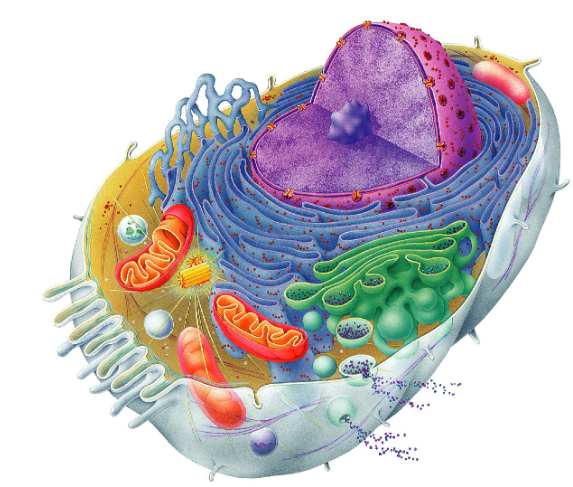
Green structure in this image
-
Principal parts of the cell
- Cell membrane/plasma membrane/plasmalemma
- cytoplasm
- nucleus
-
What is the cell membrane and what is it made of?
Boundary wall and made of:
phospholipid bilayer
cholesterol
membrane proteins (integral and peripheral proteins)
membrane carbohydrates
microvilli
-
The cell membranes phospholipid bilayer: does what and is made of what?
Made of:
phosphate head group (hydrophillic)
Fa tails (hydrophobic)
and it divides Intracellular fluid and extracellular fluid
-
The cell membranes cholesterol: does what?
Scattered throughout the membrane and adds stability to membrane, it also moves throughout (is mobile)
Also since its in/passing through membrane it must be hydrophobic
-
The cell membranes membrane proteins: does what and is made of what?
2 Types:
- Integral proteins (big) are integrated within the membrane, some go all the way through (then called transmembrane proteins)
- Peripheral proteins, smaller and attached to integral proteins (surface level)
possible fcns: transports nutrients in and out of cell, channel nutrients in and our, receive chemical messages from in and out of cell, anchor cell to certain regions or cells, identity markers (tells immune system cell is domestic)
-
The cell membranes membrane carbohydrates: does what and is made of what?
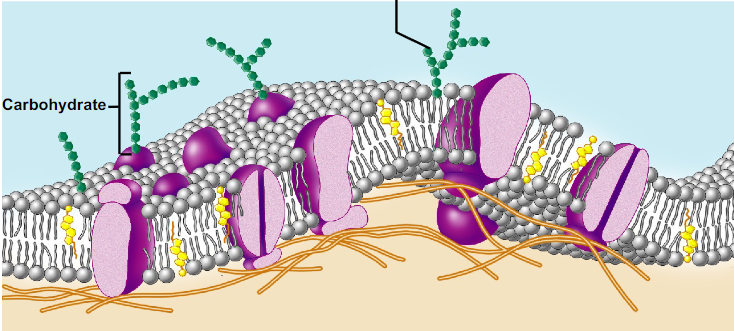
Only on outer surface of cell, bound to proteins or lipids and fcns to anchor cells together or as cell recognition (ex: sperm cell recognizes egg cell)
-
The cell membranes Microvilli: does what and is made of what?
Fcn to increase surface area of cell (to absorb more nutrients), they are small projections of cell membrane (best seen on kidneys and small intestine)
-
What is the Fluid Mosaic Model of the cell membrane?
The cell membrane is fluid and moves (we just only see still photos of it), but the membrane constituents move fluidly throughout (some proteins and phospholipids) while other proteins stay in dot like surface (looks like mosaic)
-
What is cytoplasm and its 2 divisions?
Cytoplasm is area between cell membrane and nucleus
The 2 divisions:
- Cytosol, this is the gel like intracellular fluid (contains water and ions like K+ and Na+) and may contain inclusions (pigments and nutrients)
- Organelles, these are what's suspended in the cytoplasm, they're either non-membranous (direct contact with cytosol) or membranous (surrounded by membrane)
-
What are the non-membranous organelles?
Ribosomes, centrosomes, and the cytoskeleton
-
What are the membranous organelles?
Mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum (smooth and rough), golgi apparatus, and lysosomes
-
What is the function of ribosomes?
They are a site for protein synthesis, contain rRNA and proteins, and either float in cytosol making proteins or are attached to the rough endoplasmic reticulum and make proteins
-
What are centrosomes made of and what is their function?
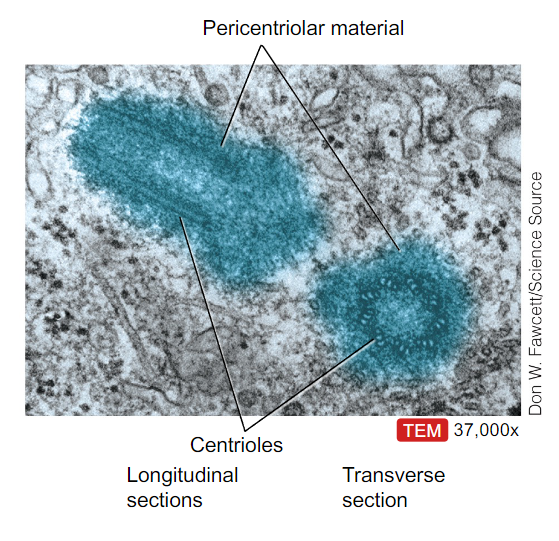
- They consist of a pair of centrioles and the pericentriolar matrix
- Are organizing centers for microtubules (spindle apparatus for cell division and organizing cytoskeleton)
-
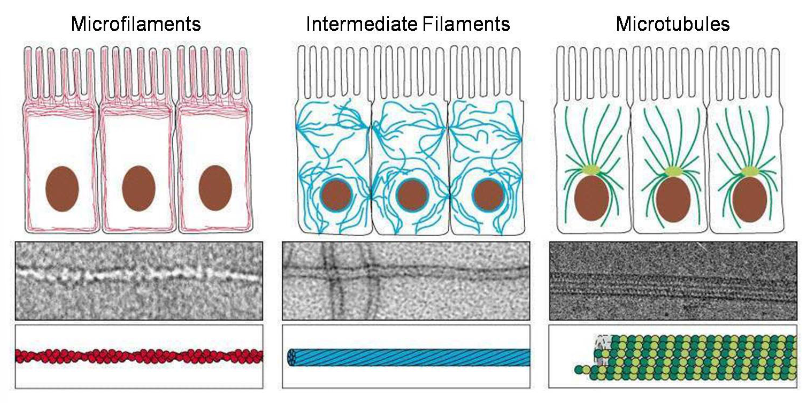
What is the cytoskeleton made of and what is its function and types?
Formed of proteins, and used for structural support of cell shape, important for cell movement, division, and anchoring of organelles
3 types: Microfilaments, intermediate filaments, Microtubules
-
What are the details of cytoskeleton types?
3 Types:
- Microfilaments (made of the protein actin, used for muscle contraction, cell locomotion and cytokinesis when diving cells)
- intermediate filements (composition is tissue specific)
- Microtubules ( hollow tubes made of tubulin, present in centrioles, the spindle apparatus, cilia, flagella (sperm tail) and fcn to move or secure organelles in place
-
What is the mitochondria made of and what does it do?
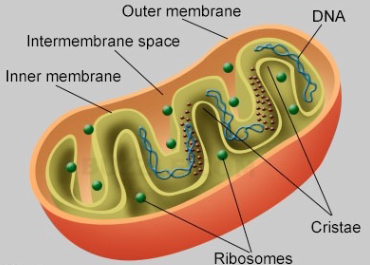
Has a double membrane and contains DNA, RNA, and proteins. Fcns as a site for ATP synthesis
-
What are the placement of the different cytoskeleton types?
-
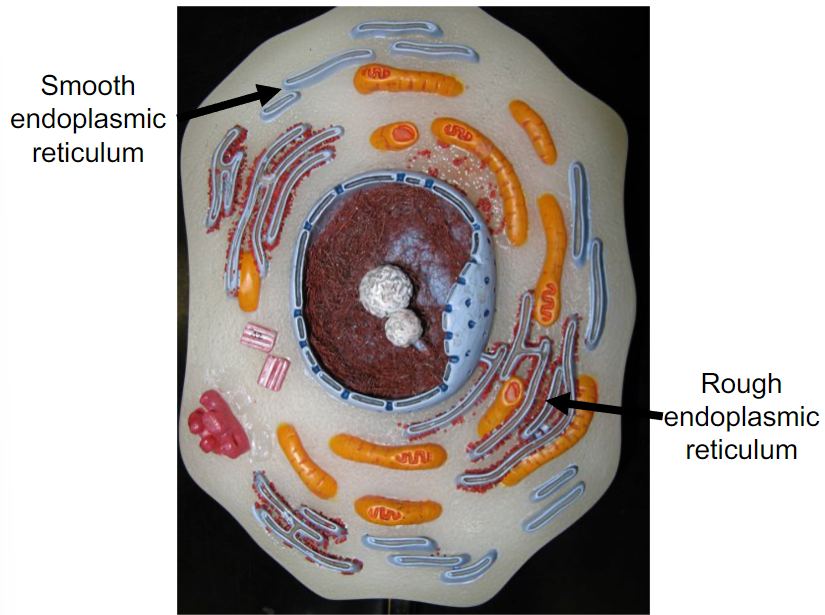
What is the Endoplasmic reticulum made of and what does it do?
It is a membranous network throughout cytoplasm and has two types.
Rough ER: Ribosomes attached, fcns in protein processing
Smooth ER: No ribosomes, calcium storage, and synthesizes lipids and steroid hormones
-
-
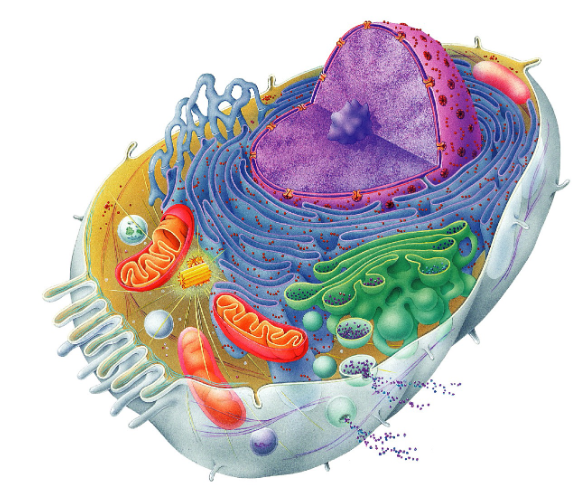
What is the Golgi Apparatus made of and what does it do?
It is a stack of membrane discs, it modifies proteins by trimming or adding carbs and lipids, then sorts, packages and delivers them to cell membrane, lysosomes, or for secretion (cellular post office)
-
What are Lysosomes made of and what does they do?
Theyre filled with digestive enzymes and digest bacteria, viruses, and worn out organelles, dead cells (they're the clean up fcn)
-
Where is the Lysosome?
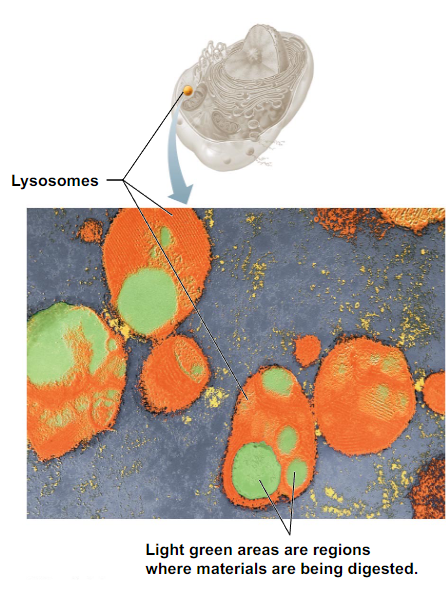
-
What is the nucleus and what is it made of?
Its the largest membranous organelle and cell control center (some cells have multiple). Made up of a nuclear envelope (a double membrane with nuclear pores, and connected to rough ER), nucleolus, and chromosomes/chromatids.
-
What is inside the nucleus?
- The nucleolus, is non-membranous and dense, a region of DNA, RNA, and proteins where ribosomes are made and assembled
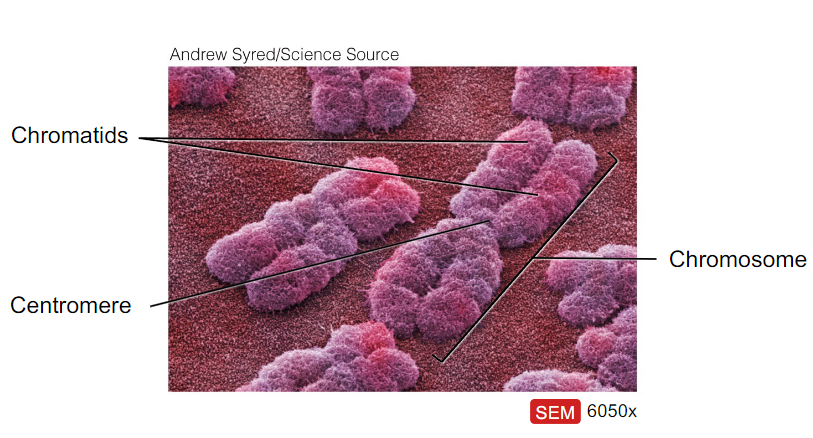
- Chromosomes/chromatids, contain DNA and histone proteins. When cell is not dividing the DNA is uncoiled in chromatid form and not individually visible. During mitosis and Meiosis becomes condensed into chromosomes and individually visible
-
Chromosome shape and anatomy