-
Events from egg and sperm to embryo
Sperm fertilizes egg -> fertilized egg (zygote) goes through cell division repeatedly -> embryonic stem cells differentiate and become embryo
-
Specialized vs stem cells
Specialized: become tissues -> organs -> organ systems
Stem cells: undifferentiated cells that become differentiated into one or more types of specialized cells
-
Levels of organization from cell to organism
Organism: individual member of a species
Organ system: set of organs working together for a common function
Organ: set of tissues working together for a common function
Tissue: group of cells working together for a common function
Cell: most basic unit of life that has all the characteristics of life
-
Two main purposes for cell division
Growth and repair
-
Homologous chromosome pair before/after S phase
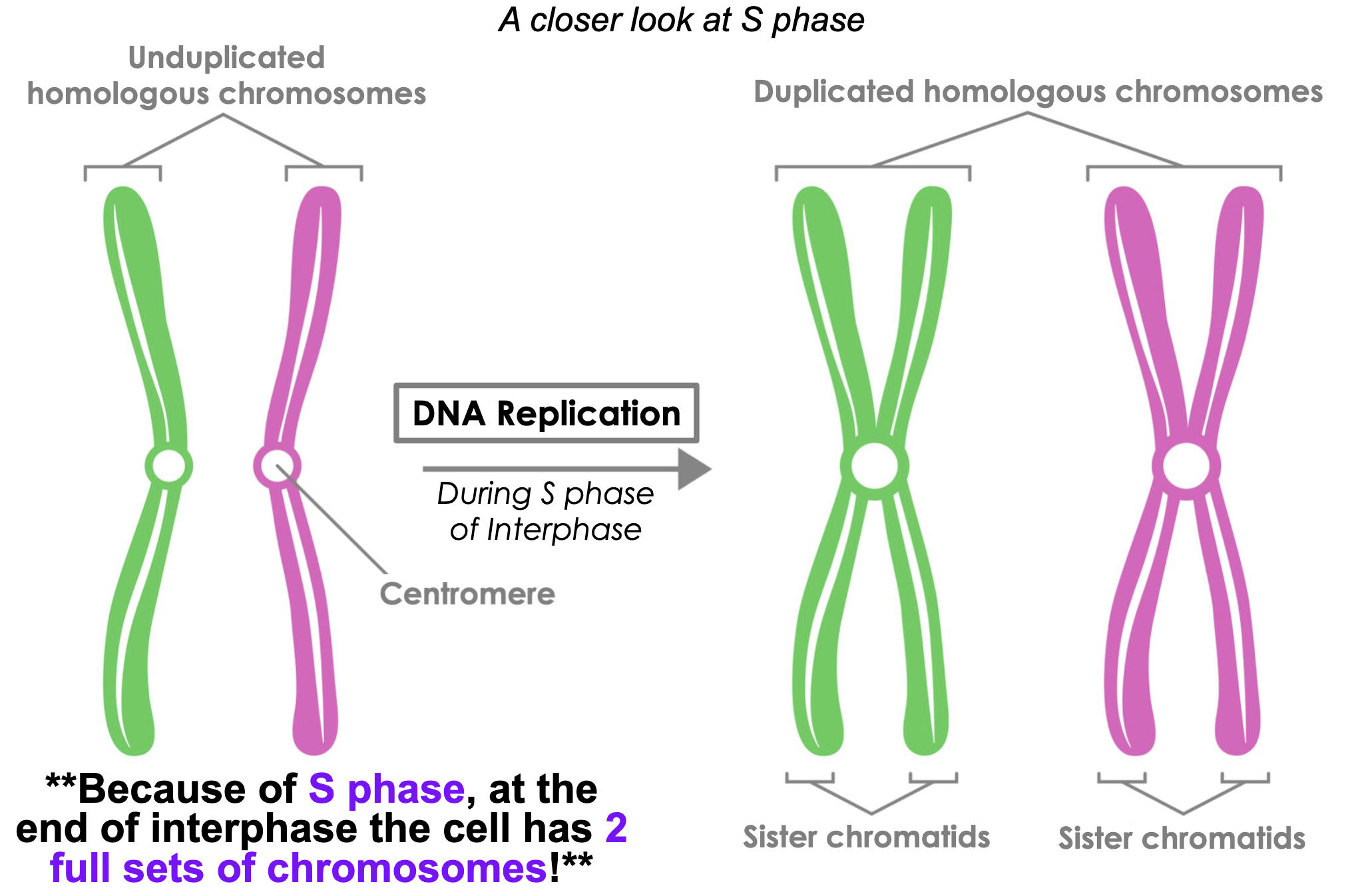
-
Interphase
Growth phase
Gap 1, Synthesis, Gap 2
-
Gap 1
cell grows and makes proteins
-
Synthesis
DNA replication occurs, doubling chromosomes
-
Gap 2
more cell growth and protein synthesis
-
Mitosis
Division phase
Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
-
Prophase
chromosomes condense & are visible as sister chromatids (Xs), nuclear membrane disappears, spindle fibers form out of centrioles
-
Metaphase
spindle fibers connect to the centromeres, chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell
-
Anaphase
sister chromatids separate and become individual chromosomes, chromatids move to opposite ends of the cell
-
Telophase
chromosomes decondense and start to look like chromatin again, nuclear membrane reforms, spindle fibers break down, cytokinesis begins
-
Cytokinesis
division of cytoplasm into 2 individual cells
-
Cytokinesis in plants vs animals
Plant cells: cell plate forms midway between divided nuclei and gradually develops into a membrane
Animal cells: forms a cleavage furrow that pinches the cell into 2 equal parts
-
How do cells know when they need to divide?
Cell cycle is controlled by a chemical control system that starts and stops
-
Internal regulation
signals that come from the cell’s own nucleus (DNA inside of the cell)
-
External regulation
signals that come from outside of the cell (Hormones, nutrients etc)
-
Role of checkpoints
critical point where stop and go signals can regulate the cycle
-
Role of apoptosis
internal/external signals activate genes that produce self-destructive enzymes (ex: web fingers/toes)
-
Define tumors
clumps of cells that divide uncontrollably
-
Benign tumor
abnormal cells that typically remain clustered together, may be harmless and easily removed
-
Malignant tumor
cancer cells that break away from the tumor and move to other parts of the body
-
List causes of cancer
Biological factors (age, skin type etc)
Lifestyle choices (diet, exposure to UV radiation etc)
Viruses and other infections (HPV)
Exposure to carcinogens (tobacco, asbestos etc)
-
Differentiation
a process that creates special structures and functions
-
Stem cells
undifferentiated cells that become differentiated into one or more types of specialized cells
-
Cell cycle
a repeated pattern of growth, DNA duplication and cell division that occurs in eukaryotic cells
-
Chromosome
one long continuous thread of DNA that consists of thousands of genes and regulatory information
-
Gene
a section of DNA with the instructions for making a protein
-
Sister chromatids
two identical chromatids
-
Centromere
region of the condensed chromosomes that looks pinched
-
Telomere
ends of the DNA molecule
-
Cancer
uncontrolled cell division
-
Metastasize
spreading of disease from one organ to others
-
Carcinogens
cancer causing agents; chemicals that cause cancer by mutating DNA


