Unit 19 - Nervous System pt. 3 (spinal cord, PNS structures)
Spinal cord, PNS structures
-
What is the general structural over view of the spinal cord?
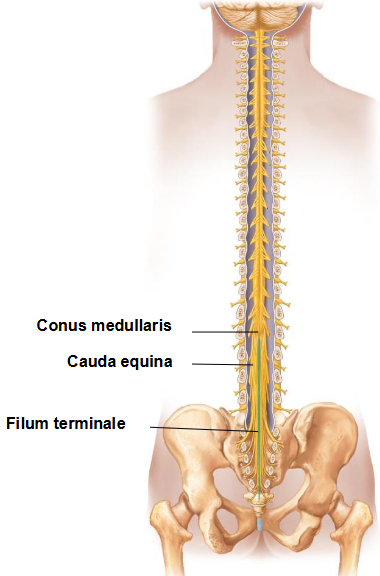
location: foramen magnum to L1/L2 (conus medullaris)
nerves continue down from spinal cord through vertebral foramina as cauda equina (horse’s tail) and exit at intervertebral foramina
filum terminale: a connective tissue extension of pia mater that anchors conus medullaris of spinal cord to coccyx
-
Where are CSF samples taken?
filum terminale in the spinal cord
-
What are the components of the cross-sectional structure of the spinal cord?
- anterior median fissure and posterior median sulcus: separate cord into right and left halves
- central canal: contains CSF
- Gray Matter
- White Matter
-
What does the Grey matter of the cross sectional structure of the spinal cord contain? What is its makeup?
- cell bodies and dendrites of motor neurons and interneurons
- H-shaped:
o cross bar = gray commissures
o horns: dorsal horn (sensory), lateral horn (motor), ventral horn (motor)
-
What does the white matter of the cross sectional structure of the spinal cord contain? What is its makeup?
myelinated axons containing ascending (sensory) or descending (motor) tracts
forms columns: dorsal column, lateral column, and ventral column
-
What are the functions of the spinal cord?
- sensory and motor impulses
- produces reflexes (fast, predictable, automatic responses to changes in environment e.g. withdrawal reflex)
-
What are the structures of the peripheral nervous system?
Cranial nerves and spinal nerves
-
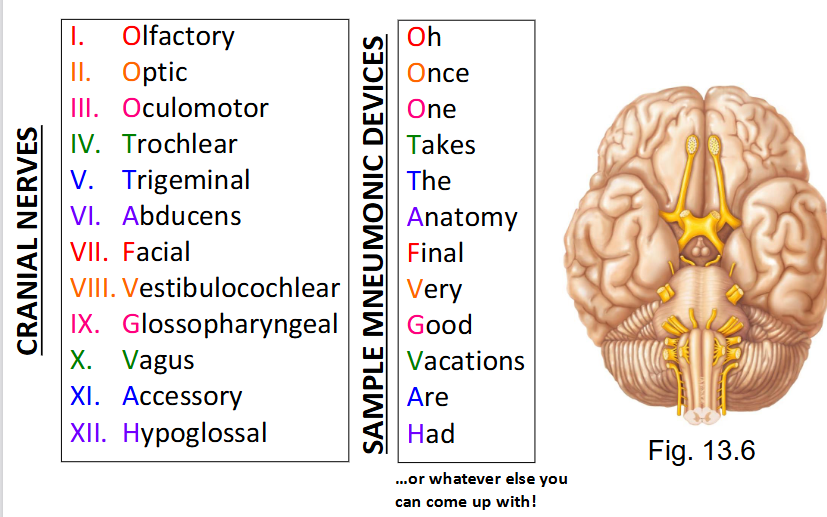
What are the 12 pairs of cranial nerves?
-
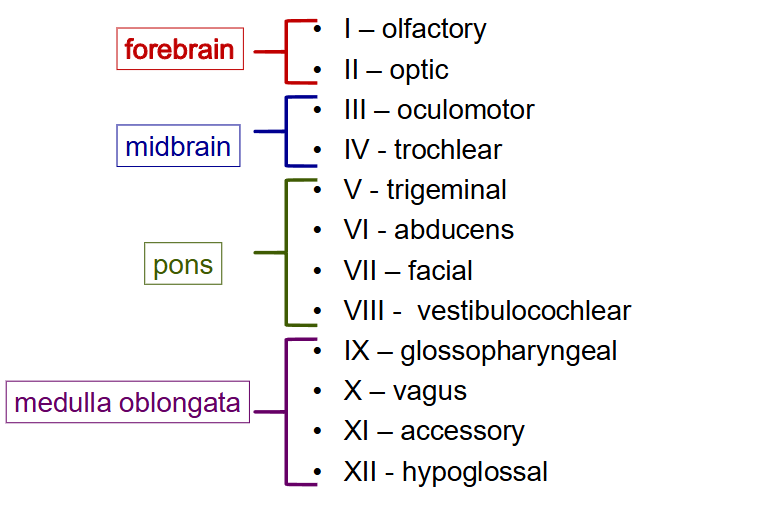
What brain regions are associated with the 12 pairs of cranial nerves?
-
What cranial nerves are associated with the forebrain?
- olfactory and optic (1-2 of pneumonic)
- they are also the only neurons that are "only sensory neurons"
-
What cranial nerves are associated with the midbrain?
oculomotor and trochlear (3-4 of pneumonic)
-
What cranial nerves are associated with the pons?
trigeminal, abducens, and vestibulocochlear (5-8 of pneumonic)
-
What cranial nerves are associated with the medulla oblongata?
- 9-12 of pneumonic
- glossopharyngeal, vagus, accessory, and hypoglossal
-
What pair of cranial nerves are mainly sensory neurons?
vestibulocochlear (9 in pneumonic)
-
Where do motor and sensory neurons have their cell bodies?
- motor neurons have cell bodies in brainstem nuclei
- sensory neurons have cell bodies in ganglia of PNS
-
What are the motor and sensory fcns of the trigeminal nerve (5 in pneumonic)?
- motor function = chewing
- sensory function = conveys general sensations (touch, pressure, pain, temperature) from face to CNS
-
What are the 9 pairs of cranial nerves that carry both sensory and motor neurons?
oculomotor, trochlear, trigeminal, abducens, facial, glossopharyngeal, vagus, accessory, and hypoglossal
-
What are the 31 pairs of spinal nerves?
o 8 cervical
o 12 thoracic
o 5 lumbar
o 5 sacral
o 1 coccygeal
- all mixed nerves
-
Where do spinal nerves exit?
exit via intervertebral foramina (except 1st – between atlas and occipital)
-
What are the dorsol and ventral roots? How many points of attachment do they have to the spinal cord?
- Dorsal Root: sensory neurons; cell bodies in dorsal root ganglion
- Ventral Root: autonomic and somatic motor neurons; cell bodies in ventral or lateral horn
- 2 points of attachment
-
What does the spinal nerve do? What is it?
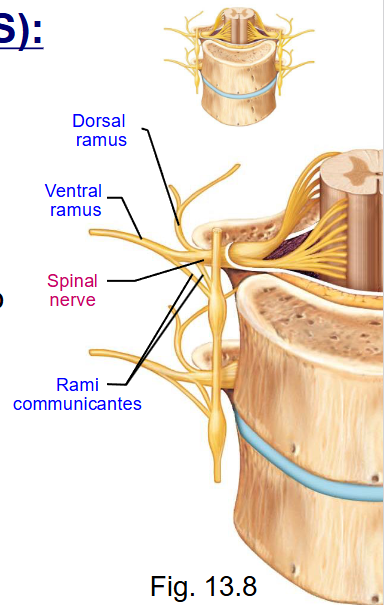
- joining of dorsal and ventral roots
- immediately divide into branches (rami): dorsal ramus, ventral ramus, and rami communicantes
-
What does the dorsal ramus do?
innervate skin and muscles of the back
-
What does the ventral ramus do?
forms thoracic nerves (T2 – T12) ) OR further branch and join up forming nerve plexuses (= nerve network)
-
What does the rami communicantes do?
connect ventral ramus (spinal nerve) to sympathetic trunk
contain autonomic nerve fibres (neurons)
-
What are the 4 spinal nerve plexuses? What spinal nerves are the formed by? What important nerves arise from them?
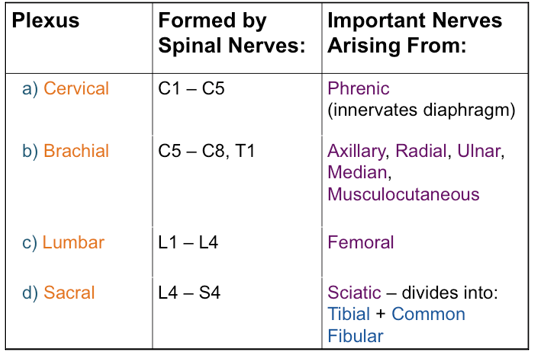
-
What is at the cross section of a nerve? What are the different kinds?
- CT wrappings:
- Epineurium: around whole nerve
- Perineurium: around fascicles
- Endoneurium: around axon and myelin
-
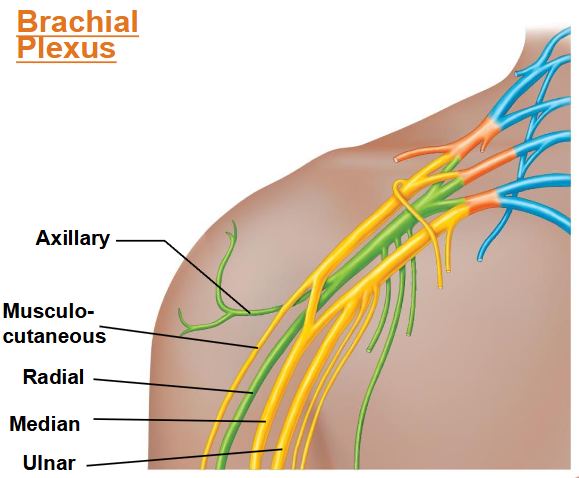
What important nerves arise from brachial plexus? Where is it?
-
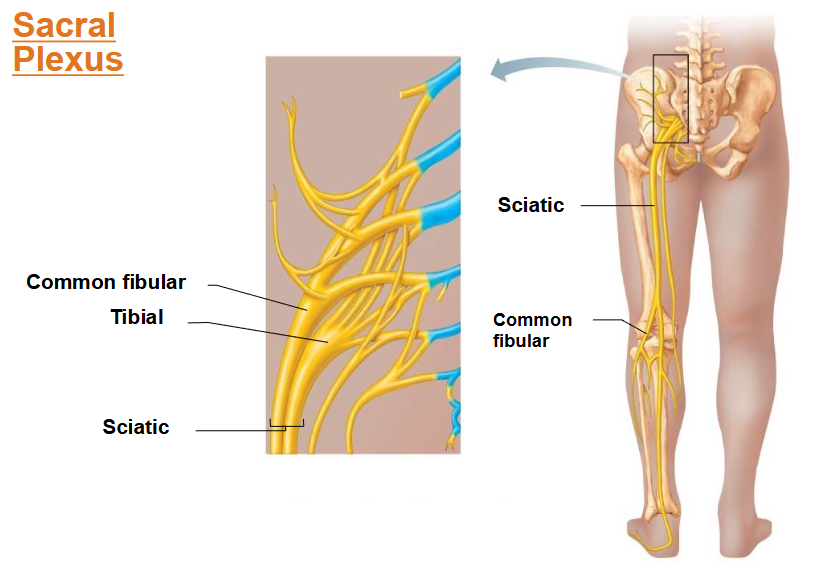
What important nerves arise from sacral plexus? Where is it?