-
What are the 2 divisions of the nervous system?
- central nervous system (CNS)
- peripheral nervous system (PNS)
-
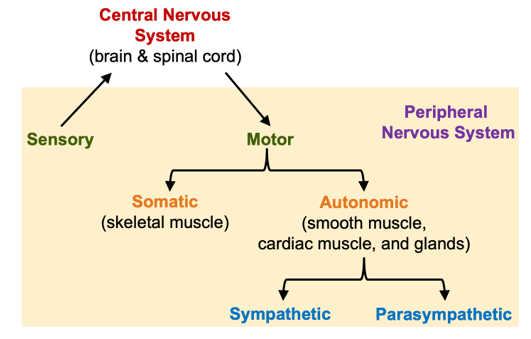
What is the central nervous system (CNS)?
“command centre”
brain and spinal cord
processes and integrates info
-
What does the peripheral nervous system consist of?
- cranial nerves: to/from brain
- spinal nerves: to/from spinal cord
-
What are the 2 divisions of the peripheral nervous system (PNS)?
- sensory/afferent division
- motor/efferent division
-
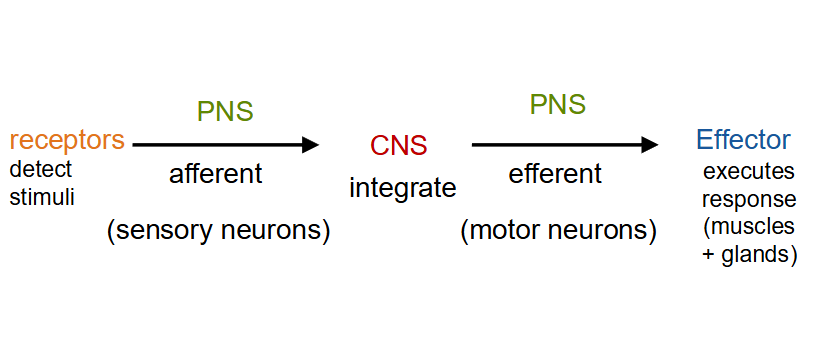
What do afferent and efferent mean?
afferent: info from the body coming to central nervous system
efferent: info from the central nervous system to body, to initiate action
-
What does the sensory/afferent division on the PNS do?
has sensory receptors that detect stimuli (change in internal or external environments)
-
What does the motor/efferent division on the PNS do?
nerves convey impulses away from CNS
innervates (supplies nerves to) effectors = muscles and glands (endocrine or exocrine)
-
What is the relationship between CNS and PNS?
-
What is the nervous system organization?
-
What are the different cell types in the nervous system?
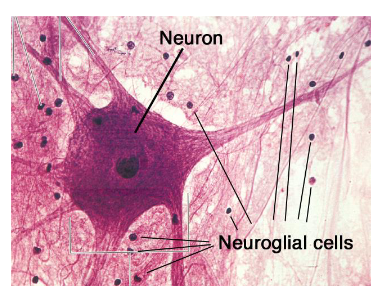
Neurons and neuroglia (glial cells)
-
What do neurons do?
conduct impulses
make up CNS and PNS
mostly amitotic (irreplaceable)
o exceptions = taste, olfaction, memory
-
What is the structure of the cell body of the neuron?
typical organelles
RER called - Nissl Bodies
groups/clusters in CNS = nuclei (gray matter)
groups/clusters in PNS = ganglia
-
What are the two processes of the cell body of a neuron?
dendrites and axon
-
What do dendrites do?
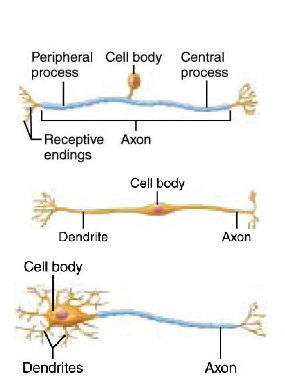
receive incoming messages and relay to cell body
-
What do axon do?
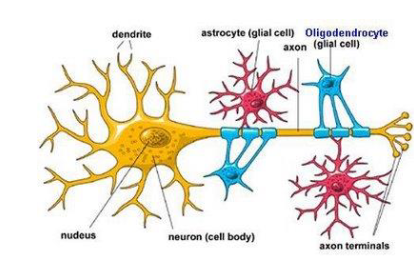
carry impulses away from cell body
-
What are axon hillock and axon terminal?
axon hillock = where axon meets cell body
axon terminal = typically branched with synaptic end bulbs (enlarged tips)
-
What does myelinated mean for axon?
- they may be myelinated or unmyelinated (just no myelin)
- myelinated - – wrapped in many layers of cell membrane from Schwann cells (PNS) or oligodendrocytes (CNS)
- myelinated axon bundles in:
o CNS = tracts (white matter)
o PNS = nerves
-
What does myelin do for axons?
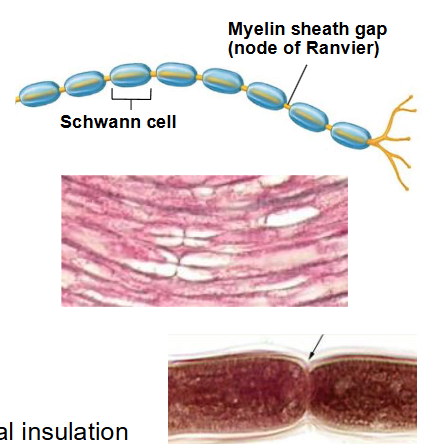
- electrical insulation
- gaps in myelin sheath are called Nodes of Ranvier
-
What do neuroglia cells do?
support neuron cells = can undergo mitosis (prone to cancer – brain tumor)
-
What are the two types of glial cells?
- CNS neuroglia
- PNS neuroglia
-
What are the cells in CNS neuroglia?
oligodendrocytes, microglia, astrocytes, and ependymal (neural epithelia)
-
What do oligodendrocytes do?
produce myelin around axon
-
What do microglia do?
protective – become phagocytic if detect infected, dead, or damaged neurons (because immune cells can’t enter CNS)
-
What do astrocytes do?
surround blood capillaries to form part of blood brain barrier (BBB)
help control capillary permeability
-
What does ependymal do(neural epithelia)?
line brain ventricles and central canal of the spinal cord
secrete cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and circulate it (cilia)
-
What are the cells in PNS neuroglia? What do they do?
- Schwann cells: form myelin around axons in PNS
- Satellite cells: surround neuron cell bodies in ganglia – protection and support
-
What are the neuron classifications?
Structural/Anatomical types and Functional types
-
What is Structural/Anatomical type of neuron classification based on and what are the types?
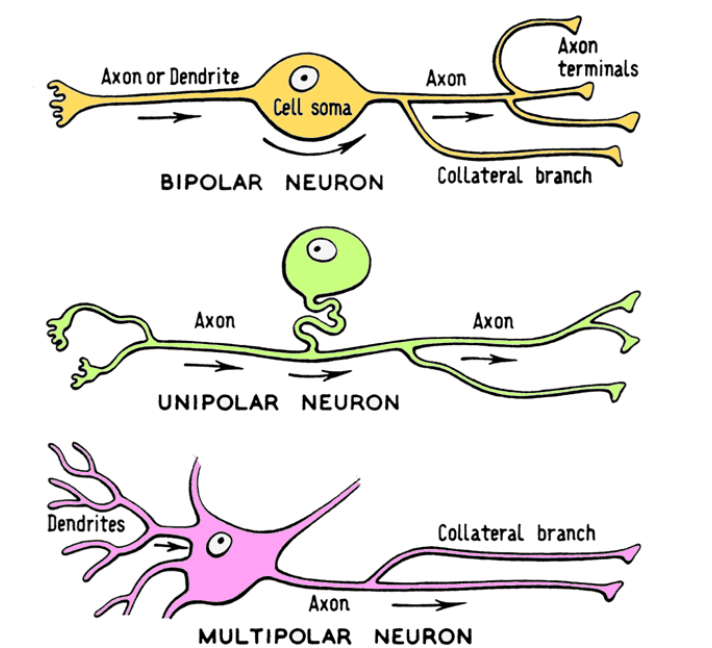
- based on # of cell processes off of cell body
- Unipolar, Bipolar, and Multipolar
-
What are the features of Unipolar cell bodies?
1 process that divides into two: central and peripheral
peripheral end has dendrites = sensory receptors (pain, touch etc) - remainder is axon
always sensory
-
What are the features of Bipolar cell bodies?
2 processes: 1 axon, 1 process with dendrites
sensory – retina, nose (olfaction)
-
What are the features of multipolar cell bodies?
3 or more processes: 1 axon, many dendrites
all interneurons and motor neurons
-
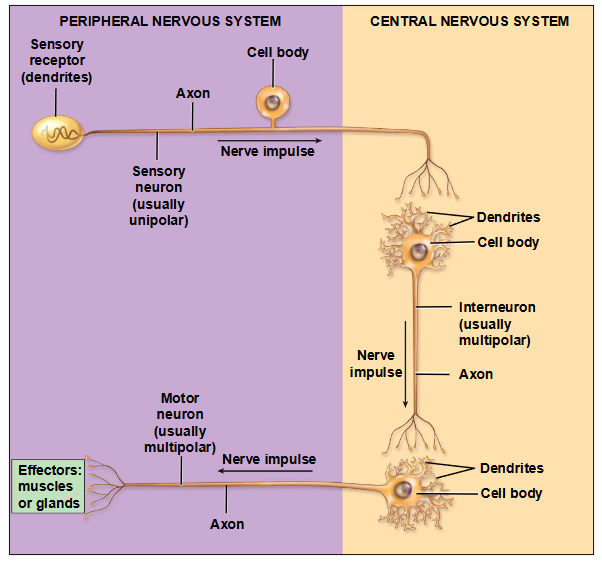
What is functional type of neuron classification based on and what are the types?
- based on direction of impulse conduction
- types: Sensory/Afferent Neurons, Interneurons, Motor/Efferent Neurons
-
What are the characteristics of sensory/afferent neurons?
mostly unipolar
from sensory receptors to CNS
-
What are the characteristics of interneurons?
- within CNS (between sensory and motor)
- 99% of neurons (mostly multipolar)
-
What are the characteristics of motor/efferent neurons?
- CNS to effectors (all multipolar)
- effectors are parts of the body that respond to stimuli (muscles, glands, etc)
-
What are the 3 kinds of neuron junctions (synapses)?
1) Neuronal junction:
2) Neuromuscular junction:
3) Neuroglandular junction:
-
What are the neuronal junctions between?
neuron to neuron
can be chemical (use neurotransmitters) or electrical (ions)
-
What is the neuromuscular junction between?
motor neuron to skeletal muscle
-
What is the neuroglandular junction between?
motor neuron to gland
-
What are chemical neuronal synapses?
- the most common neuron junction
- a structure of: Presynaptic Neuron, Axon Terminal, Synaptic Cleft, Postsynaptic Neuron
-
What is a presynaptic neuron?
neuron bringing impulse
-
Where is the axon terminal? What does it contain?
within synaptic end bulbs
o inside the end bulb (presynaptic membrane) = synaptic vesicles containing neurotransmitter (nt)
-
What is a synaptic cleft?
space between neurons
-
What is a Postsynaptic Neuron?
receives the impulse
has postsynaptic membrane, which is a cell membrane of dendrites or cell body with receptor sites for nt
-
How to the PNS and CNS nervous system communicate in terms of histology?
-
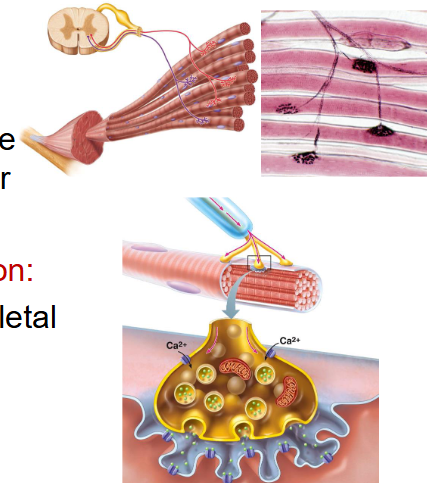
What neuron junction is this?
- neuromuscular junction

