-
What is the endocrine system?
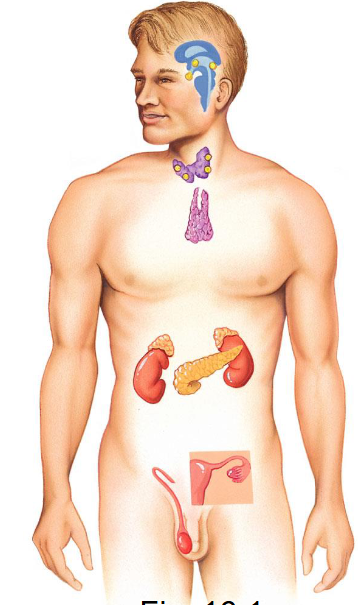
ductless glands and endocrine tissues within other organs
-
What does the endocrine system do?
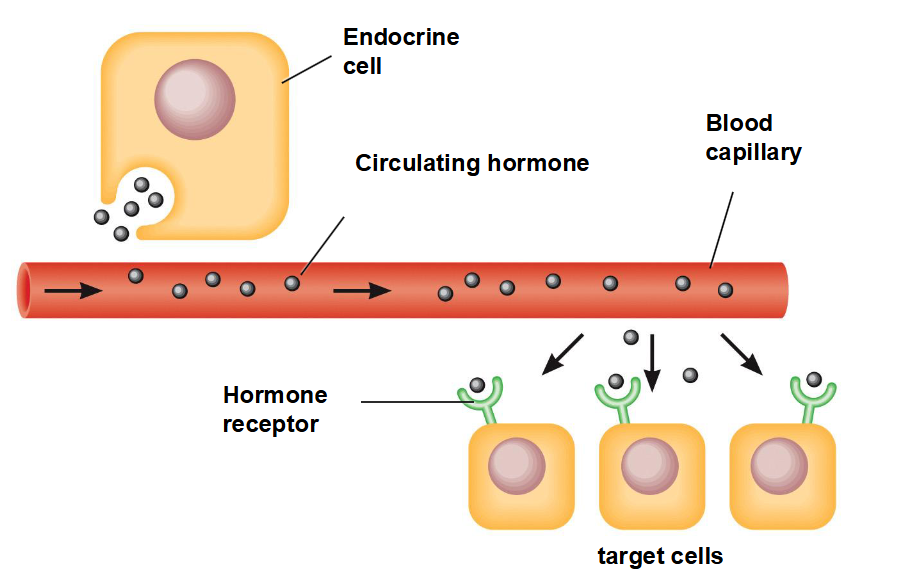
secrete chemical signals called hormones which travel in the circulation and bind to receptors on/within target cells to initiate a change in the cell (a response)
o target cell = cell with receptor specific for that hormone
-
What are the 3 hormone classes?
1. steroids
2. hormones derived from amino acids
3. peptide and protein hormones
-
What are steroids? What are they synthesized from?
Synthesized (made) from cholesterol
testosterone, estrogen, vitamin D
-
What hormones are formed from tyrosine? what hormone class is that?
- hormones derived from amino acids
- thyroxine/T4: a thyroid hormone, controls cellular metabolism, growth and development
- epinephrine and norepinephrine (adrenaline and noradrenaline): secreted by the adrenal medulla as part of the fight or flight stress response and sexual climax (orgasm)
-
What are peptide and protein hormones?
chains of amino acids held together by peptide bonds
e.g. oxytocin, antidiuretic hormone (ADH), growth hormone (GH), insulin
-
What does the endocrine system do? (visualize)
-
What do endocrine glands do?
their function is to produce and secrete hormones
-
What are the pure endocrine glands?
pituitary gland, thyroid gland, parathyroid glands, and adrenal glands
-
What are pituitary glands?
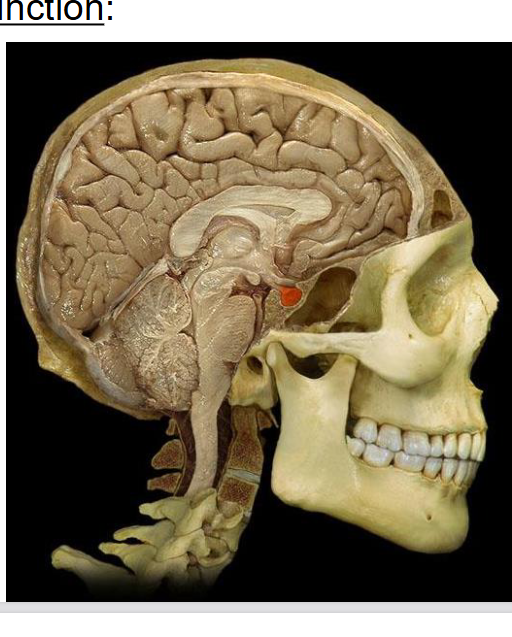
suspended from hypothalamus
in sella turcica of sphenoid bone
2 lobes: anterior and posterior pituitary
-
What does the anterior pituitary gland do?
glandular epithelial tissue
anterior pituitary hormone secretion regulated by hormones released by the hypothalamus
secretes the following hormones: growth hormone (GH), Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH), Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), Gonadotropins (reproductive hormones), and prolactin (PRL)
-
What does the posterior pituitary gland do?
- nervous tissue (extension of brain structure called the hypothalamus)
- stores and secretes hormones produced in hypothalamus, including: oxytocin and antidiuretic hormone (ADH, also known as vasopressin)
-
What does oxytocin do?
stimulates uterine contractions and milk ejection during suckling
-
What do antidiuretic hormones (ADH, also known as vasopressin) do?
enhances water reabsorption by collecting duct cells of nephrons in the kidney
-
What does the growth hormone (GH) do?
affects growth and metabolism
-
What does the Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) do?
stimulates secretions by the thyroid gland
-
What does Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH) do?
stimulates secretion of steroid hormones from the adrenal gland
-
What do Gonadotropins (reproductive hormones) do?
- Luteinizing Hormone (LH) – stimulates ovulation and formation of corpus luteum in the ovary; stimulates testosterone production by interstitial endocrine (Leydig) cells in the testes
- Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) – stimulates sustentocytes and follicle cells
-
What does prolactin (PRL) do?
stimulates milk production by mammary glands
-
What is the thyroid gland?
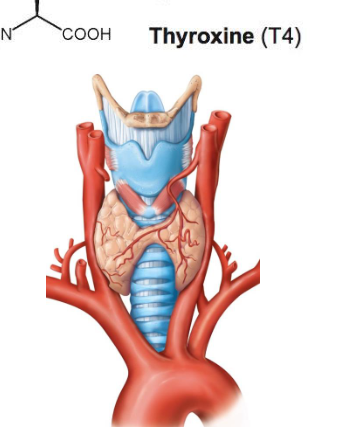
butterfly shaped gland on anterior surface of the superior part of the trachea (inferior to larynx)
-
What is the histology of the thyroid?
- Follicles: walls of the follicles are composed of epithelial (follicular) cells that secrete the hormone thyroxine (T4)
- thyroxine is converted to its active form (T3) in target cells
- Parafollicular cells: between follicles, secrete calcitonin to increase Ca++ uptake into bone (bone formation) which lowers blood Ca++
-
What are parathyroid glands? What do they do?
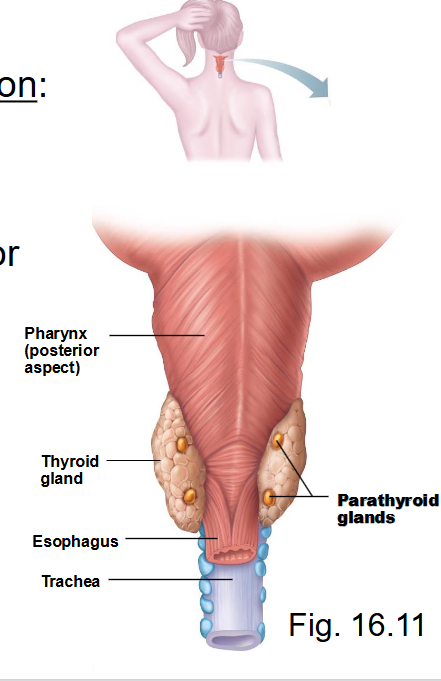
4 (usually) glands embedded in posterior thyroid
secrete parathyroid hormone (PTH): acts on bone, kidneys to increase blood calcium levels
-
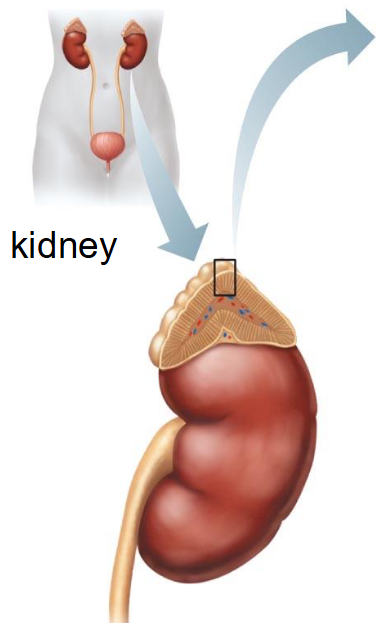
What are the adrenal glands?
Located on the superior surface of each kidney
parts: adrenal cortex (outer) and adrenal medulla (inner)
-
What is the adrenal medulla (inner) part of the adrenal glands?
- modified nervous tissue
- synthesizes hormones that regulate “fight or flight” response: Epinephrine (80%), Norepinephrine (20%)
-
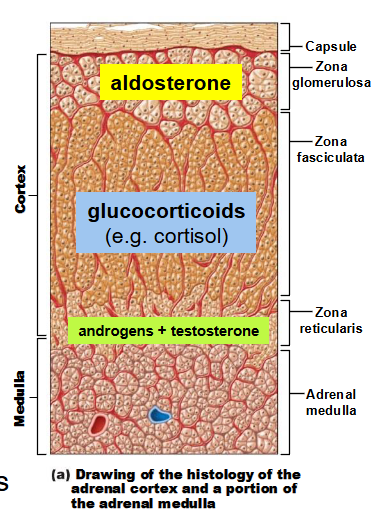
What is the adrenal cortex (outer) part of the adrenal glands?
epithelial tissue forming glands
secretes only steroids
3 layers (a single class of hormones is secreted by each layer): zona glomerulosa, zona fasciculata, and zona reticularis)
-
What does the zona glomerulosa layer of the adrenal cortex (outer) part of the adrenal gland do?
Mainly secretes aldosterone
o acts on nephrons to regulate salt balance
-
What does the zona fasciculata layer of the adrenal cortex (outer) part of the adrenal gland do?
secretes mainly cortisol
o regulates many body processes during long-term stress
-
What does the zona reticularis layer of the adrenal cortex (outer) part of the adrenal gland do?
secretes androgens (sex hormones)
o converted to testosterone or estrogens in other tissues
-
What are endocrine tissues?
Hormone secreting cells or tissues located in organs that have other functions (i.e. are not strictly glands that secrete hormones)
-
What are the endocrine tissues covered in class?
- Pancreatic Islets of Langerhans in Pancreas
- Hypothalamus (part of the brain)
- gonads
-
What does the endocrine tissue of the gonads do for testes?
o Interstitial endocrine (Leydig) cells - secrete testosterone
-
What does the endocrine tissue of the gonads do for ovaries?
o granulosa cells of secondary and vesicular follicles secrete estrogen
o corpus luteum secretes estrogen and progesterone
-
What does the endocrine tissue of the Pancreatic Islets of Langerhans in Pancreas do?
- α-cells: secrete glucagon which increases blood glucose concentration
- β-cells: secrete insulin which decreases blood glucose concentration
-
What does the endocrine tissue of the Hypothalamus do?
produces and secretes hormones that stimulate or inhibit the secretion of hormones from the anterior pituitary
produces hormones that are stored and secreted by the posterior pituitary
-
What does the endocrine tissue of the Hypothalamus secrete/produce that stimulate or inhibit the secretion of hormones from the anterior pituitary?
a) GHRH (Growth Hormone Releasing Hormone)
b) GHIH (Growth Hormone Inhibiting Hormone; also known as somatostatin)
c) GnRH (Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone) – for FSH and LH secretion

