-
What are the structures in the Urinary system?
o 2 kidneys
o 2 ureters
o 1 urinary bladder
o 1 urethra
-
What are the fcns of the urinary system?
regulation and elimination
-
What does the urinary system eliminate?
wastes e.g. urea, uric acid,
hormones
drugs (e.g. antibiotics)
toxins
-
What does the urinary system regulate?
blood volume
blood pressure
pH (concentrations of H+ and HCO3-)
concentrations of each ion in the blood (Na+, Ca++, K+, Cl-)
secretion of renal hormones
-
What is the external anatomy of a kidney?
- retroperitoneal
- right lower than left
- supported and protected by 3 layers of connective tissue
- renal hilus (hilum)
-
what 3 layers of connective tissue support the external anatomy of the kidney?
a) fibrous capsule – outer layer
b) perirenal fat capsule – middle layer
c) renal fascia – inner layer
-
What is the renal hilus (hilum)?
- medial indentation of kidney
- entry point of:
o renal artery (superior)
o renal vein (inferior)
o ureter
o nerves
-
What is the internal anatomy of the kidney?
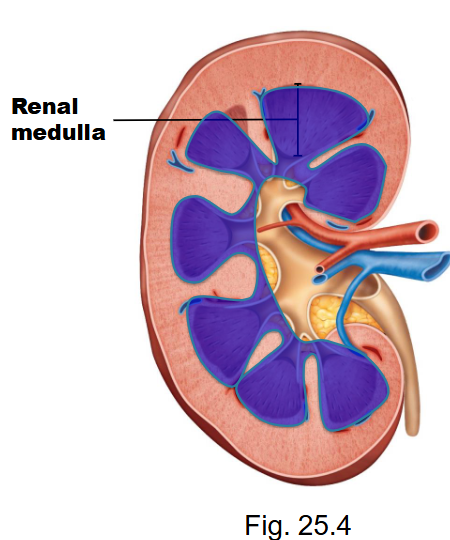
o renal cortex (superficial layer)
o renal medulla
o renal pelvis
-
What is the renal cortex (superficial layer)? (internal anatomy of kidney)
contains parts of nephrons
contains afferent and efferent arterioles as well as capillary beds called glomeruli
-
What is the renal medulla?
- renal pyramids (apex of pyramid is called the renal papilla, contain parts of nephrons)
- renal columns (projections of cortex into the medulla, separate pyramids, contains arteries, veins and nerves that supply the cortex)
-
What is the renal pelvis?
central collecting chamber for filtrate/urine
receives filtrate/urine from major calyces
-
What do major calyces do?
major calyces receive filtrate/urine from minor calyces which are small cup shaped structures that surround the renal papilla
-
What are nephron?
- functional unit of kidney (microscopic)
- two types: cortical, and juxtamedullary
- composed of: renal corpuscle and renal tubules
-
What are cortical nephrons?
make up majority of nephrons
renal corpuscles near kidney surface in cortex
short nephron loop that dips into the outer medulla
has peritubular capillaries that branch from efferent arteriole and surround DCT and PCT
-
What are juxtamedullary nephrons?
renal corpuscles in cortex near medulla
long nephron loops that penetrate deep into medulla (allows for production of dilute or concentrated urine depending on need)
has capillaries that branch from efferent arterioles called vasa recta that run parallel to the nephron loop
-
What are renal cortex?
- in cortex
- site of blood filtration (first step in urine formation), consists of (glomerulus, afferent arteriole, efferent arteriole, glomerular (bowman's) capsule)
- filtration membrane
-
What is the glomerulus part of renal corpuscle (which is part of nephron)?
= capillary bed (endothelium formed of simple squamous epithelium)
has many fenestrations (pores) between cells
-
What is the afferent arteriole part of renal corpuscle (which is part of nephron)?
- enters glomerulus
- carries blood delivered to kidney from the renal artery
-
What is the efferent arteriole part of renal corpuscle (which is part of nephron)?
- exits glomerulus
- drains into peritubular (of cortical nephrons) and vasa recta (of juxtaglomerular nephrons)
-
What is the glomerular (bowman's) capsule part of renal corpuscle (which is part of nephron)?
- surrounds and collects filtrate (filtered blood plasma) from glomerulus
- 2 layers:
Outer layer is a simple squamous epithelium
Inner layer is made of cells called podocytes that wrap around glomerular capillaries
-
What does the filtration membrane of nephron consist of?
- glomerular endothelium (capillaries)
- podocytes (of glomerular capsule)
- shared basement membranes of the two above bullet points
-
What is glomerular endothelium (capillaries)?
- part of the filtration membrane of renal corpuscles of nephrons which are a microscopic part of the kidneys
- fenestrations (pores) in the simple squamous epithelium allow plasma through, but not formed elements or most large proteins
-
What is glomerular podocytes (of glomerular capsule)?
- part of the filtration membrane of renal corpuscles of nephrons which are a microscopic part of the kidneys
- have many finger-like projections that form a network of filtration slits
-
What are the 4 parts of renal tubules? What are renal tubules?
- renal tubules are part of the composition of nephrons
- parts: Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT)
- Nephron Loop
- Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT)
- Collecting Ducts
-
What are Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT)?
- component of renal tubules which is a component of nephrons
- in cortex
receives filtrate from glomerular capsule
cells are cuboidal epithelium with dense microvilli
reabsorbs most useful substances (e.g. glucose, amino acids) from the filtrate
secretes waste products into filtrate
-
What is a nephron loop?
- component of renal tubules which is a component of nephrons
- In the medulla
Descending limb (thin) (Simple squamous epithelium, highly water permeable)
Ascending limb (thick) (Simple cuboidal epithelium, water-impermeable)
-
What is a distal convoluted tubule (DCT)?
- component of renal tubules which is a component of nephrons
- in cortex
- cuboidal epithelium
-
What are collecting ducts?
- component of renal tubules which is a component of nephrons
in cortex & medulla
drain filtrate from numerous nephrons into minor calyces
contain cells that regulate water and Na+ reabsorption and acid/base balance of the blood
-
What is the Juxtaglomerular complex (apparatus)?
- regulates the rate of filtrate formation
- point of contact between end of ascending limb, afferent and efferent arterioles at renal corpuscle of same nephron
- Parts: tubular portion (macula densa), vascular (arteriolar) portion
-
What is the tubular portion (macula densa) of the Juxtaglomerular complex (apparatus)?
modified (tall and narrow) distal convoluted tubule cells
monitor filtrate composition
-
What is the Vascular (Arteriolar) Portion of the Juxtaglomerular complex (apparatus)?
- afferent and efferent arteriolar portion = granular (juxtaglomerular cells)
-
What is the afferent and efferent arteriolar portion of the Vascular (Arteriolar) Portion of the Juxtaglomerular complex (apparatus)?
- modified smooth muscle cells that monitor blood pressure
- secrete an enzyme/hormone that helps to regulate blood pressure and ion balance
-
What do Ureters do?
transports urine from renal pelvis to bladder
retroperitoneal
-
What is the histology or ureters?
- Mucosa: transitional epithelium (stretches)
- Muscularis externa: smooth muscle
- Adventitia: connects ureter to body wall
-
What does the urinary bladder do?
short term storage of urine
retroperitoneal
-
What is the retroperitoneal?
the space behind the abdominal cavity and in front of the lower back
-
What is the histology of the urinary bladder?
- Mucosa: transitional epithelium with rugae
- Muscularis externa: is detrusor muscle - smooth muscle, contraction of detrusor muscle causes urination
- Adventitia/Serosa (mostly adventitia, serosa covers the superior surface)
-
What does the urethra do?
- drains urine from the bladder
- transports urine and when testes are present, also transports semen
- 2 sphincters (both surround proximal end of urethra)
-
What is the histology of the urethra?
- Mucosa – transitions from transitional epithelium to stratified squamous epithelium
- Muscularis externa – is smooth muscle
- Adventitia only
-
What are the two sphincters surrounding the proximal end or urethra?
- internal urethral sphincter (smooth muscle): thickening of detrusor muscle at base of bladder
- external urethral sphincter (skeletal muscle), in urogenital diaphragm
-
How does the urinary system filtrate movement?

-
What is a Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)?
bacterial infection of the mucosa of the bladder and/or urethra (most common). Can also involve ureters and kidneys (less common).
-
What is Glomerulonephritis?
inflammation of the glomeruli and structures of the filtration membrane that impairs their ability to filter blood plasma

