Unit 15 - Digestive tract pt 2
Accessory organs of Digestive track, duct system of accessory organs, abdominopelvic quadrants, lower GI tract blood circulation, and related medical conditions
-
What are the three organs accessory organs to the digestive tract?
- Pancreas (in retroperitoneal (behind peritoneum)), liver, and gall bladder
- they all produce exocrine and/or endocrine secretions involved in the digestive process
-
What are the parts of the pancreas? What does it contain?
- parts: head, body, tail
- contains: exocrine (that secrete pancreatic juice (digestive enzymes and alkaline fluid) into the duodenum) and endocrine glands
-
What are the two types of cells for exocrine glands and what do they do in the pancreas?
- acinar cells (most of pancreas)
secrete digestive enzymes into ducts
- duct cells
secrete alkaline fluid to neutralize stomach acid
-
What do the endocrine glands do in the pancreas?
are formed by the Islets of Langerhans (in between clusters of acinar cells)
secrete hormones: insulin (from beta cells) and glucagon (from alpha cells) that regulate blood sugar levels
-
What does the liver do?
- 4 lobes: right, left, quadrate, caudate
- liver cells are called hepatocytes
- performs many metabolic and digestive roles
-
What are some of the metabolic and digestive roles the liver plays?
- processes, modifies and detoxifies absorbed material from GI tract before being transported to the rest of the body
- produces bile which aides in fat digestion
-
What is the gall bladder?
- muscular sac attached to inferior surface of liver
- general histology similar to GI tract histology, but no submucosa and has rugae (when empty) for expansion
- stores and concentrates bile
- contraction releases bile into duodenum
-
What is the duct system for accessory organs?
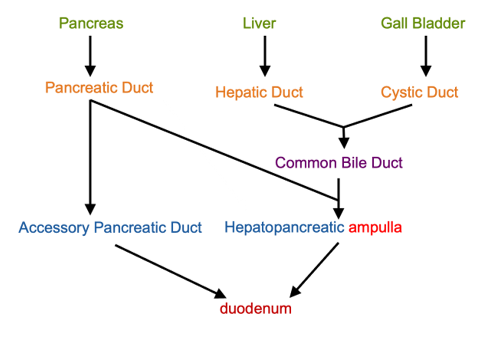
-
What are the Abdominopelvic Quadrants?
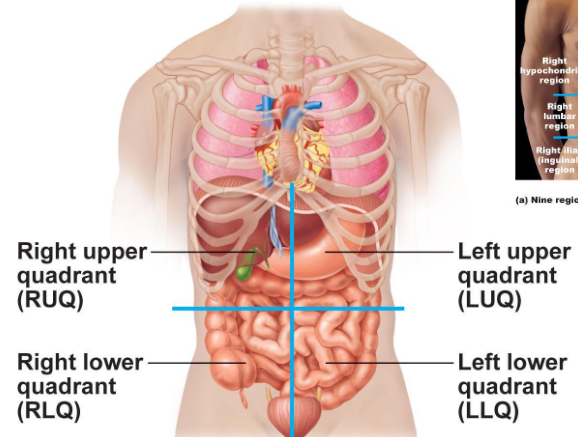
-
What does the right upper quadrant include?
a. liver
b. gall bladder
c. duodenum
d. head of pancreas
e. right kidney and right adrenal gland
f. hepatic flexure of colon
-
What does the right lower quadrant include?
a. caecum
b. appendix
c. ascending colon
d. right ovary/uterine tube
e. right ureter
-
What does the left lower quadrant include?
a. descending colon
b. sigmoid colon
c. ovary/uterine tube
left ureter
-
What does the left upper quadrant include?
a. stomach
b. spleen
c. left lobe of liver
d. body of pancreas
e. left kidney and left adrenal gland
f. splenic flexure of colon
g. parts of transverse and descending colon
-
Where is the greater omentum?
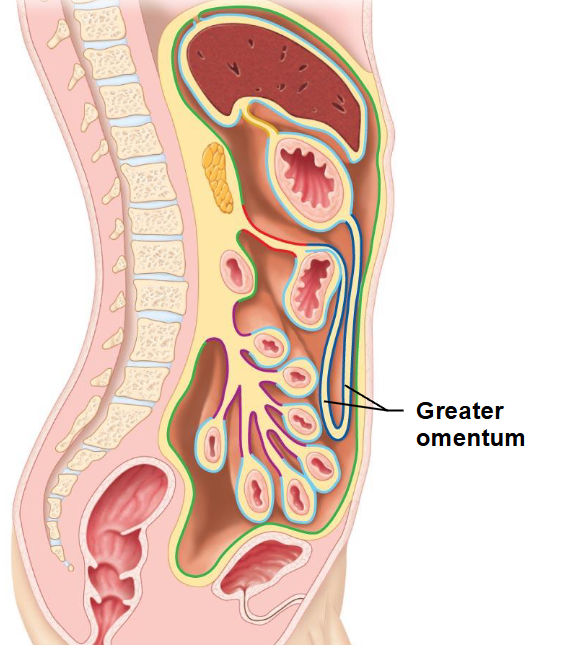
-
Where is the mesentry?
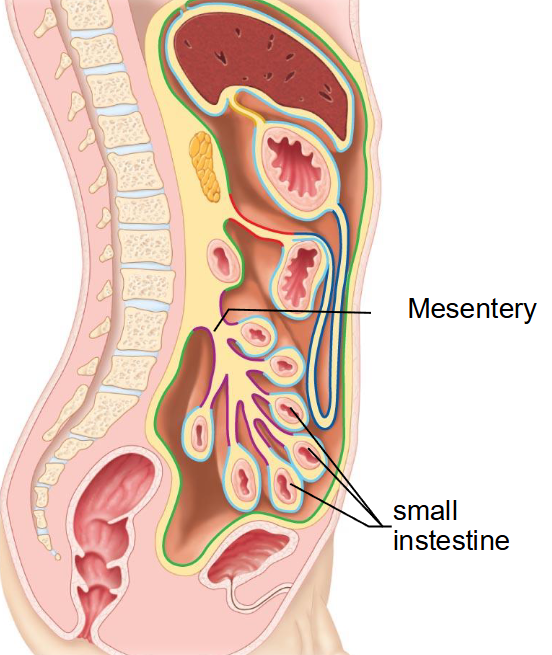
-
What is the circulatory route of the GI tract?
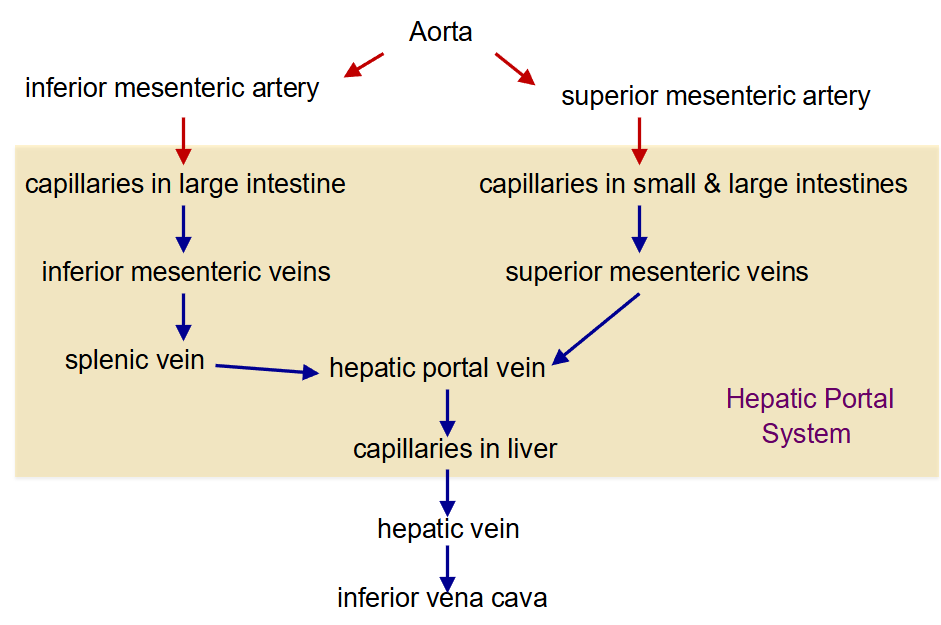
-
What is the portal system?
blood vessels that are connected to capillary beds on both ends (i.e. blood does not return to the heart before moving to a second capillary bed)
-
What is Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)?
stomach contents flow into esophagus
-
What is appendicitis?
inflammation of the appendix, causes pain in right lower quadrant
-
What is cholecystitis?
inflammation of gall bladder often due to blockage of cystic duct with gall stone; pain in right upper quadrant

